Chapter: Biochemical Pharmacology : The ionic basis of cell excitation
Anion channels
Anion channels
All the ions we have covered
so far are cations. What about anions? The major anion involved in electrical
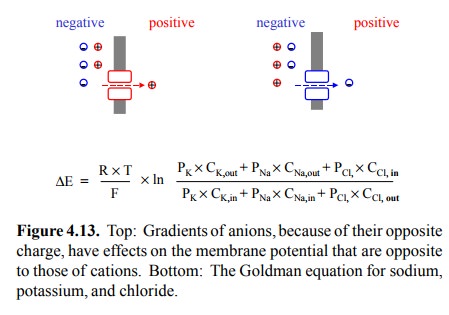
ex-citation is chloride. Figure 4.13 summarizes how it fits into the picture:
Because of its opposite charge, chloride actually opposes the excitatory action
of Na+, although it closely resembles the latter in its distribution across the
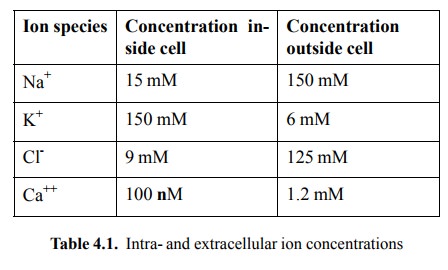
cell membrane (cf. table 4.1). The opening of chloride chan-nels therefore will
inhibit rather than promote membrane depolarization. Accordingly, chloride
channels occur in inhibitory synapses
within in the central nervous system. Inhibitory
synapses do not trigger action potentials; they rather suppress their formation
in nearby excitatory synaps-es that engage the same postsynaptic cell (see
Figure 7.1). Such chloride channels are mostly actuated by the inhibito-ry
transmitters glycine and GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid). GABA receptors are of
central importance in the pharma-cology of anaesthetic and sedating drugs.
Related Topics