Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio zoology Human Body higher secondary school
Algea : Reproduction
Algea : Reproduction
It takes place by the following methods.
1. Vegetative Reproduction
Vegetative reproduction
The vegetative filaments break accidentally into many small fragments. Each such fragment developes into a new filament.
a. By parthenospore
Some times the contents of a cell recede from the cell wall and lie in the middle. A thick wall surrounds the whole content which is called a parthenospore. It directly forms a new plant.
Parthenogenesis
The formation of parthenospores or azygospores, has been observed in many species. Here the conjugation does not take place and the contents of the cells become rounded. The walls are serrated around these protoplasts and they are called parthenospores (or) azygospores. Azygospore formation occurs in S. greenlandica. The process of formation of parthenospores is known asparthenogenesis.
b. By akinetes
In S. farlowi thick walled akinetes are formed. The entire cell content of the akinete gives rise to a new plant.
c. By aplanospores
During unfavourable conditions, aplanospores are formed in Spirogyra. The contents recede from the cell wall and the whole structure comes to rest. It is non-motile. On the return of favurable conditions the old cell wall of the parent is cast off and new wall develops. They directly give rise to a new plant.
Sexual Reproduction
In Spirogyra the sexual reproduction takes place by special gametes called aplanogametes and the process is aplanogamy. The motile gametes are always lacking. Aplanogammy takes place by conjugation, which may be scalariform or lateral. In each cell a single aplanogamete is produced which moves into the other cell through a conjugation tube in amoeboidal fashion. The species may be homothallic or heterothallic Scalariform conjugation is the process of reproduction of heterothallic species. Lateral conjugation, takes place in homothallic species. In scalariform conjugation the aplano gametes of two filaments opposite to one another, unite where as in lateral conjugation the aplanogametes of the two adjacent cells of the same filament unite.
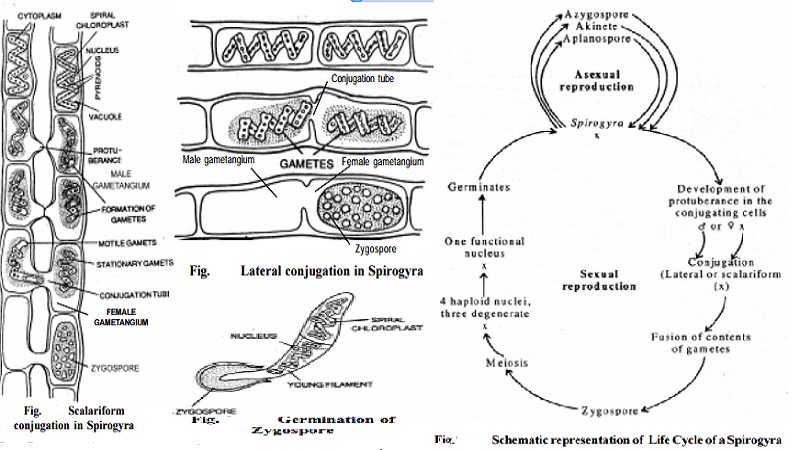
Scalariform conjugation
This type of reproduction is found in majority of the species of Spirogyra. The filaments taking part in conjugation lie side by side. Very soon the out growths are given out from the lateral walls of the opposite cells of the filaments. The out growths of opposite cells touch each other very soon the wall of contact dissolves and a tubular passage is formed between the two opposite cells of the two filaments lying side by side. This tubular passage is called conjugation tube. Simultaneously the contents of the cells retract and aplanogametes are developed. A single aplanogamete is developed in each cell. The aplanogametes formed in the cells of one filament pass into the opposite cells of the other filament through conjugation tubes in amoeboid fashion. The plasmogamy is followed by karyogamy. The transferring aplanogametes are considered to be male gametes while the receiving aplanogametes arefemale gametes. Just after the fusion the walls are formed around the zygote and they are called zygospores. A single zygospore develops in each cell of the female filament. The wall of the female decays and the zygospores are set free in the water. Each zygospore germinate into a new plant after a resting period.
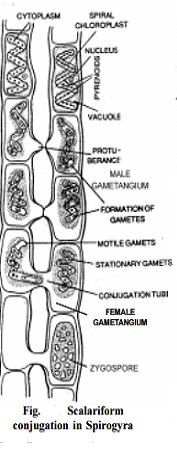
Lateral conjugation
This type of reproduction occurs in homothallic species. Here the aplanogametes of the adjacent cells of the same filament Male gametangium Female gametangium unite. At the septum a tube like structure develops and through this opening the content of one cell passes into the other. Then both a manosomefes fuse to form a zygote. The empty cells are considered as male gametangia and the cells with zygotes are female gametangia. Very soon a thick wall is secreted around each zygote and dark coloured zygospores develop. They undergo a period of rest and germinate under favourable conditions.
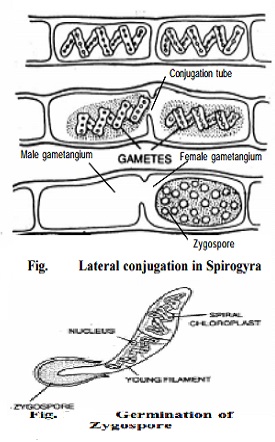
Germination of zygospore
Prior to germination, the diploid nucleus divides meiotically and, four haploid nuclei are formed. Three of the four haploid nuclei disintegrate and only one remains functional. The zygospore wall breaks and the germling comes out which soon develops into a new filament.
Related Topics