Environmental Issues - Air Pollution | 12th Zoology : Chapter 13 : Environmental Issues
Chapter: 12th Zoology : Chapter 13 : Environmental Issues
Air Pollution
Air Pollution
Earth is surrounded by a gaseous envelope which
is called atmosphere. The gaseous blanket of the atmosphere acts as a thermal
insulator and regulates the temperature of the earth by selectively absorbing
The UV rays of solar radiation. The adverse effects of pollution include
depletion of Ozone by Chlorofluorocarbons or CFCs, used as refrigerants and
global warming by elevated CO2 (industries, deforestation, and partial
combustion).
The alterations or changes in the composition of the earthŌĆÖs atmosphere by natural or human activities (anthropogenic factors) are referred as Air Pollution. Pollutants include the abundant presence of solid, liquid or gaseous substances produced by human or natural activity. The nature and concentration of a pollutant determines the severity of detrimental effects on organisms and human health.
Along with
atmospheric factors (humidity, precipitation, wind, air currents, altitude)
prevailing at a place and time, its effects can be far reaching and
catastrophic.
Air pollutants can be
┬Ę
discharge of dusts or particulate matter (PM: 2.5 ,10)
┬Ę
discharge of gases (SO2, NO2, CO, CO2)
Carbon monoxide (CO) is produced mainly due to
incomplete combustion of fossil fuels. Automobiles are major causes of CO
pollution in large cities and towns Automobile exhausts, fumes from factories,
emission from power plants, forest fires and burning of fire-wood contribute to
CO pollution.
With rapid urbanization, major amount of carbon
dioxide and sulphur dioxide (SO2) is released in the atmosphere. From
automobiles, aeroplanes, power plants and other human activities that involving
the burning of fossil fuels (coal, oil etc.,) CO2 is the main pollutant
that is leading to global warming.
Nitrogen oxides are also major air
pollutants. Fossil fuel combustion and automobiles exhausts are the source of
nitrogen oxides. Sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides are the major causes of
acid rain.
Particulate matters are tiny particles of solid
matter suspended in a gas or liquid. Combustion of fossil fuels, fly ash
produced in thermal power plants, forest fires, asbestos mining units, cement
factories are the main sources of particulate matter pollution.
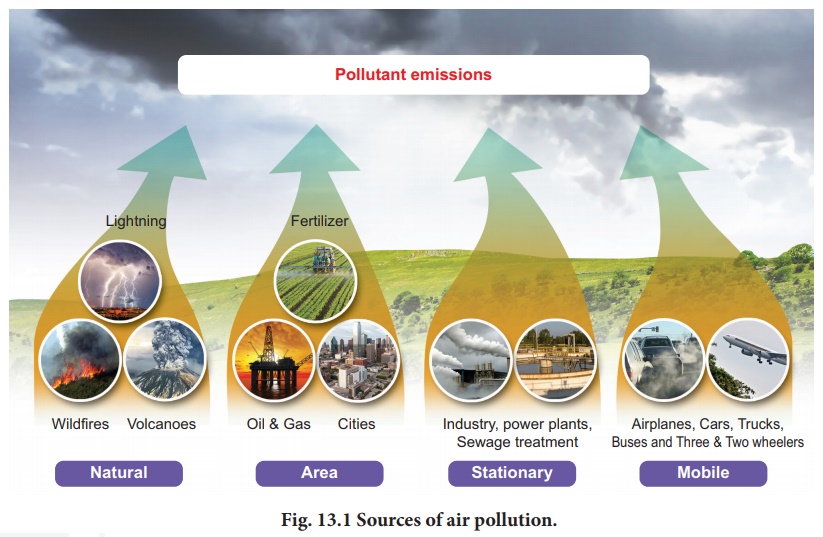
1. Sources
The main sources of air pollution are:
ŌĆó Transport sources (Fig13.1) ŌĆō cars, buses,
airplanes, trucks, trains
ŌĆó Stationary sources ŌĆō power plants, incinerators,
oil refineries, industrial facilities, and factories
ŌĆó Area sources ŌĆō agricultural - wood /
stubble burning, fireplaces
ŌĆó Natural sources ŌĆō wind-blown dust, wildfires,
volcanoes (Fig. 13.1).
2. Effects of Air Pollution
ŌĆó Affects all organisms as they depend on the
atmosphere for respiration.
ŌĆó Causes irritation in the throat, nose, lungs
and eyes. It causes breathing problems and aggravates existing health
conditions such as emphysema and asthma.
ŌĆó Contaminated air reduces the bodyŌĆÖs defense
mechanism and decreases the bodyŌĆÖs capacity to fight other infections in the
respiratory system.
ŌĆó Frequent exposure to polluted air increases
the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Breathing air that is filled with fine
particulate matter can induce hardening of the arteries, triggering cardiac
arrhythmia or even a heart attack.
ŌĆó People who exercise outdoors can sometimes be
susceptible to adverse effects of air pollution because it involves deeper and
faster breathing. Hence it is advisable to walk or jog in the mornings in
places with ample tree cover.
ŌĆó Gas leaks can be lethal or affect the quality
of air in the affected area.
ŌĆó CO in the atmosphere interferes with O2 transport since
haemoglopin has greater affinity for carbon monoxide. At low concentration it causes
headache and blurred vision. In higher concentration, it can lead to coma and
death.
3. Other notable effects of Air Pollution
Smog is a type of air pollution caused by tiny
particles in the air. The word comes from a mixture of the words smoke and fog
.
Today, smog generally refers to photochemical
smog, which is created when sunlight reacts with nitrogen oxides and volatile
organic compounds found in fossil fuel emissions from automobiles, factories,
and power plants. These reactions create ground-level ozone and particulate
matter, reducing visibility. Smog can make breathing more difficult, especially
for people with asthma.
Smog also affects plants and animals. It damages
crops as well as causes health problems in pets, farm animals and human beings.
Smog has also been known to cause corrosive damage to buildings and vehicles.
Peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) is a secondary pollutant
present in photochemical smog. It is thermally unstable and decomposes into
peroxyethanol radicals and nitrogen dioxide gas causing eye irritation.
Global warming: Increase in the concentrations of
greenhouse gases such as CO2, methane, nitrous oxide, CFCs, and ozone causes greenhouse
effect, warming of the earth, resulting in sea level rise, submerging of
islands and sea shores of various parts of the world.
Ozone depletion: Thinning of the stratospheric
ozone layer is known as ozone depletion. Such depletion causes the ŌĆśozone
holeŌĆÖ, resulting in poor screening of the harmful UV rays and increase in
incidences of skin cancer. Some of the common agents that deplete ozone are
CFCs.
Acid rain: Acid rain is a form of precipitation that
contains acidic components, such as sulfuric acid or nitric acid. It damages
trees, crops and harms marine animals (coral reefs) and induces corrosion.
4. Control of Air Pollution
Certain measures help to remove pollutants,
reduce their presence or prevent their entry into the atmosphere.
ŌĆó Trees are the best remedy for urban
particulate and gaseous pollution
ŌĆó Forests act as carbon sinks and lungs of the
planet
ŌĆó Catalytic converters in vehicles help to reduce
polluting gases drastically
ŌĆó Diesel exhaust filters in automobiles cuts particulates
ŌĆó Electrostatic precipitators reduce release of
industrial pollutants.
ŌĆó Cost effective air pollution treatment systems
like indoor plants and high performance biofilters can improve indoor air
quality.
The Taj Mahal, a UNESCO world heritage site,
is facing deterioration and damage by industrial gases due to several
industrial units around Agra. The white marble has decolorized to yellow.
5. Legal Protection
ŌĆó The Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution)
Act was enacted in 1981 and amended in 1987 for the prevention, control
and abatement of Air pollution in India.
ŌĆó Traffic Emissions Standards: The Government
has decided to enforce Bharat Stage VI norms from 2020.
ŌĆó The Green Bench and the National Green Tribunal
(NGT) give judicial safeguard to environmental protection.
Steps taken by the Central and the State
governments in India:
ŌĆó Road traffic rationing, encourage public transport,
carpooling.
ŌĆó Increase green cover alongside roads (planting
avenue trees).
ŌĆó Promoting Swachh Bharat Abhiyan
ŌĆó Enactment and Enforcement of stricter
environmental laws
ŌĆó Maintenance of air standards by proper enforcement
and monitoring
ŌĆó Reducing carbon emissions
ŌĆó Encourage use of renewable energy
ŌĆó Limiting the sale of firecrackers and
developing eco-friendly crackers
ŌĆó Make Environmental Impact Assessment mandatory
Air Quality Index (AQI) is a number used by government agencies
o communicate to the public how polluted the air is at a given time.

Related Topics