Chapter: Ophthalmology: Eye Optics and Refractive Errors
Aberrations of Lenses and Eyeglasses - Correction of Refractive Errors
Aberrations of Lenses and Eyeglasses
Optical lens systems (eyeglasses or lenses)
always have minor aberrations. These aberrations are not material flaws, rather
they are due to the laws of physics. Expensive optical systems can reduce these
aberrations by using many different lenses in a specific order.
Chromatic Aberration (Dispersion)
This means that the refractive power of
the lens varies according to thewavelength of the light.
Light consists of a blend of various
wavelengths. Light with a shortwavelength
such as blue is refracted more than light with a long wavelength such as red (Fig. 16.20). This is why monochromatic light (light of a
single wavelength) produces a sharper image on the retina.
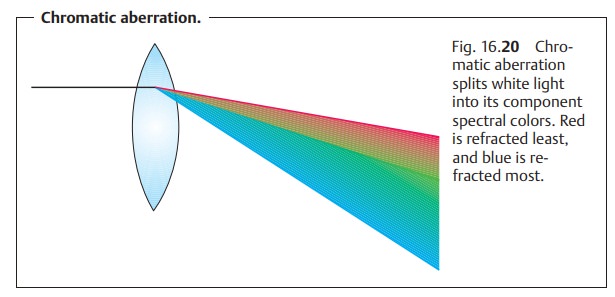
Chromatic aberration is the basis of the red-green test used for fine refraction testing.
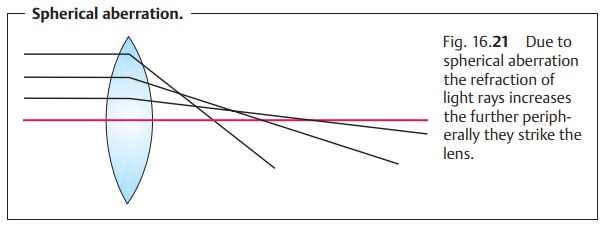
Spherical Aberration
This means that the refractive power of the lens varies according to the loca-tion at which the light ray strikes the lens.
Patients may report being able to see better when
looking through a disk with a pinhole (a stenopeic aperture) than without it.
This usually is a sign of an uncompensated refractive error in the eye.
The further peripherally the light ray strikes
the lens, the more it will be refracted (Fig. 16.21). The iris intercepts a large share of these
peripheral light rays. A narrow pupil will intercept a particularly large share
of peripheral light rays, which improves the depth of field. Conversely, depth
of field is signif-icantly poorer when the pupil is dilated.
Patients who have received mydriatic agents should refrain from driv-ing.
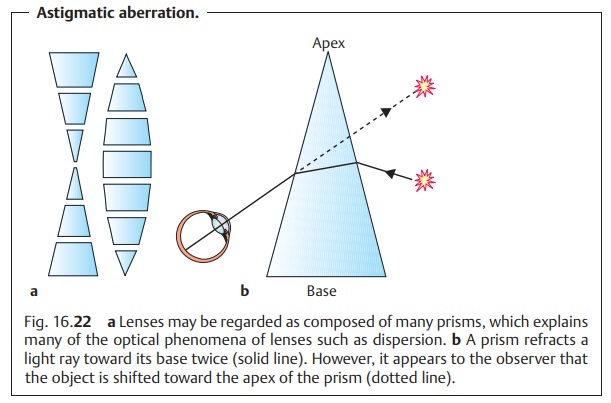
Astigmatic Aberration
A punctiform object viewed through a spherical lens appears as a line.
If one looks through a lens obliquely to its
optical axis, it will act as a prism
(Fig. 16.22a). A prism refracts a light ray toward its base (Fig. 16.22b). In addi-tion to this, the light is split into its component
spectral colors. Light with a short
wavelength (blue) is refracted more than light with a long wavelength (red). Astigmatic aberration is an undesired side
effect that is present whenever one looks through a lens at an oblique angle.
This phenomenon should be distinguished from astigmatic or toric lenses, which
correct for astigmatism of the eye when the patients looks through them along the optical axis.
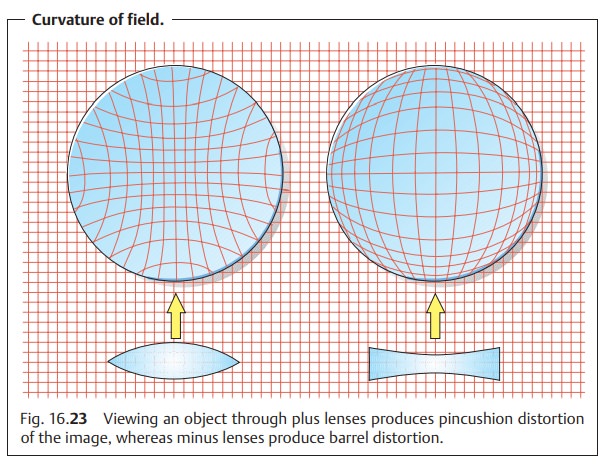
Curvature of Field
This means that the magnification of the image changes as one approachesthe
periphery. The result is a
sharp image with peripheral curvature. Convexor plus lenses produce pincushion distortion; concave or minus
lenses pro-duce barrel distortion
(Fig. 16.23).
Related Topics