Chapter: Java The Complete Reference : The Java Library : Introducing the AWT: Working with Windows, Graphics, and Text
Window Fundamentals - AWT Classes
Window Fundamentals
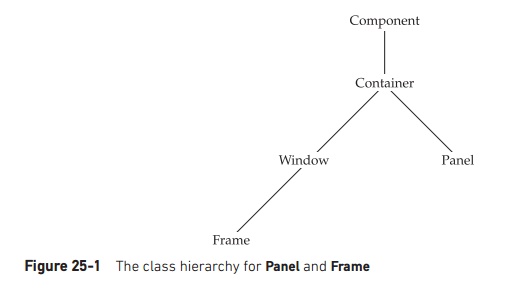
The AWT defines windows according to a class hierarchy that adds
functionality and specificity with each level. The two most common windows are
those derived from Panel, which is
used by applets, and those derived from Frame,
which creates a standard application window. Much of the functionality of these
windows is derived from their parent classes. Thus, a description of the class
hierarchies relating to these two classes is fundamental to their
understanding. Figure 25-1 shows the class hierarchy for Panel and Frame. Let’s
look at each of these classes now.
Component
At the top of the AWT hierarchy is the Component class. Component
is an abstract class that encapsulates all of the attributes of a visual
component. Except for menus, all user interface elements that are displayed on
the screen and that interact with the user are
subclasses of Component.
It defines over a hundred public methods that are responsible for managing
events, such as mouse and keyboard input, positioning and sizing the window,
and repainting. (You already used many of these methods when you created
applets in Chapters 23 and 24.) A Component
object is responsible for remembering the current foreground and background
colors and the currently selected text font.
Container
The Container class is a
subclass of Component. It has
additional methods that allow other Component
objects to be nested within it. Other
Container objects can be stored inside of a Container (since they are themselves instances of Component). This makes for a
multileveled containment system. A
container is responsible for laying out (that is, positioning) any components
that it contains. It does this through the use of various layout managers,
which you will learn about in Chapter 26.
Panel
The Panel class is a
concrete subclass of Container. A Panel may be thought of as a
recursively nestable, concrete screen component. Panel is the superclass for Applet.
When screen output is directed to an applet, it is drawn on the surface of a Panel object. In essence, a Panel is a window that does not contain
a title bar, menu bar, or border. This is why you don’t see these items when an
applet is run inside a browser. When you run an applet using an applet viewer,
the applet viewer provides the title and border.
Other components can be added to a Panel object by its add( )
method (inherited from Container).
Once these components have been added, you can position and resize them manually using the setLocation( ), setSize( ), setPreferredSize(
), or setBounds( ) methods
defined by Component.
Window
The Window class creates
a top-level window. A top-level window
is not contained within any other object; it sits directly on the desktop.
Generally, you won’t create Window
objects directly. Instead, you will use a subclass of Window called Frame,
described next.
Frame
Frame encapsulates what is commonly
thought of as a “window.” It is a subclass of Window and has a title bar, menu bar, borders, and resizing
corners. The precise look of a Frame
will differ among environments. A number of environments are reflected in the
screen captures shown throughout this book.
Canvas
Related Topics