Chapter: Business Science : Security Analysis and Portfolio Management : Investment Setting
Types of Risks in Investment
TYPES OF RISKS:
Personal Risks
This
category of risk deals with the personal level of investing. The investor is
likely to have more control over this type of risk compared to others.
Timing risk
is the risk of buying the right security at the wrong time. It
also refers to selling the right security at the wrong time. For
example, there is the chance that a few days after you sell a stock it will go
up several dollars in value. There is no surefire way to time the market.
Tenure risk
is the risk of losing money while holding onto a security. During
the period of holding, markets may go down, inflation may worsen, or a
company may go bankrupt. There is always the possibility of loss on the
company-wide level, too.
Company Risks
There are
two common risks on the company-wide level. The first, financial risk is
the danger that a corporation will not be able to repay its debts. This has a
great affect on its bonds, which finance the company's assets. The more assets
financed by debts (i.e., bonds and money market instruments), the greater the
risk. Studying financial risk involves looking at a company's management, its
leadership style, and its credit history.
Management
risk is the risk that a company's management
may run the company so poorly that it is unable to grow in value or pay
dividends to its shareholders. This greatly affects the value of its stock and
the attractiveness of all the securities it issues to investors.
Market Risks
Fluctuation in the market as a whole may
be caused by the following risks:
Market risk
is the chance that the entire market will decline, thus affecting
the prices and values of securities. Market risk, in turn, is influenced
by outside factors such as embargoes and interest rate changes. See Political
risk below.
Liquidity
risk is the risk that an investment, when
converted to cash, will experience loss in its value. When you want to
sell the stock you are currently holding, there is nobody there to buy your
stock, meaning that there is no volume in that stock.
Interest
rate risk is the risk that interest rates will
rise, resulting in a current investment's loss of value. A bondholder,
for example, may hold a bond earning 6% interest and then see rates on that
type of bond climb to 7%.
Inflation
risk is the danger that the dollars one
invests will buy less in the future because prices of consumer goods
rise. When the rate of inflation rises, investments have less purchasing power.
This is especially true with investments that earn fixed rates of return. As
long as they are held at constant rates, they are threatened by inflation.
Inflation risk is tied to interest rate risk, because interest rates often rise
to compensate for inflation. Return of investment (ROI) is less than
the market inflation rate. e.g. Return of investment (ROI) : 5%; Market
Inflation rate (IR) : 8.5%
Exchange
rate risk is the chance that a nation's currency
will lose value when exchanged for foreign currencies.
Reinvestment
risk is the danger that reinvested money will
fetch returns lower than those earned before reinvestment. Individuals
with dividend-reinvestment plans are a group subject to this risk. Bondholders
are another.
National And International
Risks
National and world events can profoundly
affect investment markets.
Economic
risk is the danger that the economy as a
whole will perform poorly. When the whole economy experiences a
downturn, it affects stock prices, the job market, and the prices of consumer
products.
Industry
risk is the chance that a specific industry
will perform poorly. When problems plague one industry, they affect the
individual businesses involved as well as the securities issued by those
businesses. They may also cross over into other industries. For example, after
a national downturn in auto sales, the steel industry may suffer financially.
Tax risk is the danger that rising taxes will make investing less
attractive. In general, nations with relatively low tax rates, such as
the United States, are popular places for entrepreneurial activities.
Businesses that are taxed heavily have less money available for research,
expansion, and even dividend payments. Taxes are also levied on capital gains,
dividends and interest. Investors continually seek investments that provide the
greatest net after-tax returns.
Political
risk is the danger that government
legislation will have an adverse affect on investment. This can be in
the form of high taxes, prohibitive licensing, or the appointment of
individuals whose policies interfere with investment growth. Political risks
include wars, changes in government leadership, and politically motivated
embargoes.
Investors and speculators:
Investors:
The
investors buy the securities with a view to invest their savings in profitable
income earning securities. They generally retain the securities for a
considerable length of time. They are assured of a profit in cash. They are
also called genuine investors.
Speculators:
The
speculators buy securities with a hope to sell them at a profit in future. They
do not retain their holdings for a longer period. They buy the securities with
the object of selling them and not to retain them. They are interested only in
price differentials. They are not genuine investors.
Differences between
investors and speculators:
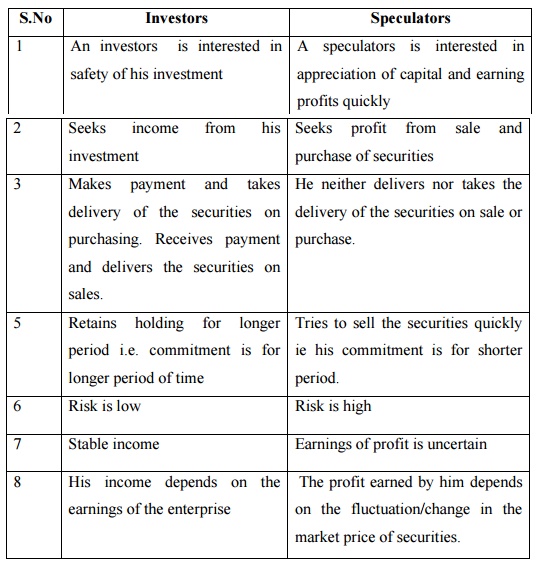
Investors
1 An investors is
interested in safety of his investment
2 Seeks income from his
investment
3 Makes payment and
takes delivery of the securities on purchasing. Receives payment and delivers
the securities on sales.
4 Retains holding for
longer period i.e. commitment is for longer period of time
5 Risk is low
6 Stable income
7 His income depends on
the earnings of the enterprise
Speculators
1 A speculators is
interested in appreciation of capital and earning profits quickly
2 Seeks profit from
sale and purchase of securities
3 He neither delivers
nor takes the delivery of the securities on sale or purchase.
4 Tries to sell the
securities quickly ie his commitment is for shorter period.
5 Risk is high
6 Earnings of profit is
uncertain
7 The profit earned by
him depends on the fluctuation/change in the market price of securities.
Speculation:
Speculation
refers to the buying and selling of securities in the hope of making a profit
from expected change in the price of securities. Those who engage in such
activity are known as speculators.
A
speculator may buy securities in expectation of rise in price. If his
expectation comes true, he sells the securities for a higher price and makes a
profit. Similarly a speculator may expect a price to fall and sell securities
at the current high price to buy again when prices decline. He will make a
profit if prices decline as expected. The benefits of speculation are:
1. It leads to smooth change and prevents wide fluctuations in
security prices at different times and places
2. Speculative activity and the resulting effect in the prices of
securities provided a guidance to the public about the market situation.
Differences between speculation and gambling:
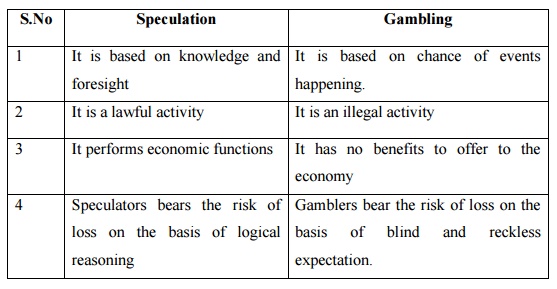
Speculation
1 It is based on
knowledge and foresight
2 It is a lawful
activity
3 It performs economic
functions
4 Speculators bears the
risk of loss on the basis of logical reasoning
Gambling
1 It is based on chance
of events happening.
2 It is an illegal
activity
3 It has no benefits to
offer to the economy
4 Gamblers bear the
risk of loss on the basis of blind and reckless expectation.
Related Topics