Chapter: Biochemistry: The Importance of Energy Changes and Electron Transfer in Metabolism
The Nature of Metabolism
The Nature of Metabolism
What is metabolism?
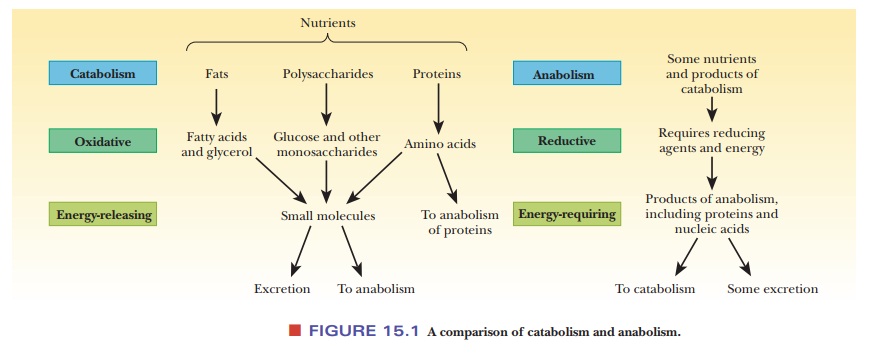
Until now, we have discussed some basic chemical principles and investigated the natures of the molecules of which living cells are composed. We have yet to discuss the bulk of chemical reactions of biomolecules themselves, which constitute metabolism, the biochemical basis of all life processes. The molecules of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins taken into an organism are processed in a variety of ways (Figure 15.1). The breakdown of larger molecules to smaller ones is called catabolism. Small molecules are used as the starting points of a variety of reactions to produce larger and more complex molecules, including proteins and nucleic acids; this process is called anabolism. Catabolism and anabolism are separate pathways; they are not simply the reverse of each other.
Catabolism is an oxidative process that releases energy; anabolism
is a reduc-tive process that requires energy.
Summary
Metabolism is the sum total of the chemical reactions of
biomolecules in an organism.
Related Topics