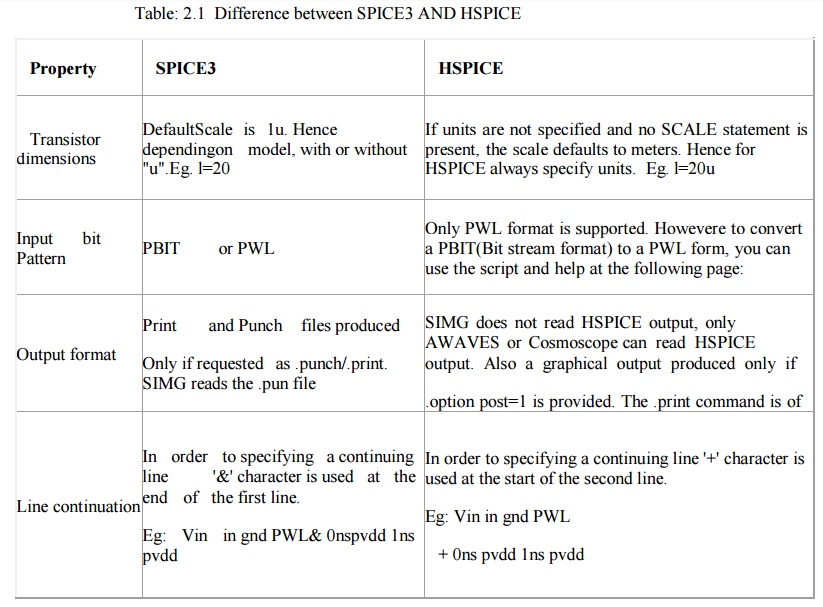
Chapter: VLSI Design : Circuit Characterization and Simulation
Spice Tutorial
SPICE TUTORIAL
1. Introduction
Given
below is a brief introduction to simulation using HSPICE and AWAVES/Cosmoscope
in the UTD network.
HSPICE is
a device level circuit simulator from Synopsys.
HSPICE
takes a SPICE file as input and produces output describing the requested
simulation of the circuit.
The
simulation output can be viewed with AWAVES (or) Cosmos cope from Synopsys. A
short example is provided to illustrate the basic procedures involved in
running HSPICE.
2. Setting up your account
to access HSPICE
This
section shows how to setup your environment for running HSPICE.
For users
who have a working CAD setup, you may just want to check that the
LM_LICENSE_FILE has the following values in the list of all the other
licenses,/home/cad/flexlm/ti-license:/home/cad/flexlm/hspice.flx.
If not,
follow the procedures below: Instructions for both bash and tcsh/csh users is provided
here:
bash
users:
Add the
following line to the .bash_profile
LM_LICENSE_FILE=$LM_LICENSE_FILE:/home/cad/flexlm/hspice.flx
; export
LM_LICENSE_FILE
tcsh/csh
users:
Add the
following line to your
.tcshrc
setenv
LM_LICENSE_FILE
${LM_LICENSE_FILE}:/home/cad/flexlm/hspice.flx
To test
if the above procedure has setup your environment successfully, invoke a new
shell (this will ensure that the new environment variables are in place).
Also you
will need a HSPICE input file to test this (You can copy paste the HSPICE
example given below to test this). The input Spice file is typically named with
extension *.sp.
%
hspice<your_input_file>.sp
The
following message indicates trouble with invocation:
If the
error is "hspice: command not found" make sure that the HSPICE
directory " /home/cad/synopsys/hspice/U-2003.09-SP1/sun58/" is
included in the $PATH variable.
Cannot
execute /home/cad/synopsys/hspice/U-2003.09-SP1/sun58/hspice
or
lic:
Using FLEXlm license file:
lic:
/home/cad/flexlm/hspice.flx
lic:
Unable to checkout hsptest
The above
error may indicate that the license server maybe down, or the machine is not
able to run HSPICE.
On the
other hand if the procedure was successful, you will simply see a message
indicating successful completion of simulation or errors in simulation, both of
which indicate HSPICE has run your file.
3. Setting up the
HSPICE input file
Consider
a self loaded min geometry inverter circuit.
The
objective of the HSPICE input file below is to measure the tpLH and tpHL both
graphically
and otherwise.
The
following HSPICE file is stored in "inv.sp".
The
HSPICE input file is commented adequately about the different options used in
it.
It will
be beneficial to
keep in mind
the following differences
between SPICE3 and HSPICE.
HSPICE Example File
*
Self loaded min geometry inverter, sample HSPICE
file
*
Include the model files
*
Include the hspice model files for 0.18u
technology.
.include /home/cad/vlsi/models/hspice/cmos0.18um.model
*
The subcircuit for the inverter
.subckt
invert in outvddgnd
.param
length=0.2u
m01 out
in vddvddpfet w='4*length' l='length' m02 out in gndgndnfet w='1.5*length'
l='length'
.ends
*
The main inverter
X1 in
outvddgnd invert
* Four
loads for the inverter
X2 out
out1 vddgnd invert X3 out out2 vddgnd invert X4 out out3 vddgnd invert X5 out
out4 vddgnd invert
*
PWL pattern for the input, represents a bit stream
1100101
*
Slew=1ns, bit time=5ns
Vin in
gnd PWL 0ns pvdd 1ns pvdd 5ns pvdd 6ns pvdd 7ns 0 10ns 0 + 15ns 0 16ns pvdd
21ns pvdd 22ns 0 25ns 0 26ns pvdd *Parametricdefinitions
.parampvdd=2.0v
*
Power supplies vvddvdd 0 pvddvgndgnd 0 0
*
Control statements
.option
post=1
.TR
0.05ns 30ns
.print TR
V(in out)
*
Measure statements help in calculating TPLH, TPHL
etc, without
*
opening the waveform viewer
.measure
trantplh trig v(in) val='0.5*pvdd' fall=1 targ v(out) val='0.5*pvdd' rise=1
.measure
trantphl trig v(in) val='0.5*pvdd' rise=1 targ v(out) val='0.5*pvdd' fall=1
.END
4. Running HSPICE
simulations
The
following commands can be used to simulate the above HSPICE file stored in
inv.sp and store all the simulation results with file prefix as "inv"
%
hspiceinv.sp -o inv
This
results in the creation of the following output files: inv.ic -> Operating
point node voltages (initial conditions) inv.lis -> Output listing
inv.mt0
-> Transient analysis measurement results
inv.pa0 ->Subcircuit
cross-listing
inv.st0
-> Output status
inv.tr0
-> Transient analysis results
5.
Analyzing the outputs
In the
above example, the output data can be analyzed both graphically as well as in
text form.
Text
outputs:
To view
the results of the .measure computation, execute:
% cat inv.mt0
$DATA1
SOURCE='HSPICE' VERSION='2003.09-SP1'
.TITLE '
'
tplh tphl temper alter#
3.416e-10 1.002e-09 25.0000 1.0000
As can be
seen above, the values of propogation delay have been obtained even before the
waveform analysis software has been opened.
Graphical
outputs:
I.
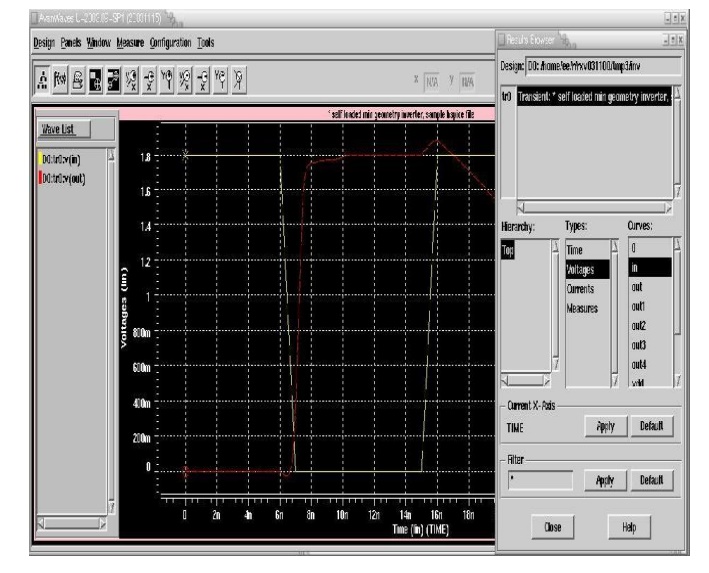
Synopsys Awaves:
To invoke
AWAVES run the following command:
% awaves
If you
get the error "awaves: command not found" make sure that the AWAVES
directory "/home/cad/synopsys/hspice/U-2003.09-SP1/sun58/" is
included in the $PATH variable.
Once
invoked, open the designusing the pull down menu options: Design->Open and
select inv.sp and then highlight the tr0 (Transient response)
item in
the select box.
You will
also see the hierarchy of the netlist and the types of analysis and the
individual signals in separate lists in the window. Select Hierarchy -> Top,
Types -> Voltages and select the voltages you want to observe.
For eg.in
and out by double clicking on the names. You will see the screen below for the
stimulus provided in inv.sp.
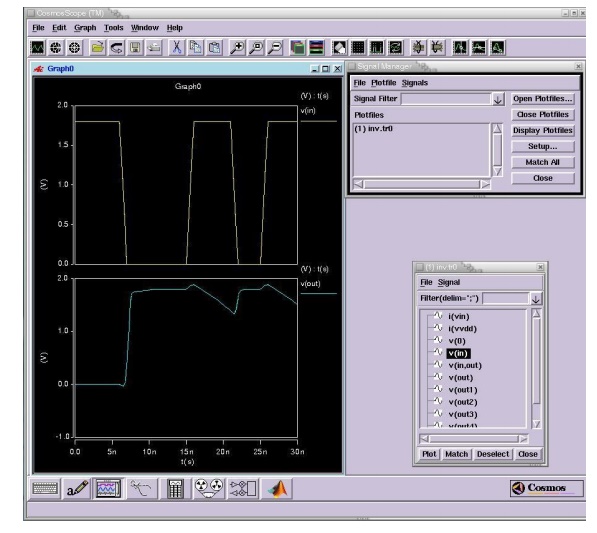
II. Synopsys Cosmoscope:
To invoke
Cosmoscope run the following command:
%cscope
If you get the error "awaves: command not
found" make sure that the AWAVES directory "
/home/cad/synopsys/cosmo/ai_bin/" is included in the $PATH variable.
Once
invoked, open the design using the pull down menu options: File -> Open
-> Plot files and select file inv.tr0 in the working directory.
A Signal
Manager Window and signal window opens.
Select
the necessary signals to be plotted by double-clicking them. For example v(in)
and v(out) by double clicking on the signal names in the signal window
You will
see the screen below for the stimulus provided in invest.
Related Topics