Chapter: Introduction to Botany: Tissues and organs; How the Plant is built
Plant Organs and Organ Systems
Organs and Organ Systems
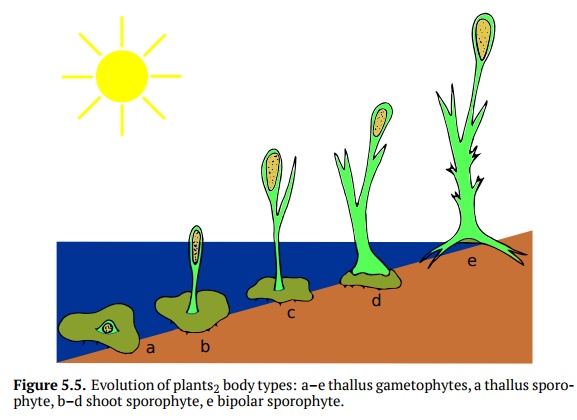
Vegetabilia (Fig. 6.1) have three different types of body construction
(Fig. 5.5). The most primitive plants have
thallus body, more advanced is the shoot (unipo-lar) plant body, and most land
plants have the bipolar plant body. The thal-lus
plant body is flat, similar to leaf but do not differentiated into
particularorgans. Most gametophytes (except true mosses) have this type, and
also few sporophytes (which mostly are reduced water plants). Shoot (unipolar) plantbody consists
only of branching shoots, roots are absent. This is typical to allBryophyta
sporophytes, mosses (Bryopsida) gametophytes, and also to sporo-phytes of
Psilotopsida ferns. Finally, bipolar
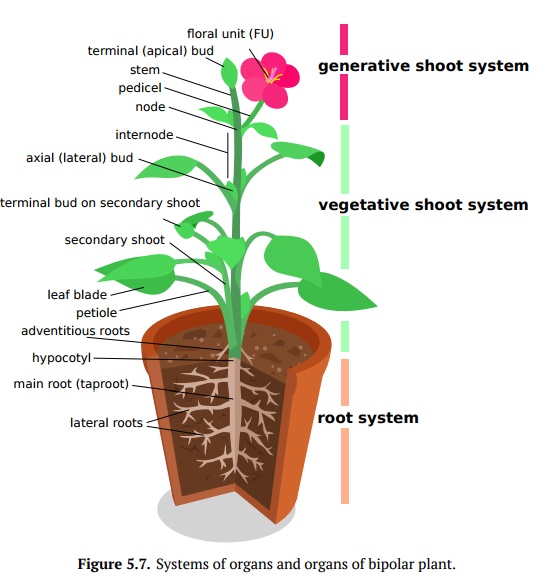
plant body has both shoots and roots (Fig 5.7).
Most bipolar plants have shoots consist of stems and leaves, but this is not an
absolute requirement since young plant stems are normally green and can do
photosynthesis.
Typical organs of
bipolar plant are stems (axial aerial organs with continuous growth), leaves
(flat lateral organ with restricted growth), roots (axial soil or-gan modified
for absorption) and floral units (FU)
which are elements of the generative system (fructifications) such as a pine
cone or any flower.
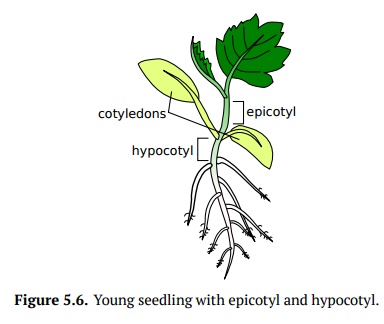
Buds, fruits, seeds
and specific to seedlings hypocotyl and epicotyl are non-organs for different reasons: buds are just young shoos,
fruit is the ripe flower, hypocotyl is
a part of stem between first leaves of the seedling (cotyledons)and root (i.e.,
stem/root transition place), epicotyl
is first internode of stem (Fig. 5.6), and
finally, seed is a chimeric
structure with three genotypes so it is impossible to call it “organ”.
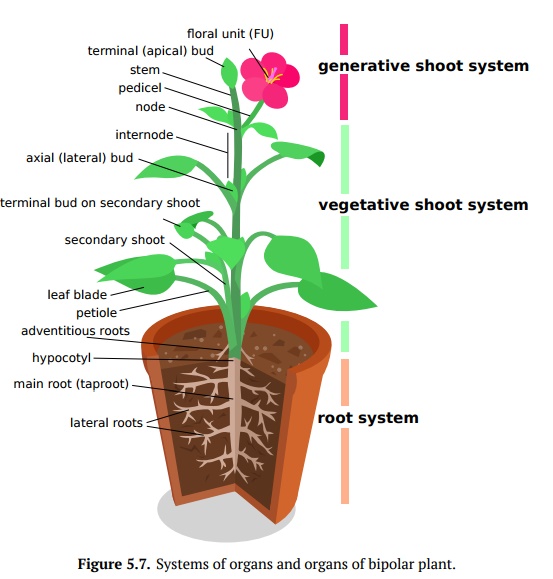
Root, stem, leaf and
FU are four basic plant organs which
in bipolar plant could be grouped in root and shoot system; the latter is
frequently split into generative shoot system (bearing FU), and vegetative
shoot system (without FU). Vegetative shoot system usually consists of main and
secondary shoots; shoots contain ter-minal buds, axillary (lateral) buds, stem
(nodes and internodes) and leaves. We will start from leaves.
Related Topics