Chapter: Paediatrics: Growth and puberty
Paediatrics: Precocious puberty: management
Precocious puberty: management
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is based on
demonstrating progressive pubertal develop-ment and increased growth rate,
together with laboratory evidence of increased sex steroid production.
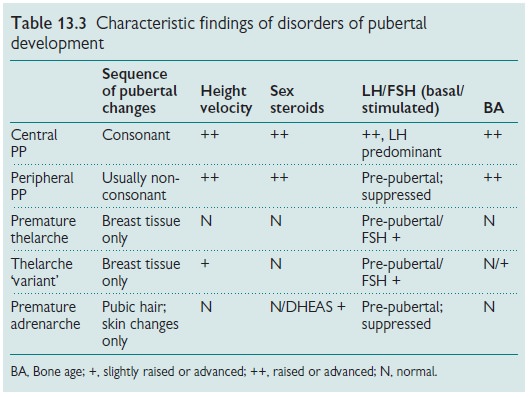
Distinguishing central and peripheral PP and PP from other normal variants of
pubertal development may be diffi-cult (see Table 13.3). In CPP there is
evidence of consonance in sequence of pubertal development in keeping with the
normal physiological activa-tion of puberty.
Management
The management of precocious
puberty is aimed at the following:
·Detection
and treatment of underlying pathological causes of PP: this is especially important in males in whom early puberty is invariably
due to organic disease.
·Reducing
the rate of skeletal maturation, if necessary: accelerated skeletal maturation and growth rate
occur and will result in the affected child being tall during childhood
relative to peers. However, skeletal maturation exceeds concominant growth and
thus growth potential is reduced, growth is complete prematurely, and final
adult height is reduced and potentially below the predicted expected familial
target height range.
·Reducing
and halting, if necessary, the rate of physical pubertal development.
·Addressing
potential behavioural and psychological difficulties: sexual and reproductive characteristics advance inappropriately for age,
leading to mature appearance. Early menstruation occurs in girls, and
spermatogenesis and ejaculation in boys. Sexualized behaviour may occur and
interactions with age-peers and adults may be based on assumed, but
age-inappropriate, mental and social expectations.
Before therapy is considered, it
is essential that an explanation of the physiology and physical consequences of
precocious puberty should be discussed with the parents and the child. The
decision on therapy should be made jointly with the parents.
Treatment of precocious puberty
Central PP
·Suppression of the
hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis with a long-acting GnRH analogue is the
only currently effective treatment for central PP. These agents work by
providing continuous stimulation of the GnRH receptor on the pituitary
gonadotrophes, resulting in down-regulation of the receptor and thus decreased
LH and FSH secretion.
·GnRH analogues are administered by
either SC or IM injection, monthly (or 3-monthly in depot preparations).
Treatment efficacy should be
assessed by monitoring growth rate and pubertal stage. In addition, serum LH
and FSH levels (basal and stimulated) should be measured to ensure
hypothalamic–pituitary– gonadal axis suppression.
Related Topics