Types, Merits, Demerits - Moist Heat Methods of Cooking | 11th Home Science : Chapter 3 : Food Science
Chapter: 11th Home Science : Chapter 3 : Food Science
Moist Heat Methods of Cooking
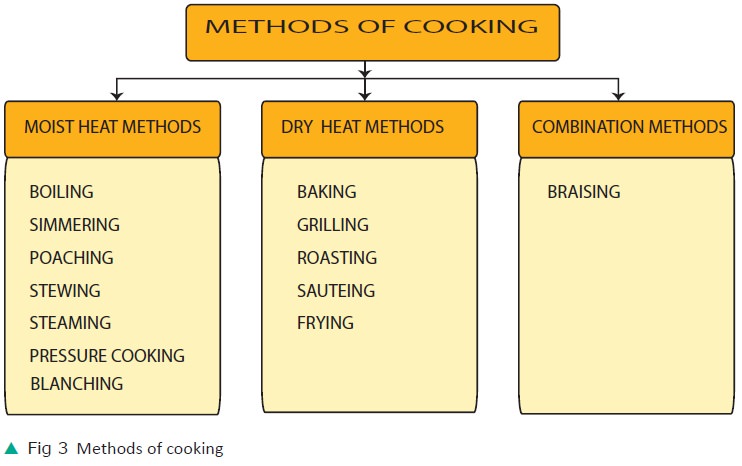
Moist Heat Methods
i. Boiling:
Boiling is cooking foods by just immersing them in water at 100°C and maintaining the water at that temperature till the food is tender. It does not require special skill and equipment. It is time consuming.
Merits:
· Simple method, does not require skill or any particular equipment.
· Uniform cooking can be achieved.
Demerits:
1. Continuous boiling damages the struc-ture and texture of food.
2. There is a loss of vitamins B and C if the cooking water is discarded.
3. It is time consuming and may lead to increased use of fuel.
4. Loss of colour —Water soluble pig-ments may be lost during cooking.

ii) Simmering
When food is cooked in a pan with a well fitted lid at a temperature just below the boiling point 82°–99°C, it is known as simmering. It is a useful method when foods have to be cooked for a long time to make it tender. (eg) vegetables.
Merits:
1. Food can be cooked with less chances of burning.
2. The flavour of the food can be enhanced.
3. Does not require any skill or specific equipment.
Demerits:
1. Takes a long time for cooking the food.
2. Precaution must be taken to ensure that the food does not get burnt.
iii) Poaching
This involves cooking in the minimum amount of liquid at a temperature of 80°– 85°C. Foods generally poached are eggs and fish.
Merits:
1. No special equipment is needed.
2. It is a quick method of cooking and thus saves fuel.
3. Poached foods are easily digested as no fat is added.
Demerits:
1. Poached foods may not appeal to ev-erybody as they are bland to taste.
2. Foods can get burnt if not monitored closely.
3. Water soluble nutrients may be lost if they are leached into the water.
iv) Stewing
This is a gentle method of cooking in a pan with a tight fitting lid, using small quan-tities of liquid to cover only half the food. The liquid is brought to a boiling point and then the heat applied is reduced to maintain the cooking at simmering temperature ie., 98°C. Apples can be cooked by this method.
Merits:
1. Loss of nutrients is avoided as the wa-ter used for cooking is not discarded.
2. Flavour is retained.
Demerits:
· The process is time consuming and there is wastage of fuel.
v) Steaming
This method requires the food to be cooked in steam. This is generated from vigorously boiling water or liquid in a pan so that the food is completely surrounded by steam and not in contact with the water or liquid. Here the food gets cooked at 100 degrees.
Merits:
· Less chances of burning.
· Texture of food is better, as it is made light and fluffy.
· Saves time and fuel.
· Steamed foods like idli and idiappam have very negligible fat and are easy to digest, and are good for children, elderly and therapeutic diets.
Demerits:
1. Steaming equipment is required.
2. This method is limited to the prepara-tion of selected foods.
vi) Pressure cooking
In pressure cooking escaping steam is trapped and kept under pressure so that the temperature of the boiling water and steam can be raised above 100°C thus reducing cooking time. Foods cooked in pressure cooker are rice, dhal, vegetables and meat.
Merits:
1. Cooking time is less compared to oth-er methods.
2. Nutrient and flavour loss is minimized.
3. Conserves time and fuel and different items can be cooked at the same time.
4. Less chance of burning.
5. Constant monitoring is not necessary.
Demerits:
1. The initial investment cost may not be affordable by everybody.
2. Knowledge of the use, care and main-tenance of the cooker is required to prevent accidents.
3. Careful watch on the cooking time is necessary to prevent over cooking.

vii) Blanching
In meal preparation, it is often necessary only to peel off the skin of fruits and veg-etables without making them tender. This can be achieved by the method of blanch-ing. In this method food is dropped in boiling water for 5 seconds to 2 minutes depending on the texture of food. This helps to remove the skin without softening the food.
Blanching can also be done by pouring enough hot water on the food to immerse it for some time or subjecting foods to boiling temperatures for short periods and then immediately immersing them in cold water. This process causes the skin to become loose and then can be peeled off easily.
Merits:
1. Peels can easily be removed to improve digestibility.
2. Destroys enzymes that bring about spoilage.
3. Texture can be maintained, while im-proving the colour and flavor of the food.
Demerits:
Loss of nutrients if cooking water is discarded.
Related Topics