Chapter: Electric Energy Generation and Utilisation and Conservation : Wind Energy
Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWT): Schematic Structure, Advantage, Disadvantages
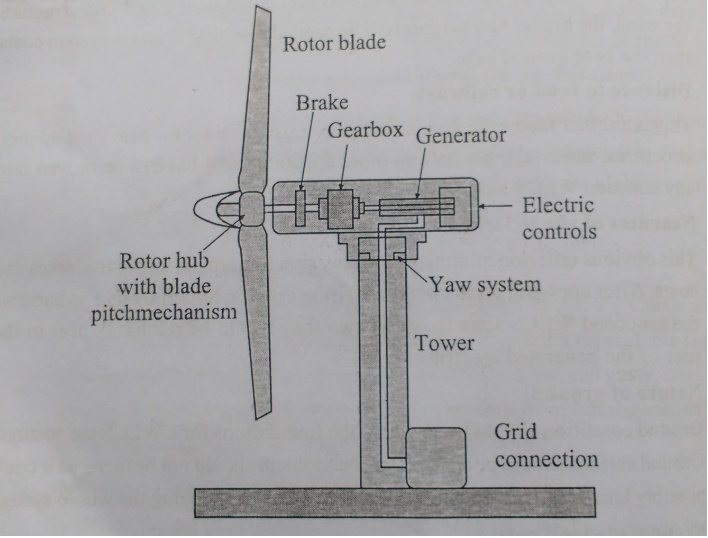
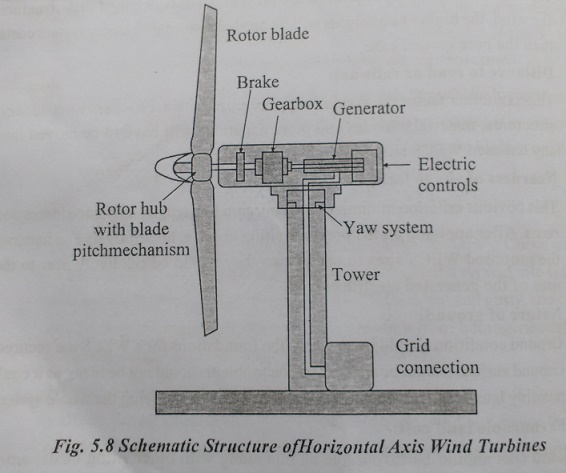
Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWT)
Horizontal axis wind turbines, also shortened to HAWT, are the common style that most of us think of a wind turbine. A HAWT has a similar design to a windmill, it has blades that look like a propeller that spin on the horizontal axis as shown in figure.
Horizontal axis wind turbines have the main rotor shaft and electrical generator at the top of a tower, and they must be pointed into the wind. Small turbine are pointed by a simple wind vane placed square with the rotor (blades), while large turbines generally use a wind sensor coupled with a servo motor to turn the turbine into the wind. Most large wind turbines have a gearbox, which turns the slow rotation of the rotor into a faster rotation that is more suitable to drive an electrical generator.
Since a tower produces turbulence behind it, the turbine is usually pointed upwind of the tower. Wind turbine blades are made stiff to prevent the blades from being pushed into the tower by high winds. Additionally, the blades are placed a considerable distance in front of the tower and are sometimes tilted up a small amount.
Downwind machines have been built, despite the problem of turbulence, because they don’t need an additional mechanism for keeping them in line with the wind. Additionally, in high winds the blades can be allowed to bend which reduces their swept area and thus their wind resistance. Since turbulence leads to fatigue failures, and reliability is so important, most HAWTs are upwind machines.
Important point to remember recording HAWT:
(1) Lift is the main force
(2) Much lower cyclic stress
(3) 95% of the existing turbines are HAWTs
(4) Nacelle is placed at the top of the tower
(5) Yaw mechanism is required
HAWT Advantage
1. The tall tower base allows access to stronger wind in sites with wind shear. In some wind shear sites, every ten meters up the wind speed can increase by 20% and the power output by 34%.
2. High efficiency, since the blades always move perpendicular to the wind, receiving power through the whole rotation. In contrast, all vertical axis wind turbines, and most proposed airborne wind turbine designs, involve various types of reciprocating actions, requiring airfoil surfaces to the wind leads to inherently lower efficiency.
HAWT Disadvantages
1. Massive tower construction is required to support the heavy blades, gearbox, and generator.
2. Components of horizontal axis wind turbine (gearbox, rotor shaft and brake assembly) being lifted into position.
3. Their height makes them obtrusively visible across large areas, disrupting the appearance of the landscape and sometimes creating local opposition.
4. Download variants suffer from fatigue and structural failure caused by turbulence when a blade passes through the tower’s wind shadow (for this reason, the majority of HAWTs use an upwind design, with the rotor facing the wind in front of the tower).
5. HAWTs require an additional yaw control mechanism to turn the blades toward the wind.
6. HAWTs generally require a braking or yawing device in high winds to stop the turbine from spinning and destroying or damaging itself.
Related Topics