Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio zoology Human Body higher secondary school
Female Menstrual cycle - 28 days
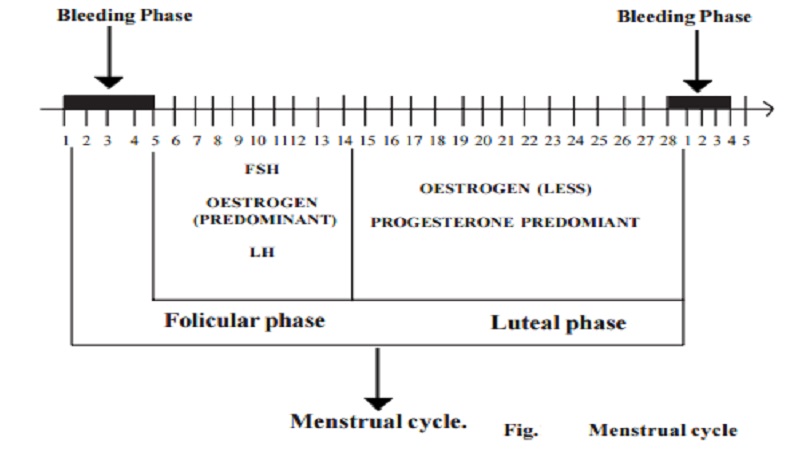
Female Menstrual cycle
The functioning of the reproductive system in human adult female is characterized by the menstrual cycle. While the changes concerned within ovula-tion and the formation of the corpus luteum, are going on in the ovary, the uterine endometrium shows striking cyclical changes. The rhythmical series of changes in the sex organs occur for about 28 days through out the reproductive life of women from puberty to menopause (except during times of pregnancy). It is called the menstrual cycle.
The most prominent feature of this cycle is a monthly flow of blood from the genital canal. This is called menstruation or menses. A menstrual cycle begins with the onset of menstrual bleeding and ends just before the next menstruation.
The menstrual cycle is usually divided into the following phases on the basis of changes taking place in the uterine endometrium.
The follicular phase or Proliferative phase ( 5th day - 14th day)
The follicular phase is initiated by the release of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) from the anterior pituitary gland. During this phase, a primary follicle begins to enlarge. While it is growing, the follicles secrete oestrogen and smaller quantities of progesterone into the blood. Under the effects of oestrogen from the developing follicle, the endometrium starts regenerating from the basal portion. Deeper parts of the glands start proliferating. By day 14, graffian follicle has matured and pushed up against the ovary surface. The secretion of FSH ceases at the end of follicular phase.
The Luteal phase or Premenstrual phase (15th day - 28th day)
The luteal phase begins at day 14. Under the influence of Leutenizing hormone (LH) released by the anterior pituitary, rupture of graffian follicle and release of ovum (ovulation) occurs. After ovulation, the empty follicle is transformed into a transitory endocrine gland called corpus luteum. The corpus luteum slowly increases in size and releases a large quantity of progestrone and smaller amount of oestrogen into the blood. The progesterone acts on endometrium of the uterus, preparing it to receive the fertilized ovum. To maintain pregnancy and to prevent the contraction of uterus, the progesterone hormone is highly essential. If there is no fertilisation, the corpus luteum degenerates and is reabsorbed by the ovary at the end of luteal phase.
The menstrual phase (1st - 5th day)
The decline in progesterone and oestrogen initiates shedding of the endometrium and severe bleeding in a process called mensus or menstruation. During this phase, all the extra layers are sloughed off along with unfertilized egg. At the termination of menstruation, the corpus luteum is converted into a scar tissue called corpus albicans.
Fertilization
The union of the egg and the sperm is called fertilization. It results in the production of a single diploid cell called zygote.
At the time of ovulation, the ovum is fully matured and it enters the infundibulum of the uterine tube and passes into the ampulla. Fertilization of the ovum occurs in the ampulla of the uterine tube. One spermatozoan pierces the egg membrane, zona pellucida and enters the ovum. Polygamy (entry of more sperms) is avoided by the formation of fertilization membrane around the ovum.
In vitro fertilization (Test tube babies)
The so called test tube babies are produced by the technique of in vitro fertilization. (In vitro = outside the body, as against in vivo = within
the body). This technique is being increasingly used in couples who are not able to achieve fertilization in the normal way
Gonadotropins are administered to the woman to stimulate growth of follicles in the ovary. Just before ovulation, the ovum is removed (using an aspirator) and is placed in a suitable medium. Spermatozoa are added to the medium. Fertilization and early development of the embryo takes place in this medium.
The process is carefully monitored. When the embryo is at the 8-celled stage, it is put inside the uterine endometrium. Successful implantation takes place in about 20 percent of such trials. The techniques are complex and need a team of well trained experienced personnel with high degree of skill. The success rate is only about 20% and 2 or 3 attempts may be necessary. It is also very expensive. The first success with this technique was achieved by Steptoe and Edwards of UK in 1978. However successful 'test tube babies' have been produced in many countries including India.
Related Topics