Types, Merits, Demerits - Dry Heat Methods of Cooking | 11th Home Science : Chapter 3 : Food Science
Chapter: 11th Home Science : Chapter 3 : Food Science
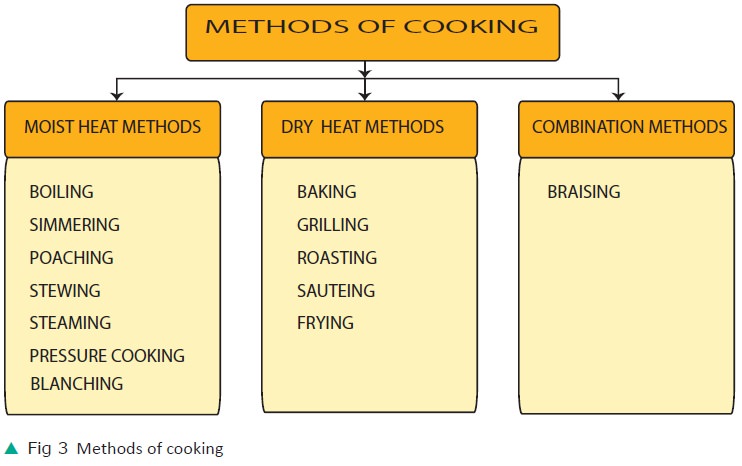
Dry Heat Methods of Cooking
Dry Heat Methods
In this either air or fat is used as the medium of cooking.
Air as a Medium of Cooking
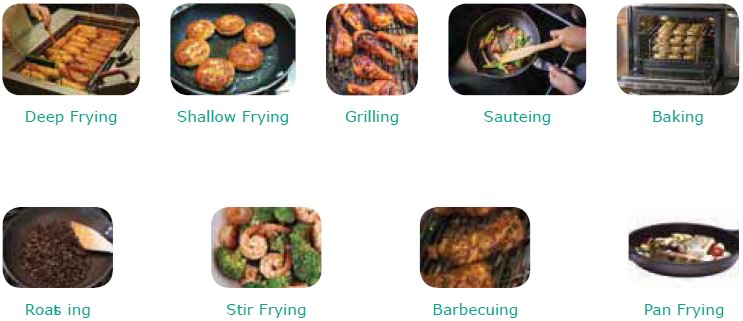
i) Grilling
Grilling consists of placing the food below or above or in between a red-hot surface. This results in the browning of the food.
Merits:
· Quick method of cooking.
· It improves the appearance, texture and flavour of the food.
· Minimum oil is used.
Demerits:
· Foods can be burnt due to carelessness.
· Grilling denatures the proteins reduc-ing their availability.
ii) Pan broiling or roasting
When food is cooked uncovered on heated metal or a frying pan, the method is known as pan-broiling, (e.g) chapathis.
Merits:
· Quick method of cooking.
· It improves the appearance, texture and flavor of the food.
· Minimum oil is used.
Spices are easily powdered if they are first roasted.
Demerits:
· Foods can be burnt due to carelessness.
· Grilling denatures the proteins.
iii) Baking
Here food gets cooked by hot air inside the oven. Foods baked are generally brown and crisp on the top and soft and porous in the centre, (eg) cakes and breads. The temperature that is nor-mally maintained in the oven is between 120°C–260°C.
Merits:
· It gives a unique flavour to food.
· Foods are made light and fluffy – cakes, rolls, custard, bread.
· Certain foods can be prepared only by this method – bread, cakes.
· Uniform and bulk cooking can be achieved.
· Flavour and texture of the food is en-hanced.
· A variety of dishes can be made.
Demerits:
· Special equipment like oven is re quired.
· Baking skills are necessary to obtain a product with ideal texture, Flavour and colour characteristics.
· Careful monitoring needed to prevent scorching.
Fat as a Medium of Cooking
i) Sauteing
This method involves cooking in just enough of oil to cover the base of the pan. Foods cooked by sauteing are generally vegetables used as side dishes in a menu.
Merits:
· Takes less time.
· Simple technique.
· Minimum oil is used.
· Constant monitoring is needed to pre-vent scorching.
Demerits:
Constant monitoring is needed to pre-vent scorching.
ii) Shallow and deep fat frying
Here food is cooked on a tava with little oil (eg) chapathi, cutlets, etc. Deep fat frying Food is totally immersed in hot oil and cooked. The temperature maintained is 180°–220°C (eg.) Samosa, Bajji, etc. The taste of the food is improved along with texture.
Merits:
· Very quick method of cooking.
· The calorific value of food is increased as fat is the medium of cooking.
· It gives a delicious flavour and appear-ance to the food.
· Taste and texture are improved.
Demerits:
· Constant monitoring is needed to pre-vent scorching.
· The food may become soggy due to too much fat absorption.
· Fried foods are not easily digested.
Repeated use of heated oils will have ill effects on health.
Related Topics