Definition, Theorem, Solved Example Problems | Mathematics - Conditional Probability | 11th Mathematics : UNIT 12 : Introduction to Probability Theory
Chapter: 11th Mathematics : UNIT 12 : Introduction to Probability Theory
Conditional Probability
Conditional Probability
Illustration 12.8
Consider the following example to understand the concept of conditional probability.
Suppose a fair die is rolled once, then the sample space is S = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}. Now we ask two questions
Q1: What is the probability of getting an odd number which is greater than 2?
Q2: If the die shows an odd number, then what is the probability that it is greater than 2?
Case 1
The event of getting an odd number which is greater than 2 is {3, 5}.
Let P1 be the probability of getting an odd number which is greater than 2
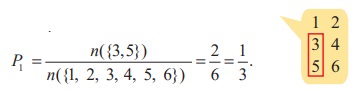
Case 2
ŌĆśIf the die shows an odd numberŌĆÖ means we restrict our sample space S to a subset containing only odd number.
That is, S1 = {1, 3, 5}. Then our interest is to find the probability of the event getting an odd number greater than 2. Let it be P2
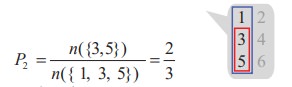
In the above two cases the favourable events are the same, but the number of exhaustive outcomes are different. In case 2, we observe that we have first imposed a condition on sample space, then asked to find the probability. This type of probability is called conditional probability.
This can be written by using sample space as
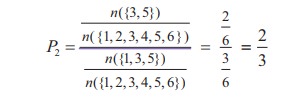
Important note: Sample space is same for probability and conditional probability.
Definition 12.14
The conditional probability of an event B, assuming that the event A has already happened is denoted by P ( B/A) and is defined as

Example 12.16
If P ( A) =0.6, P ( B)=0.5, and P (AB)=0.2

Note 12.5
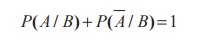
Example 12.17
A die is rolled. If it shows an odd number, then find the probability of getting 5.
Solution
Sample space S = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}.
Let A be the event of die shows an odd number.
Let B be the event of getting 5.
Then, A={1, 3, 5}, B={5}, and A Ōł® B = {5}.
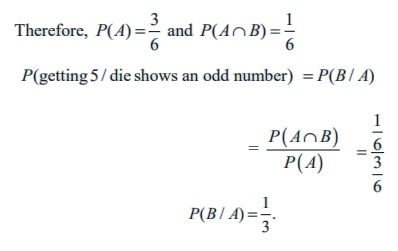
Rewriting the definition of conditional probability, we get the ŌĆśMultiplication theorem on probabilityŌĆÖ.
Theorem 12.7
(Multiplication theorem on probability)
The probability of the simultaneous happening of two events A and B is given by
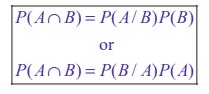
Independent Events
Events are said to be independent if occurrence or non-occurrence of any one of the event does not affect the probability of occurrence or non-occurrence of the other events.
Definition 12.15
Two events A and B are said to be independent if and only if
P ( A Ōł® B ) = P ( A) Ōŗģ P ( B)
Note 12.6
(1) This definition is exactly equivalent to
P ( A / B) = P ( A) if P (B) > 0
P (B / A) = P (B ) if P ( A) > 0
(2) The events A1 , A2 , A3 , ... , An are mutually independent if
P (A1 Ōł® A2 Ōł® A3 Ōł®ŌĆ”Ōł® An ) = P (A1 ) Ōŗģ P (A2 ) ŌĆ” P (An ).
Theorem 12.8
If A and B are independent then

Similarly one can prove (ii) and (iii).
Example 12.18
Two cards are drawn from a pack of 52 cards in succession. Find the probability that both are Jack when the first drawn card is (i) replaced (ii) not replaced
Solution
Let A be the event of drawing a Jack in the first draw,
B be the event of drawing a Jack in the second draw.
Case (i)
Card is replaced
n ( A) = 4 (Jack)
n (B) = 4 (Jack)
and n (S) = 52 (Total)
Clearly the event A will not affect the probability of the occurrence of event B and therefore A and B are independent.
P ( A Ōł® B) = P ( A) . P (B)
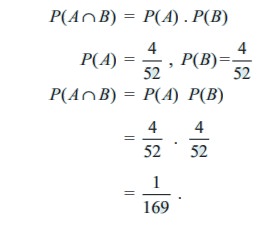
Case (ii)
Card is not replaced
In the first draw, there are 4 Jacks and 52 cards in total. Since the Jack, drawn at the first draw is not replaced, in the second draw there are only 3 Jacks and 51 cards in total. Therefore the first event A affects the probability of the occurrence of the second event B.
Thus A and B are not independent. That is, they are dependent events.
Therefore, P ( A Ōł® B) = P(A) . P(B/A)
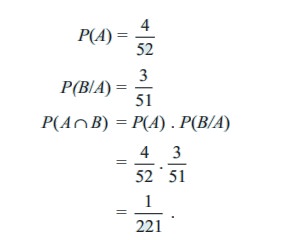
Example 12.19
A coin is tossed twice. Events E and F are defined as follows
E= Head on first toss, F = Head on second toss. Find
(i) P (E Ōł¬ F ) (ii) P (E / F )
(iii) P ( ![]() / F ) . (iv) Are the events E and F independent?
/ F ) . (iv) Are the events E and F independent?
Solution
The sample space is
S = { H , T } ├Ś{ H , T}
S = {(H , H ),(H , T ), (T , H ), (T , T )}
and E = {(H , H ), (H ,T )}
F = {(H , H ), (T , H )}
E Ōł¬ F = {(H , H ),(H , T ), (T , H )}
E Ōł® F = {(H , H )}

Note 12.7
Independent events is a property of probability but mutual exclusiveness is a set-theoretic property. Therefore independent events can be identified by their probabilities and mutually exclusive events can be identified by their events.
Theorem 12.9
Suppose A and B are two events, such that P(A) ŌēĀ 0, P(B) ŌēĀ 0.
(1) If A and B are mutually exclusive, they cannot be independent.
(2) If A and B are independent they cannot be mutually exclusive. (Without proof)
Example 12.20
If A and B are two independent events such that
P(A) = 0.4 and P( A Ōł¬ B) = 0.9. Find P(B).
Solution
P ( A Ōł¬ B) = P ( A) + P ( B ) ŌłÆ P ( A Ōł® B)
P ( A Ōł¬ B) = P ( A) + P (B ) ŌłÆ P ( A).P (B ) (since A and B are independent)
That is, 0.9 = 0.4 + P (B ) ŌłÆ (0.4) P (B)
0.9 ŌłÆ 0.4 = (1 ŌłÆ 0.4) P (B)
Therefore, P (B) = 5/6
Example 12.21
An anti-aircraft gun can take a maximum of four shots at an enemy plane moving away from it. The probability of hitting the plane in the first, second, third, and fourth shot are respectively 0.2, 0.4, 0.2 and 0.1. Find the probability that the gun hits the plane.

Solution
Let H 1 , H 2 , H 3 and H4 be the events of hitting the plane by the anti-aircraft gun in the first second, third and fourth shot respectively.
Let H be the event that anti-aircraft gun hits the plane. Therefore H is the event that the plane is not shot down. Given that

Example 12.22
X speaks truth in 70 percent of cases, and Y in 90 percent of cases. What is the probability that they likely to contradict each other in stating the same fact?
Solution
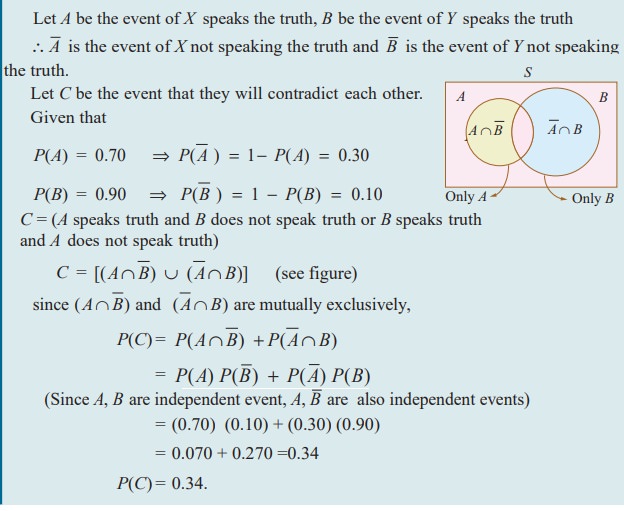
Example 12.23
A main road in a City has 4 crossroads with traffic lights. Each traffic light opens or closes the traffic with the probability of 0.4 and 0.6 respectively. Determine the probability of
(i) a car crossing the first crossroad without stopping
(ii) a car crossing first two crossroads without stopping
(iii) a car crossing all the crossroads, stopping at third cross.
(iv) a car crossing all the crossroads, stopping at exactly one cross.
Solution:
Let Ai be the event that the traffic light opens at i th cross, for i= 1, 2, 3, 4.
Let Bi be the event that the traffic light closes at i th cross, for i= 1, 2, 3, 4.
The traffic lights are all independent.
Therefore Ai and Bi are all independent events, for i= 1, 2, 3, 4.
Given that
P ( Ai ) = 0.4, i = 1, 2, 3, 4
P ( Bi ) = 0.6, i = 1, 2, 3, 4
(i) Probability of car crossing the first crossroad without stopping,
P ( A1 ) = 0.4.
(ii) Probability of car crossing first two crossroads without stopping,
P ( A1 Ōł® A 2 ) = P ( A1 A2 ) = ( 0.4 ) ( 0.4 ) = 0.16
(iii) Probability of car crossing all the crossroads, stopping at third cross
P ( A1 Ōł® A 2 Ōł® B3 Ōł® A 4 ) = P ( A1 A 2 B3 A4 ) = ( 0.4 ) ( 0.4 ) ( 0.6 ) ( 0.4 ) = 0.0384
(iv) Probability of car crossing all the crossroads, stopping at exactly one of the crossroads is P ( B1 A 2 A3 A 4 Ōł¬ A1 B 2 A3 A 4 Ōł¬ A1 A 2 B3 A 4 Ōł¬ A1 A 2 A3 B4 )
= P ( B1 A 2 A3 A 4 ) + P ( A1 B 2 A3 A 4 ) + P ( A1 A 2 B3 A 4 ) + P ( A1 A 2 A3 B4 )
= 4 ( 0.4 ) ( 0.4 )( 0.6 )( 0.4 ) = 4 ( 0.0384 ) = 0.1536
EXERCISE 12.3
(1) Can two events be mutually exclusive and independent simultaneously?
(2) If A and B are two events such that P (A Ōł¬ B ) = 0.7, P (A Ōł® B) = 0.2, and P(B) = 0.5, then show that A and B are independent.
(3) If A and B are two independent events such that P( A Ōł¬ B) = 0.6, P(A) = 0.2, find P(B).
(4) If P(A) =0.5, P(B) =0.8 and P(B/A) = 0.8, find P(A / B) and P( A Ōł¬ B) .
(5) If for two events A and B, P(A) 3/4 , P(B) 2/5 and AŌł¬B S (sample space), find the conditional probability P(A / B).
(6) A problem in Mathematics is given to three students whose chances of solving it are 1/3 , ┬╝ and 1/5 (i) What is the probability that the problem is solved? (ii) What is the probability that exactly one of them will solve it?
(7) The probability that a car being filled with petrol will also need an oil change is 0.30; the probability that it needs a new oil filter is 0.40; and the probability that both the oil and filter need changing is 0.15.
(i) If the oil had to be changed, what is the probability that a new oil filter is needed?
(ii) If a new oil filter is needed, what is the probability that the oil has to be changed?
(8) One bag contains 5 white and 3 black balls. Another bag contains 4 white and 6 black balls. If one ball is drawn from each bag, find the probability that (i) both are white (ii) both are black (iii) one white and one black
(9) Two thirds of students in a class are boys and rest girls. It is known that the probability of a girl getting a first grade is 0.85 and that of boys is 0.70. Find the probability that a student chosen at random will get first grade marks.
(10) Given P(A) = 0.4 and P ( A Ōł¬ B) = 0.7. Find P(B) if
(i) A and B are mutually exclusive
(ii) A and B are independent events
(iii) P(A / B) = 0.4
(iv) P(B / A) = 0.5
(11) A year is selected at random. What is the probability that
(i) it contains 53 Sundays (ii) it is a leap year which contains 53 Sundays
(12) Suppose the chances of hitting a target by a person X is 3 times in 4 shots, by Y is 4 times in 5 shots, and by Z is 2 times in 3 shots. They fire simultaneously exactly one time. What is the probability that the target is damaged by exactly 2 hits?
Related Topics