Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio zoology Human Body higher secondary school
Algae : Salient Features, Occurrence and Distribution, Thallus organization
Salient Features
Algae are autotrophic organisms and they have chlorophyll. They are O2 producing photosynthetic organisms that have evolved in and have exploited an aquatic environment. The study of Algae is known as Algology or phycology.
In Algae the plant body shows no differentiation into root, stem or leaf or true tissues. Such a plant body is called thallus. They do not have vascular tissues. The sex organs of this group of kingdom plantae are not surrounded by a layer of sterile cells.
Occurrence and Distribution
Most of the algae are aquatic either fresh water or marine. Very few are terrestrial. A few genera grow even in extreme condition like thermal springs, glaciers and snow.
The free floating and free swimming minute algae are known as phytoplanktons. Species that are found attached to the bottom of shallow water along the edges of seas and lakes are called Benthic. Some of the algae exhibit symbiotic association with the higher plants. Some species of algae and fungi are found in association with each other and they are called Lichens. A few species of algae are epiphytes (i.e they live on another plant or another alga) and some of them are lithophytes (i.e they grow attached to rocks)
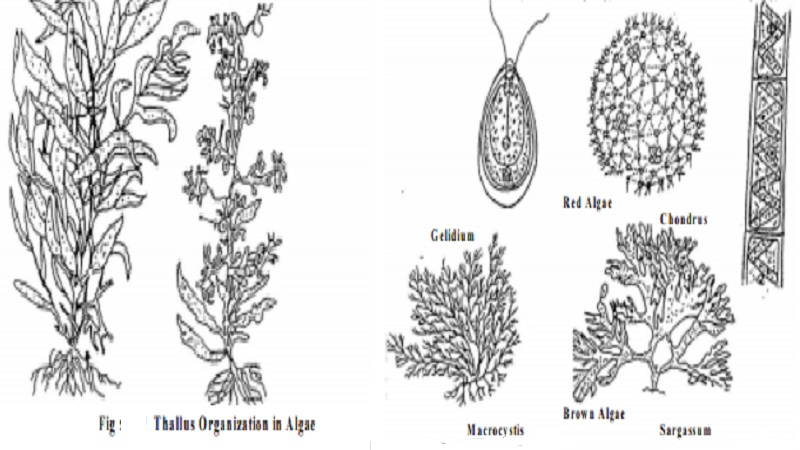
Thallus organization
The thalli of algae exhibit a great range of variation in structure and organization. It ranges from microscopic unicellular forms to giant seaweeds like Macrocystis which measures up to 100 meters long. Some of them form colonies, or filaments. The unicellular form may be motile as in Chlamydomonas or non-motile as in Chlorella. Most algae have filamentous thallus. eg. Spirogyra. The filaments may be branched. These filamentous form may be free floating or attached to a substratum. Attachment of the filament is usually effected through a simple modification of the basal cell into a holdfast. Some of the Algae are macroscopic. eg. Caulerpa,Sargassum, Laminaria, Fucus etc.where the plant body is large. In Macrocystis it is differentiated into root, stem and leaf like structures.
The chlroplasts of algae present a varied structure. For eg. they are cup shapedin Chlamydomonas, ribbon-like in Spirogyra and star shaped in Zygnema.
Related Topics