Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio zoology Human Body higher secondary school
A brief history about the discovery of cells
CELL BIOLOGY
A cell is a structural and functional unit of all living organisms. It
is microscopic and capable of independent existence. All living things are made
up of cells. The outward differences among the various biological forms may
bewilder us. But underlying these differences is a powerful uniformity. That is
all biological systems are composed of same types of molecules and they all
employ similar principles of organization at the cellular level. We shall see
for example, that all living organisms employ the same genetic code and a
similar machinery for protein synthesis.
Organisms contain organs, organs composed of tissues, tissues are made
up of cells; and cells are formed of organelles and organelles are made up of
molecules. However, in all living organisms, the cell is the functional
unit.All of biology revolves around the activity of the cell. Loewy and Siekevitz defined cell as a unit of an organism delimited by a
plasma membrane in animal cells and cell wall and plasma membrane in plant
cells. Thus cell forms the basic unit of life.
A brief history about the discovery of cells
The study of cell is impossible without microscope. Anton van Leewenhoek (1632-1723) studied the structure of bacteria,
protozoa spermatozoa, red blood cells under the simple microscope which he
examined under a simple microscope that was designed by him. The word cell was
first coined by Robert Hooke in 1665
to designate the empty honey-comb like structures viewed in a thin section of
bottle cork which he examined.
In 1838, the German botanist Schleiden
proposed that all plants are made up of plant cells. Then in 1839 his
colleague, the anatomist Theodore
Schwann studied and concluded that all animals are also composed of cells.
Even at that time the real nature of a cell was a big question. Cell theory was
again rewritten by Rudolf Virchow in
1858.
Robert Brown in 1831 discovered the presence of nucleus in the cells of orchid roots. This was an important
discovery. Purkinje coined the term
protoplasm for the slimy substance that is found inside the cells. In the 20th
century, Various modern micro techniques have been employed in cytological
investigation. With the invention of electron microscope in the year 1932 more
and more information
about
the cell and various organellses of the cells become available to us. On the
basis of the structure, the cells are classified into prokaryotic and
eukaryotic cells.
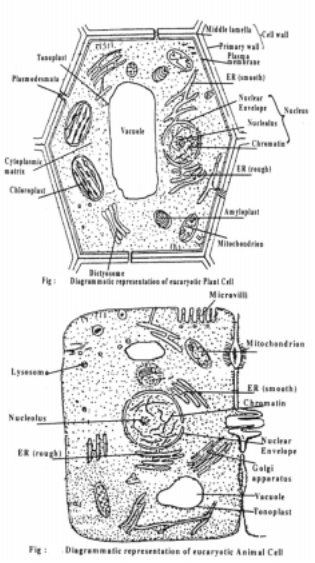
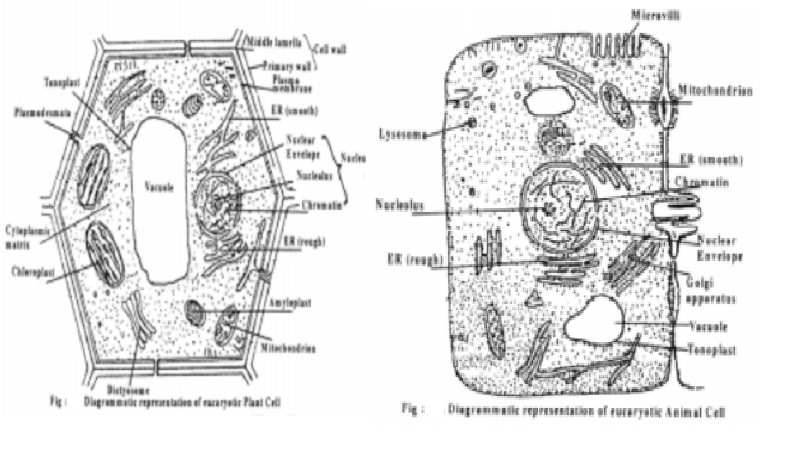
Eukaryotic
cells vary very much in shape and size. The smallest cells are found among
bacteria (0.2 to 50 microns). The largest plant cell is the ovule of Cycas. The
shape of the cells also varies considerably. It may be spherical, polygonal,
oval, rectangular, cylindrical, ellipsoidal etc.,
Dynamic nature
of cell
A
cell in an adult organism can be viewed as a steady - state system. The DNA is
constantly read out into a particular set of mRNA (transcription) which specify
a particular set of proteins (translation). As these proteins function they are
being degraded and replaced by new ones and the system is so balanced that the
cell neither grows, shrinks, nor changes its function. Considering this static
view of the cell, however, one should not miss the all-important dynamic aspect
of cellular life.
The dynamics of
a cell can be best understood by examining the course of a cell's life. A new
cell is formed when one cell divides or when two cells, (a sperm and an egg)
fuse. Both these events start a cell-replication programme. This usually
involves a period of cell growth, during which proteins are made and DNA
replicated, followed by cell division when a cell divides into two daughter
cells. Whether a given cell will grow and divide is a highly
regulated decision of the body, ensuring that adult organism replaces worn out
cells or makes new cells in response to a new need. The best example for the
latter is the growth of muscle in response to exercise or damage. However, in
one major and devastating disease namely cancer, the cells multiply even though
there is no need in the body. the understand how
cells become cancerous, biologists have intensely studied the mechanism
that controls the growth and division of cells.
Cell Cycle
The cell cycle follows a regular timing mechanism. Most eukaryotic cells
live according to an internal clock, that is they proceed through a sequence of
phases, called cell cycle. In the
cell cycle DNA is Duplicated during synthesis (S) Phase and
the copies are distributed to daughter cells during mitotic (M) phase.
Most growing plant and animal cells take 10-20
hours to double in number and some duplicate at a much slower rate.
The most complicated example of cellular dynamics occurs during differentiation i.e when a cell changes
to carry out a specialized function. This
process often involves changes in the morphology of a cell based on the
function it is to perform. This highlights the biological principle that 'form follows function'
Unchecked cell growth and multiplication produce a mass of cells, a
tumor. Programmed Cell Death (PCD)
plays a very important role by balancing cell growth and multiplication. In
addition, cell death also eliminates unecessary cells.
Related Topics