Carbohydrates - A Primary Source of Energy | 11th Biochemistry : Chapter 5 : Carbohydrates
Chapter: 11th Biochemistry : Chapter 5 : Carbohydrates
A Primary Source of Energy
A Primary Source of Energy
Digestion
of carbohydrates actually starts in the mouth. Enzymes in saliva begin to break
down carbohydrates. The Carbohydrates travel through the esophagus, stomach and
enter the small intestine.
In the
small intestine, carbohydrates get further broken down into single carbohydrate
units called monosaccharide. These single molecules get absorbed across the
intestine wall and are sent through the blood stream. Carbohydrate in the blood
is in the form of a monosaccharide called glucose. The more carbohydrate eaten
at one time, the more glucose is going to be released into the blood after
digestion.
Now it
is important to note, that fats and proteins can also be burnt to provide
energy but fats are only burned if there is non-availability of carbohydrates.
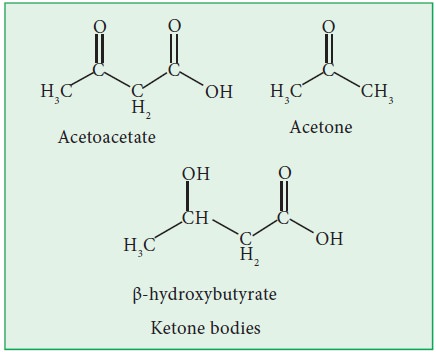
When fat is burnt in absence of carbohydrates, toxic compounds like called
ketone bodies are produced.
Accumulation
of these ketone bodies over long period causes a condition called ‘Ketosis” In
this condition, blood becomes unable to carry oxygen properly and this can be
fatal. Thus, “one of the important functions of carbohydrate is to help burn
fat properly”.
i. As a source of energy:
The main
function of carbohydrate is to supply energy for the body processes. A greater
part of the energy in the diet (more than 50-80%) is supplied by carbohydrates.
Some of the carbohydrates are
immediately utilized by the tissues and the remaining is stored as glycogen in
the liver and muscles and some are stored as adipose tissues for future energy
needs.

ii. Protein-sparing action:
Carbohydrates are mainly utilized by
the body of fulfilling the major part of the energy needs, thus sparing protein
for tissue building and repairing. The first physiological demand of the body
is the need for energy, which must be satisfied before the nutrients are used
for other functions. So, this function of carbohydrates is to spare protein for
its body building and repair of tissues.
iii. Essential for Fat Oxidation:
Even though fat yields twice as much
as energy as carbohydrate for unit weight, carbohydrate is essential for
oxidation of fats. The common expression that ‘fat burns in the fire of
carbohydrates’ is used to emphasize that in absence of carbohydrates, fats
cannot be oxidised by the body to yield energy. A breakdown product of
carbohydrate is essential for the oxidation of acetate, which is the breakdown
product of fats.
iv. Role in gastro-intestinal function:
Carbohydrates play an important role
in the gastro-intestinal functions of mammals. The digestive system changes
carbohydrates into glucose, also known as blood sugar. Some glucose is used for
energy and the rest is stored in the liver and muscles for later use. When
blood sugar rises, pancreas pumps out more and more insulin, a hormone that
tells cells to absorb glucose for energy or storage. As cells absorb wwglucose,
blood sugar levels begin to fall, which signals the pancreas to start making
glucagon, a hormone that tells the liver to release stored glucose.
v. Carbohydrate functions as Antigen:
Many antigens are glycoproteins
(which contain oligosaccharide) in nature and give immunological properties to
the blood.
vi. Carbohydrate functions as Hormone:
Many Hormones like FSH (Follicular
Stimulating Hormone which takes part in ovulation in females) and LH
(Leutinizing Hormone) are glycoprotein and help in reproductive processes.
vii. Carbohydrates provide raw material for industry:
Carbohydrates are an important
component of many industries like textile, paper, lacquers and breweries.
viii. Other Functions
Agar is polysaccharide used in
culture media, laxative and food.
Cellulose acts as roughage of food.
It stimulates peristaltic movement and in the secretion of digestive enzymes.
Hyaluronic acid found between joints
acts as synovial fluid and provides frictionless movement.
Related Topics