Gross Domestic Product and its Growth: an Introduction | Economics | Social Science - Write in detail answer | 10th Social Science : Economics : Chapter 1 : Gross Domestic Product and its Growth: an Introduction
Chapter: 10th Social Science : Economics : Chapter 1 : Gross Domestic Product and its Growth: an Introduction
Write in detail answer
V. Write in detail answer
1. Briefly
explain various terms associated with measuring of national income.
Gross National
Product (GNP): Gross National Product is the total
value of goods and services produced and income received in a year by domestic
residents of a country. It includes profits earned from capital invested
abroad.
Gross Domestic
Product (GDP): Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the
total value of output of goods and services produced by the factors of
production within the geographical boundaries of the country.
Net National Product
(NNP): Net-National Product (NNP) is arrived by making
some adjustment with regard to depreciation. We arrive at the Net National
Product (NNP) by deducting the value of depreciation from Gross National
Product.
(NNP = GNP – Depreciation)
Net Domestic Product
(NDP): Net Domestic Product (NDP) is a part of Gross
Domestic Product. Net Domestic Product is obtained from the Gross Domestic
Product by deducting the quantum of tear and wear expenses (depreciation)
(NDP = GDP – Depreciation)
Per Capita Income
(PCI):
• Per capita Income is an indicator to show the living standard
of people in a country. It is obtained by dividing the National Income by the
population of a country.
• Per capita Income = National Income / Population
Personal Income
(PI): Personal income is the total money income
received by individuals and households of a country from all possible sources
before direct taxes.
Disposable Income
(DI): Disposable income means actual income which can
be spent on consumption by individuals and families. DPI = PI - Direct Taxes
2. What
are the methods of calculating Gross Domestic Product? and explain its.
Expenditure
Approach: In this method, the GDP is measured by adding
the expenditure on all the final goods and services produced in the country
during a specified period.
Y = C + I + G + (X-M)
The Income
Approach: This method looks at GDP from the perspective
of the earnings of the men and women who are involved in producing the goods
and services. The income approach to measure GDP (Y) is Y = Wages + rent + interest
+ profit
Value Added
Approach: Take a cup of tea. It is the final goods. The
goods used to produce it, tea powder, milk and sugar are intermediate goods. To
measure the market value of the cup of tea is to add the value of each
intermediate goods used in the production of it. The sum of the value added by
all the intermediate goods used in the production gives us the total value of
the final goods produced in the economy.
Example:
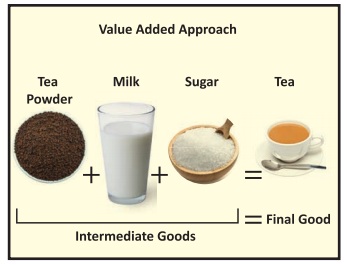
Value Added method: Tea powder + Milk + Sugar = Tea
Value of inter mediate goods =
Value of final goods
3. Write
about the composition of GDP in India.
Indian economy is broadly divided into three sectors.
Primary Sector:
(Agricultural Sector)
• Agricultural sector is known as primary sector, in which
agricultural operations are undertaken.
• Agriculture based allied activities, production of raw
materials such as cattle farm, fishing, mining, forestry, corn, coal etc. are
also undertaken.
Secondary Sector:
(Industrial Sector)
• Industrial sector is the secondary sector in which the goods
and commodities are produced by transforming the raw materials.
• Important industries
are Iron and Steel industry, cotton textile, jute, sugar, cement, paper,
petrochemical, automobile and other small scale industries.
Tertiary Sector:
(Service Sector)
• Tertiary sector is known as service sector.
• It includes scientific research, transport, communication,
trade, postal and telegraph, banking, education, entertainment, healthcare and
information technology etc.
• In the 20th century, economists began to suggest that,
traditional tertiary services could be further distinguished from 'quaternary'
and 'quinary' service sectors.
4. Write any five differences
between the growth and development.
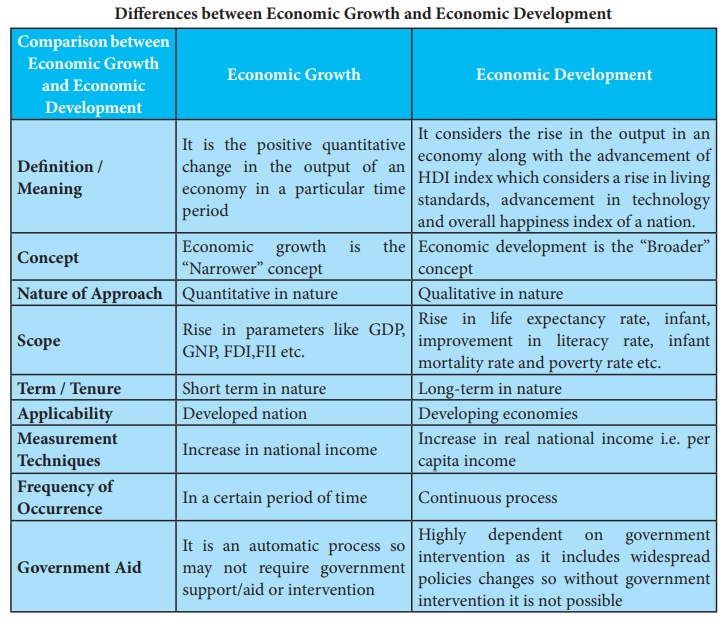
Economic Growth
Definition / Meaning : It is the positive quantitative change in the output of an economy in a particular time period
Concept : Economic growth is the “Narrower” concept
Nature of Approach : Quantitative in nature
Scope : Rise in parameters like GDP, GNP, FDI,FII etc.
Term / Tenure : Short term in nature
Applicability : Developed nation
Measurement Techniques : Increase in national income
Frequency of Occurrence : In a certain period of time
Government Aid : It is an automatic process so may not require government support/aid or intervention
Economic Development
Definition / Meaning : It considers the rise in the output in an economy along with the advancement of HDI index which considers a rise in living standards, advancement in technology and overall happiness index of a nation.
Concept : Economic development is the “Broader” concept
Nature of Approach : Qualitative in nature
Scope : Rise in life expectancy rate, infant, improvement in literacy rate, infant mortality rate and poverty rate etc.
Term / Tenure : Long-term in nature
Applicability : Developing economies
Measurement Techniques : Increase in real national income i.e. per capita income
Frequency of Occurrence : Continuous process
Government Aid : Highly dependent on government intervention as it includes widespread policies changes so without government intervention it is not possible
5. Explain the following the
economic policies
i. Agricultural Policy
ii. Industrial policy
iii. New ecnomic policy
Agricultural
policy:
• Agricultural policy is the set of government decisions and
actions relating to domestic agriculture and imports of foreign agricultural
products.
• Some over arching themes include risk management and
adjustment, economic stability, natural resources and environmental
sustainability, research and development and market access for domestic
commodities.
• Price policy, land reform policy, irrigation policy and food
policy are examples of Agricultural policy.
Industrial policy:
• Industrial development creates employment, promotes research
and development, leads to modernization and makes the economy self sufficient.
• Industrial development also boosts agricultural sector, the
service sector and also trade.
• Textile industry policy, Sugar industry policy, Small scale
industrial policy and Industrial labour policy are some of the industrial
policies.
New economic
policy:
• The economy of India had undergone policy shifts in the
beginning of the 1990s.
• This new model economic reform is known as the LPG or
Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalisation.
• These economic reforms had influenced the overall economic
growth of the country in a significant manner.
VI. Activity and Project
1. Students are collect the Gross Domestic Product datas of Tamilnadu and compare the other state of Karnataka and Kerala’s GDP.
2. Students
are collect the details of Employment growth of Tamilnadu.
Related Topics