Chapter: 10th Social Science : Geography : Chapter 2 : Climate and Natural Vegetation of India
Wildlife of India
Wildlife
The term ‘Wildlife’
includes animals of any habitat in nature. Wild animals are non-domesticated
animals and include both vertebrates (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and
mammals) and invertebrates (bees, butterflies, moths etc.). India has a rich
and diversified wildlife. The Indian fauna consists of about 81,251 species of
animals out of the world’s total of about 1.5 million species.
Our
country is home to tigers, lions, leopards, snow leopards, pythons, wolves,
foxes, bears, crocodiles, rhinoceroses, camels, wild dogs, monkeys, snakes,
antelope species, deer species, varieties of bison and the mighty Asian
elephant. Hunting, poaching, deforestation and other anthropogenic
interferences in the natural habitats have caused extinction of some species
and many are facing the danger of extinction.
The Indian Board for Wildlife (IBWL)
It was
constituted in 1952 to suggest means of protection, conservation and management
of wildlife to the government.
The
Government of India enacted Wildlife (Protection) Act in 1972 with the objective
of effectively protecting the wild life of the country and to control poaching,
smuggling and illegal trade in wildlife and its diversities.
To preserve the country’s rich and diverse wildlife
a network of 102 National Parks and
about 515 Wildlife Sanctuaries
across the country have been created.
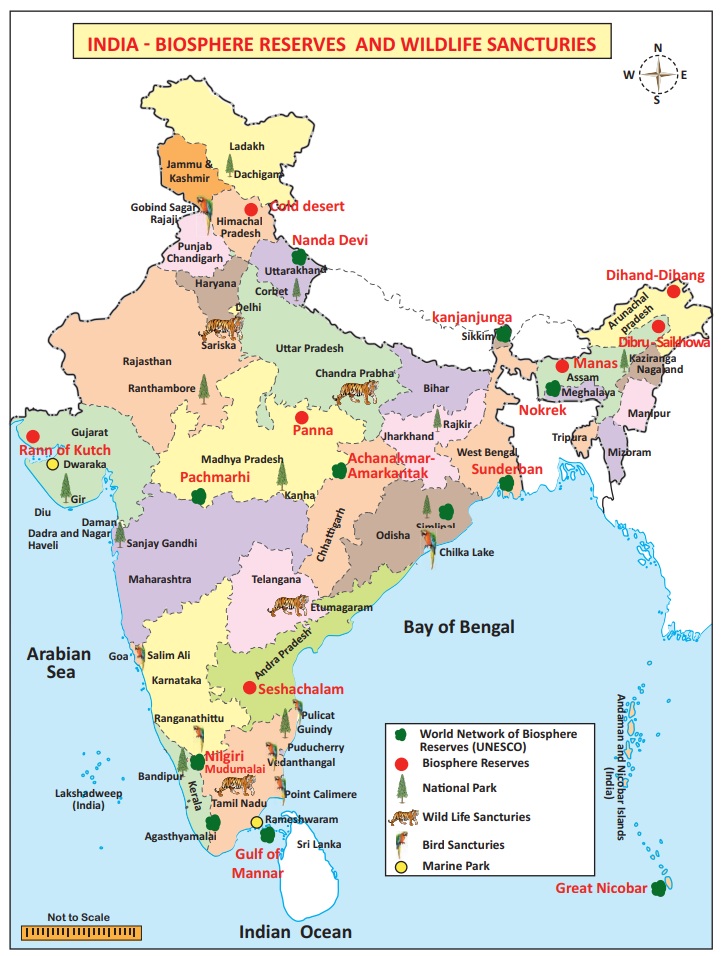
Biosphere Reserves
Biosphere
reserves are protected areas of land coastal environments
The Indian government has established 18 Biosphere
Reserves in India which protect large
areas of natural habitat which often include few National Parks with buffer
zones that are open to some economic uses.
Project Tiger was launched in April
1973 with the aim to conserve tiger population in specifically constituted
“Tiger Reserves” in India.
Biosphere Reserves in India
Eleven of the eighteen biosphere reserves (Gulf of
Mannar, Nandadevi, the Nilgiris, Nokrek, Pachmarhi, Simlipal, Sundarbans
Agasthiyamalai, Great Nicobar, Kanjanjunga and Amarkantak) of India fall under
the list of Man and Biosphere programme of UNESCO.
Related Topics