Chapter: 10th Social Science : Geography : Chapter 2 : Climate and Natural Vegetation of India
Natural Vegetation of India
Natural
Vegetation
Natural
vegetation refers to a plant community unaffected by man either directly or
indirectly. It has its existence in certain natural environment. Natural
vegetation includes all plant life forms such as trees, bushes, herbs and forbs
etc, that grow naturally in an area and have been left undisturbed by humans
for a long time.
Climate, soil and landform characteristics are the important environmental controls of natural vegetation.
On the
basis of the above factors the natural vegetation of India can be divided into
the following types.
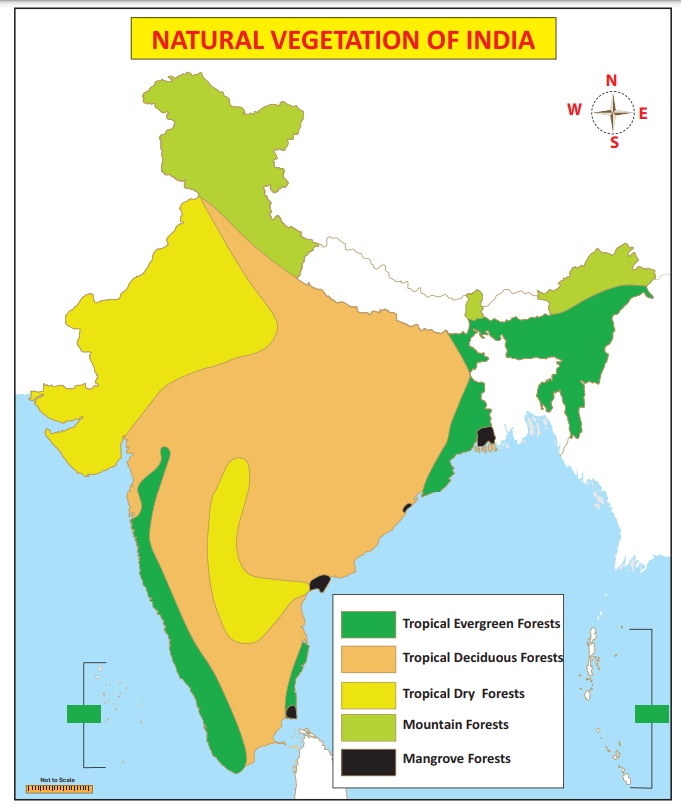
Tropical Evergreen Forest
These
forests are found in areas with 200 cm or more annual rainfall. The annual
temperature is about more than 22°C and the average annual humidity exceeds 70
percent in this region. Western Ghats in Maharashtra, Karnataka, Kerala,
Andaman-Nicobar Islands, Assam, West Bengal, Nagaland, Tripura, Mizoram,
Manipur and Meghalaya states have this type of forests. The most important
trees are rubber, mahogany, ebony, rosewood, coconut, bamboo, cinchona, candes,
palm, iron wood and cedar. These have not been fully exploited due to lack of
transport facilities.
Tropical Deciduous Forest
These are found in the areas with 100 to 200cm.
annual rainfall. These are called ‘Monsoon
Forests’. The mean annual temperature of this region is about 27oC and the
average annual relative humidity is 60 to 70 percent. The trees of these
forests drop their leaves during the spring and early summer. (Sub Himalayan -
Region from Punjab to Assam, Great Plains- Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh,
Bihar, West Bengal, Central India - Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Chattisgarh,
South India - Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Tamilnadu and
Kerala states are notable for this type of natural vegetation.) Teak and sal
are the most important trees. Sandalwood, rosewood, kusum, mahua, palas, haldu,
amla, padauk, bamboo and tendu are the other trees of economic importance.
These forests also provide fragrant oil, varnish, sandal oil and perfumes.
Tropical Dry Forest
These are
found in the areas with 50 to 100 cm. annual rainfall. They represent a
transitional type of forests. These are found in east Rajasthan, Haryana,
Punjab, Western Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Eastern Maharashtra, Telangana,
West Karnataka and East Tamilnadu. The important species are mahua, banyan,
amaltas, palas, haldu, kikar, bamboo, babool, khair etc.,
Desert and Semi-desert Vegetation: These are also called as ‘Tropical thorn forests’. These are found in the areas having annual rainfall of less than 50 cm. They have low humidity and high temperature. These forests are found in north-west India which includes west Rajasthan, south-west Haryana, north Gujarat and south-west Punjab. They are also found in the very dry parts of the Deccan plateau in Karnataka, Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh. Babul, kikar and wild palms are common trees found here.
Mountain or Montane Forest
These
forests are classified on the basis of altitude and amount of rainfall.
i. These
are found on the slopes of the mountains in north-east states. These forests
found in the altitude of 1200-2400m. Sal, Oak, Laurel, Amura, Chestnut,
Cinnamon are the main trees found here. Oak, birch, silver, fir, fine, spruce
and juniper are the major trees found at the altitude of 2400 to 3600m.
ii. The rainfall of this region is moderate. These forests are found in Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand. Upto 900 m altitude semi desert vegetation is found and it is known for bushes and small trees. In altitude from 900 to 1800m, chir is the most common tree. From 1800 to 3000m is covered with semi temperate coniferous forests.
Alpine Forest
It occurs
all along the Himalayas with above 2400 m altitude. These are purely having
coniferous trees. Oak, silver fir, pine and juniper are the main trees of these
forests. The eastern parts of Himalayas has large extent of these forests.
Tidal Forest
These forests occur in and around the deltas,
estuaries and creeks prone to tidal influences and as such are also known as
delta or swamp forests. The delta of the Ganga-Brahmaputra has the largest
tidal forest. The deltas of Mahanadi, Godavari and Krishna rivers are also
known for tidal forests. These are
also known as mangrove forest.
Related Topics