Chapter: Measurements and Instrumentation : Comparison Methods of Measurements
Wheatstone bridge(Null-type, D.C. bridge)
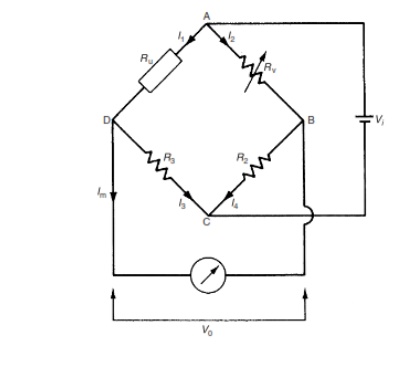
Null-type, d.c. bridge
(Wheatstone bridge)
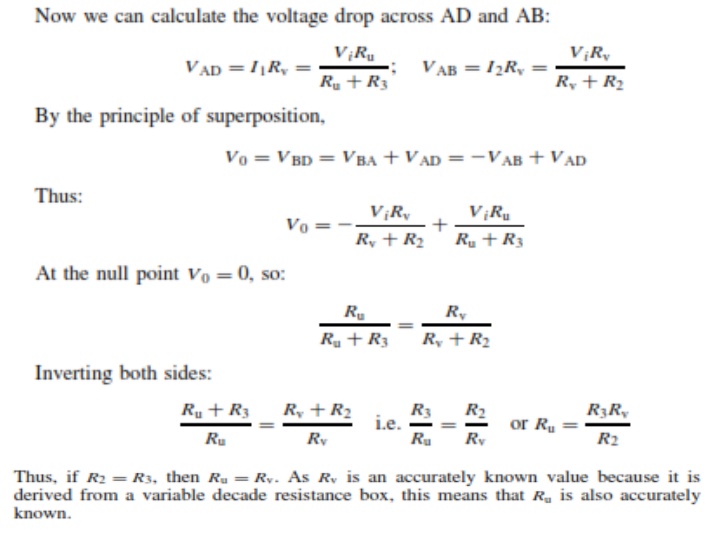
A null-type bridge with d.c. excitation, commonly known as a Wheatstone bridge, has the form shown in Figure 7.1. The four arms of the bridge consist of the unknown resistance Ru, two equal value resistors R2 and R3 and a variable resistor Rv (usually a decade resistance box). A d.c. voltage Vi is applied across the points AC and the resistance Rv is varied until the voltage measured across points BD is zero. This null point is usually measured with a high sensitivity galvanometer.
To
analyses the Whetstone bridge, define the current flowing in each arm to be I1
. . . I4 as shown in Figure 7.1. Normally, if a high impedance
voltage-measuring instrument is used, the current Im drawn by the measuring
instrument will be very small and can be approximated to zero. If this
assumption is made, then, for Im D 0:
I1
=I3 and I2 =I4
Related Topics