Chapter: Measurements and Instrumentation : Comparison Methods of Measurements
Deflection-type D.C. bridge
Deflection-type d.c. bridge
A
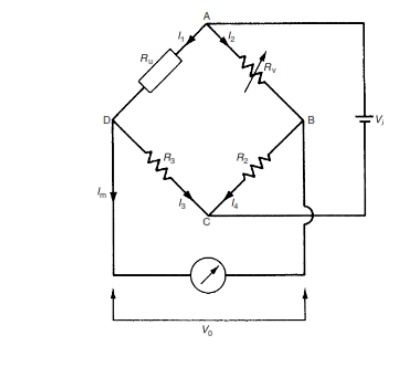
deflection-type bridge with d.c. excitation is shown in Figure . This
differs from the Wheatstone bridge mainly in that the variable resistance Rv
is replaced by a fixed resistance R1 of the same value as the
nominal value of the unknown resistance Ru . As the resistance Ru
changes, so the output voltage V0 varies, and this relationship
between V0 and Ru must be calculated.
This
relationship is simplified if we again assume that a high impedance voltage
measuring instrument is used and the current drawn by it, Im , can be
approximated to zero. (The case when this assumption does not hold is covered
later in this section.) The analysis is then exactly the same as for the
preceding example of the Wheatstone bridge, except that Rv is
replaced by R1. Thus, from equation (7.1), we have:
V0=
Vi * ( Ru / Ru + R3)- ( R1 / R1+ R2)
When Ru is at its nominal value, i.e. for Ru D R1, it is clear that V0 D0 (since R2 D R3). For other values of Ru, V0 has negative and positive values that vary in a non-linear way with Ru.
Related Topics