Chapter: Business Science : Human Resource Management : Perspectives in Human Resource Management
What is Human Resource Management?
What is Human Resource
Management?
HRM is
the study of activities regarding people working in an organization. It is a
managerial function that tries to match an organization‘s needs to the skills and
abilities of its employees.
1 Definitions of HRM(HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT)
2 Nature of HRM(HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT)
3 Features of HRM(HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT)
4 Scope of HRM(HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT)
5 Objectives of HRM(HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT)
6 Functions of HRM(HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT)
1Definitions
of HRM
Human resources management (HRM) is a
management function concerned with hiring, motivating and maintaining people in an organization. It focuses on people in
organizations. Human resource management is designing management
systems to ensure that human talent is used effectively and efficiently to accomplish organizational goals.
HRM is
the personnel function which is concerned with procurement, development,
compensation, integration and maintenance of the personnel of an organization
for the purpose of contributing towards the accomplishments of the
organization‘s objectives. Therefore, personnel management is the planning,
organizing, directing, and controlling of the performance of those operative
functions (Edward B. Philippo).
According to the Invancevich and Glueck,
―HRM is concerned with the most effective use of people to achieve
organizational and individual goals. It is the way of managing people at work,
so that they give their best to the organization‖.
According to Dessler (2008) the
policies and practices involved in carrying out the ―people‖ or human resource aspects of a management
position, including recruiting, screening, training, rewarding, and appraising
comprises of HRM.
2 Nature of HRM
HRM is a
management function that helps manager‘s to recruit, select, train and develop
members for an organization. HRM is concerned with people‘s dimension in
organizations.
The
following constitute the core of HRM
1. HRM Involves the Application of Management
Functions and Principles. The functions and principles are applied to acquiring, developing, maintaining and
providing remuneration to employees in organization.
2.
Decision
Relating to Employees must be Integrated. Decisions on different aspects of employees must be consistent with
other human resource (HR) decisions.
3.
Decisions
Made Influence the Effectiveness of an Organization. Effectiveness
of an organization will result in
betterment of services to customers in the form of high quality products
supplied at reasonable costs.
4. HRM Functions are not Confined to Business
Establishments Only but applicable to non business organizations such as education, health care, recreation
and like. HRM refers to a set of programmes, functions and activities designed
and carried out in order to maximize both employee as well as organizational
effectiveness.
3 Features of HRM or characteristics or nature
1. HRM
involves management functions like planning, organizing, directing and
controlling
2. It
involves procurement, development, maintenance of human resource
3. It helps
to achieve individual, organizational and social objectives
4. HRM is a
mighty disciplinary subject. It includes the study of management psychology
communication, economics and sociology.
5. It
involves team spirit and team work.
4 Significance/importance/need of HRM
HRM becomes significant for business organization
due to the following reasons. 1. Objective :-
HRM helps a company to achieve its objective from
time to time by creating a positive attitude among workers. Reducing wastage
and making maximum use of resources etc.
2. Facilitates professional growth :-
Due to proper HR policies employees are trained
well and this takes them ready for future promotions. Their talent can be
utilized not only in the company in which they are currently working but also
in other companies which the employees may join in the future.
3. Better relations between union and management
:-
Healthy HRM practices can help the organization to
maintain co-ordinal relationship with the unions. Union members start realizing
that the company is also interested in the workers and will not go against them
therefore chances of going on strike are greatly reduced.
4. Helps an individual to work in a team/group
:-
Effective HR practices teach individuals team work
and adjustment. The individuals are now very comfortable while working in team
thus team work improves.
5. Identifies person for the future :-
Since employees are constantly trained, they are
ready to meet the job requirements. The company is also able to identify
potential employees who can be promoted in the future for the top level jobs.
Thus one of the advantages of HRM is eparing people for the future.
6. Allocating the jobs to the right person :-
If proper recruitment and selection methods are
followed, the company will be able to select the right people for the right
job. When this happens the number of people leaving the job will reduce as the
will be satisfied with their job leading to decrease in labour turnover.
7. Improves the economy:-
Effective HR practices lead to higher profits and
better performance by companies due to this the company achieves a chance to
enter into new business and start new ventured thus industrial development
increases and the economy improves.
Scope of HRM
The major
HRM activities include HR planning, job analysis, job design, employee hiring,
employee and executive remuneration, employee motivation, employee maintenance,
industrial relations and prospects of HRM.
The scope
of Human Resources Management extends to:
Ø All the
decisions, strategies, factors, principles, operations, practices, functions,
activities and methods related to the management of people as employees in any
type of organization.
Ø All the
dimensions related to
people in their
employment relationships, and
all the
dynamics
that flow from it.
The scope
of HRM is really vast. All major activities n the working life of a worker –
from the time of his or her entry into an organization until he or she leaves
it comes under the purview of HRM. American Society for Training and
Development (ASTD) conducted fairly an exhaustive study in this field and
identified nine broad areas of activities of HRM.
These are given below: Human Resource Planning
Design of
the Organization and Job Selection and Staffing
Training
and Development Organizational Development Compensation and Benefits Employee
Assistance Union/Labour Relations
Personnel
Research and Information System
a)
Human Resource Planning: The
objective of HR Planning is to ensure that the organization has the right types
of persons at the right time at the right place. It prepares human resources
inventory with a view to assess present and future needs, availability and
possible shortages in human resource.
Thereupon,
HR Planning forecast demand and supplies and identify sources of selection. HR
Planning develops strategies both long-term and short-term, to meet the
man-power requirement.
b) Design of Organization and Job:
This is
the task of
laying down organization
structure, authority, relationship
and
responsibilities.
This will also mean definition of work contents for each position in the
organization. This is done by ―job description‖. Another important step is ―Job
specification.
Job
specification identifies the attributes of persons who will be most suitable
for each job which is defined by job description.
c) Selection
and Staffing:
This is the process of recruitment and selection of
staff. This involves matching people and their expectations with which the job specifications
and career path available within the organization.
d) Training and Development: This
involves an organized attempt to find out training needs of the individuals to meet the knowledge and skill which is needed
not only to perform current job but also to fulfil the future needs of the
organization.
e) Organizational Development: This is
an important aspect whereby ―Synergetic effect‖ is generated in an organization i.e. healthy interpersonal and
inter-group relationship within the organization.
f) Compensation and Benefits: This is
the area of wages and salaries administration where wages and compensations are fixed scientifically to meet fairness
and equity criteria. In addition labour welfare measures are involved which
include benefits and services.
g) Employee Assistance: Each
employee is unique in character, personality, expectation and temperament. By and large each one of
them faces problems everyday. Some are personal some are official. In their
case he or she remains worried. Such worries must be removed to make him or her
more productive and happy.
h) Union-Labour Relations: Healthy
Industrial and Labour relations are very important for enhancing peace and productivity in an organization. This is one
of the areas of HRM.
i)
Personnel
Research and Information System: Knowledge on behavioral science
and industrial psychology throws
better insight into the workers expectations, aspirations and
behaviour.Advancement of technology of product and production methods have
created working environment which are much different from the past.
Globalization of economy has increased competition many fold. Science of
ergonomics gives better ideas of doing a work more conveniently by an employee.
Thus, continuous research in HR areas is an unavoidable requirement. It must
also take special care for improving exchange of information through effective
communication systems on a continuous basis especially on moral and motivation.
Objectives of HRM
The
primary objective of HRM is to ensure the availability of competent and willing
workforce to an organization. The specific objectives include the following:
1) Human
capital: assisting the organization in obtaining the right number and types of
employees to fulfill its strategic and operational goals.
2)
Developing organizational climate: helping to create a climate in which
employees are encouraged to develop and utilize their skills to the fullest and
to employ the skills and abilities of the workforce efficiently.
3)
Helping to maintain performance standards and increase productivity through
effective job design: providing adequate orientation, training and development;
providing performance-related feedback; and ensuring effective two-way
communication.
4)
Helping to establish and maintain a harmonious employer/employee relationship
5) Helping to create and maintain a safe and healthy work environment
6)
Developing programs to meet the economic, psychological, and social needs of
the employees and helping the organization to retain the productive employees
7)
Ensuring that the organization is in compliance with provincial/territorial and
federal laws affecting the workplace (such as human rights, employment equity,
occupational health and safety, employment standards, and labour relations legislation).
To help the organization to reach its goals
8) To
provide organization with well-trained and well-motivated employees 9) To
increase the employees satisfaction and self-actualization
10) To
develop and maintain the quality of work life
11) To
communicate HR policies to all employees.
12)To help
maintain ethical polices and behavior.
5 Objectives of HRM
1)
Societal
Objectives: seek to ensure that the organization becomes socially responsible to the needs and challenges of the
society while minimizing the negative impact of such demands upon the
organization. The failure of the organizations to use their resources for the
society‘s benefit in ethical ways may lead to restriction.
2) Organizational Objectives: it
recognizes the role of HRM in bringing about organizational effectiveness. It makes sure that HRM is not a standalone
department, but rather a means to assist the organization with its primary
objectives. The HR department exists to serve the rest of the organization.
3) Functional Objectives: is to
maintain the department‘s contribution at a level appropriate to the organization‘s needs. Human
resources are to be adjusted to suit the organization‘s demands. The
department‘s value should not become too expensive at the cost of the
organization it serves.
4) Personnel Objectives: it is to
assist employees in achieving their personal goals, at least as far as these goals enhance the
individual‘s contribution to the organization. Personal objectives of employees
must be met if they are to be maintained, retained and motivated. Otherwise
employee performance and satisfaction may decline giving rise to employee
turnover.
Functions of HRM
Human Resources management has an important role to
play in equipping organizations to meet the challenges of an expanding and
increasingly competitive sector. Increase in staff numbers, contractual
diversification and changes in demographic profile which compel the HR managers
to reconfigure the role and significance of human resources management. The
functions are responsive to current staffing needs, but can be proactive in
reshaping organizational objectives. All the functions of HRM are correlated
with the core objectives of HRM (Table 1.1). For example personal objectives is
sought to be realized through functions like remuneration, assessment etc.
6 Functions of HRM
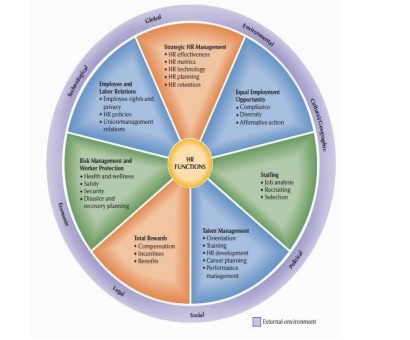
Strategic HR Management:
As a part
of maintaining organizational competitiveness, strategic planning for HR
effectiveness can be increased through the use of HR metrics and HR technology.
Human resource planning (HRP) function determine the number and type of
employees needed to accomplish organizational goals. HRP includes creating
venture teams with a balanced skill-mix, recruiting the right people, and
voluntary team assignment. This function analyzes and determines personnel
needs in order to create effective innovation teams. The basic HRP strategy is
staffing and employee development.
Equal Employment Opportunity: Compliance
with equal employment opportunity (EEO) laws and regulations affects all other HR activities.
Staffing: The aim of staffing is to provide
a sufficient supply of qualified individuals to fill jobs in an organization. Job analysis,
recruitment and selection are the main functions under staffing. Workers job design
and job analysis laid the foundation for staffing by identifying what diverse
people do in their jobs and how they are affected by them.
Job
analysis is the process of describing the nature of a job and specifying the
human requirements such as knowledge, skills, and experience needed to perform
the job. The end result of job analysis is job description. Job description
spells out work duties and activities of employees. Through HR planning,
managers anticipate the future supply of and demand for employees and the
nature of workforce issues, including the retention of employees. So HRP
precedes the actual selection of people for organization.
These
factors are used when recruiting applicants for job openings. The selection
process is concerned with choosing qualified individuals to fill those jobs.In
the selection function, the most qualified applicants are selected for hiring
from among the applicants based on the extent to which their abilities and
skills are matching with the job.
Talent Management and Development: Beginning
with the orientation of new employees, talent management and development includes different types of training.
Orientation is the first step towards helping a new employee to adjust himself
to the new job and the employer. It is a method to acquaint new employees with
particular aspects of their new job, including pay and benefit programmes,
working hours and company rules and expectations. Training and Development
programs provide useful means of assuring that the employees are capable of
performing their jobs at acceptable levels and also more than that. All the
organizations provide training for new and in experienced employee. In
addition, organization often provide both on the job and off the job training
programmes for those employees whose jobs are undergoing change.
Likewise,
HR development and succession planning of employees and managers is necessary
to prepare for future challenges. Career planning has developed as result of
the desire of many employees to grow in their jobs and to advance in their
career. Career planning activities include assessing an individual employee‘s
potential for growth and advancement in the organization. Performance appraisal
includes encouraging risk taking, demanding innovation, generating or adopting
new tasks, peer evaluation, frequent evaluations, and auditing innovation
processes.
This
function monitors employee performance to ensure that it is at acceptable
levels. This strategy appraises individual and team performance so that there is
a link between individual innovativeness and company profitability. Which tasks
should be appraised and who should assess employees‘ performance are also taken
into account.
Total Rewards: Compensation in the form of pay,
incentives and benefits are the rewards given to the employees for performing organizational work. Compensation
management is the method for determining how much employees should be paid for
performing certain jobs.
Compensation
affects staffing in that people are generally attracted to organizations
offering a higher level of pay in exchange for the work performed. To be
competitive, employers develop and refine their basic compensation systems and
may use variable pay programs such as incentive rewards, promotion from within
the team, recognition rewards, balancing team and individual rewards etc.
This
function uses rewards to motivate personnel to achieve an organization‘s goals
of productivity, innovation and profitability. Compensation is also related to
employee development in that it provides an important incentive in motivating
employees to higher levels of job performance to higher paying jobs in the
organization.
Benefits
are another form of compensation to employees other than direct pay for the
work performed. Benefits include both legally required items and those offered
at employer‘s discretion.Benefits are primarily related to the area of employee
maintenance as they provide for many basic employee needs.
Risk Management and Worker Protection: HRM addresses
various workplace risks to
ensure
protection of workers by meeting legal requirements and being more responsive
to concerns for workplace health and safety along with disaster and recovery
planning.
Employee and Labor Relations: The
relationship between managers and their employees must be handled legally and effectively. Employer and employee rights must
be addressed. It is important to develop, communicate, and update HR policies
and procedures so that managers and employees alike know what is expected. In
some organizations, union/management relations must be addressed as well.
The term
labour relation refers to the interaction with employees who are represented by
a trade union. Unions are organization of employees who join together to obtain
more voice in decisions affecting wages, benefits, working conditions and other
aspects of employment. With regard to labour relations the major function of HR
personnel includes negotiating with the unions regarding wages, service
conditions and resolving disputes and grievances.
Related Topics