Chapter: Business Science : Human Resource Management : Perspectives in Human Resource Management
Functions of HRM(Human Resource Management)
Functions of HRM
Human Resources management has an important role to
play in equipping organizations to meet the challenges of an expanding and
increasingly competitive sector. Increase in staff numbers, contractual
diversification and changes in demographic profile which compel the HR managers
to reconfigure the role and significance of human resources management. The
functions are responsive to current staffing needs, but can be proactive in
reshaping organizational objectives. All the functions of HRM are correlated
with the core objectives of HRM (Table 1.1). For example personal objectives is
sought to be realized through functions like remuneration, assessment etc.
Functions of HRM
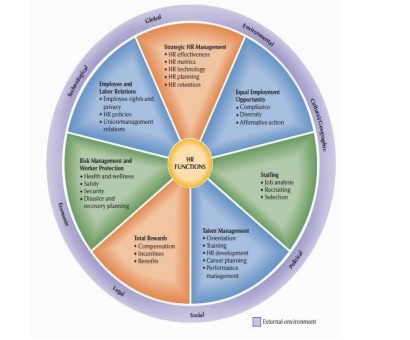
Strategic HR Management:
As a part
of maintaining organizational competitiveness, strategic planning for HR
effectiveness can be increased through the use of HR metrics and HR technology.
Human resource planning (HRP) function determine the number and type of
employees needed to accomplish organizational goals. HRP includes creating
venture teams with a balanced skill-mix, recruiting the right people, and
voluntary team assignment. This function analyzes and determines personnel
needs in order to create effective innovation teams. The basic HRP strategy is
staffing and employee development.
Equal Employment Opportunity: Compliance
with equal employment opportunity (EEO) laws and regulations affects all other HR activities.
Staffing: The aim of staffing is to provide
a sufficient supply of qualified individuals to fill jobs in an organization. Job analysis,
recruitment and selection are the main functions under staffing. Workers job
design and job analysis laid the foundation for staffing by identifying what
diverse people do in their jobs and how they are affected by them.
Job
analysis is the process of describing the nature of a job and specifying the
human requirements such as knowledge, skills, and experience needed to perform
the job. The end result of job analysis is job description. Job description
spells out work duties and activities of employees. Through HR planning,
managers anticipate the future supply of and demand for employees and the
nature of workforce issues, including the retention of employees. So HRP
precedes the actual selection of people for organization.
These
factors are used when recruiting applicants for job openings. The selection
process is concerned with choosing qualified individuals to fill those jobs.In
the selection function, the most qualified applicants are selected for hiring
from among the applicants based on the extent to which their abilities and
skills are matching with the job.
Talent Management and Development: Beginning
with the orientation of new employees, talent management and development includes different types of training.
Orientation is the first step towards helping a new employee to adjust himself
to the new job and the employer. It is a method to acquaint new employees with
particular aspects of their new job, including pay and benefit programmes,
working hours and company rules and expectations. Training and Development
programs provide useful means of assuring that the employees are capable of
performing their jobs at acceptable levels and also more than that. All the
organizations provide training for new and in experienced employee. In
addition, organization often provide both on the job and off the job training
programmes for those employees whose jobs are undergoing change.
Likewise,
HR development and succession planning of employees and managers is necessary
to prepare for future challenges. Career planning has developed as result of
the desire of many employees to grow in their jobs and to advance in their
career. Career planning activities include assessing an individual employee‘s
potential for growth and advancement in the organization. Performance appraisal
includes encouraging risk taking, demanding innovation, generating or adopting
new tasks, peer evaluation, frequent evaluations, and auditing innovation
processes.
This
function monitors employee performance to ensure that it is at acceptable
levels. This strategy appraises individual and team performance so that there
is a link between individual innovativeness and company profitability. Which
tasks should be appraised and who should assess employees‘ performance are also
taken into account.
Total Rewards: Compensation in the form of pay,
incentives and benefits are the rewards given to the employees for performing organizational work. Compensation
management is the method for determining how much employees should be paid for
performing certain jobs.
Compensation
affects staffing in that people are generally attracted to organizations
offering a higher level of pay in exchange for the work performed. To be
competitive, employers develop and refine their basic compensation systems and
may use variable pay programs such as incentive rewards, promotion from within
the team, recognition rewards, balancing team and individual rewards etc.
This
function uses rewards to motivate personnel to achieve an organization‘s goals
of productivity, innovation and profitability. Compensation is also related to
employee development in that it provides an important incentive in motivating
employees to higher levels of job performance to higher paying jobs in the
organization.
Benefits
are another form of compensation to employees other than direct pay for the
work performed. Benefits include both legally required items and those offered
at employer‘s discretion.Benefits are primarily related to the area of employee
maintenance as they provide for many basic employee needs.
Risk Management and Worker Protection: HRM addresses
various workplace risks to
ensure
protection of workers by meeting legal requirements and being more responsive
to concerns for workplace health and safety along with disaster and recovery
planning.
Employee and Labor Relations: The
relationship between managers and their employees must be handled legally and effectively. Employer and employee rights must
be addressed. It is important to develop, communicate, and update HR policies
and procedures so that managers and employees alike know what is expected. In
some organizations, union/management relations must be addressed as well.
The term
labour relation refers to the interaction with employees who are represented by
a trade union. Unions are organization of employees who join together to obtain
more voice in decisions affecting wages, benefits, working conditions and other
aspects of employment. With regard to labour relations the major function of HR
personnel includes negotiating with the unions regarding wages, service
conditions and resolving disputes and grievances.
Related Topics