Characteristics, Functions, Classification, Absorption, Food sources, Deficiency - Vitamins | 12th Nursing : Chapter 5 : Applied Nutrition
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 5 : Applied Nutrition
Vitamins
Vitamins
Vitamins are essential organic, compounds that are needed in small
amounts in the diet both to prevent deficiency diseases and to support optimal
health. The term vitamin (vital amines) was coined by Casmir Funk. The term vital
denoting essential for life and amines because these compounds contained an
amine functional group.
Characteristics of vitamins
·
Vitamins are vital,
organic, dietary substance that is necessary in only very small amounts to
perform a specific metabolic function or prevent an associated deficiency
disease.
·
Vitamins are not
synthesized by the body and therefore must be supplied through food.
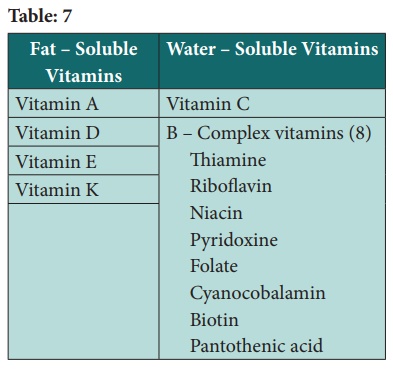
Table: 7
Functions of Vitamins
Each vitamin has its specific metabolic task. However the general
functions are:
·
Function as control
agents in cell metabolism
·
Components of body –
tissue construction.
·
Prevent specific
nutritional deficiency disease, which is considered as a result of their
primary role in cell metabolism.
Classification of Vitamins
Thirteen (13) recognized vitamins classified in two groups, based
on their solubility in fat or in water are as follows:
1. Fat – soluble vitamins
The four fat – soluble vitamins – vitamins A, D, E and K are often
present in the fat portion of foods, they are not easily lost from foods or
destroyed by exposure to water, heat, air, or light.
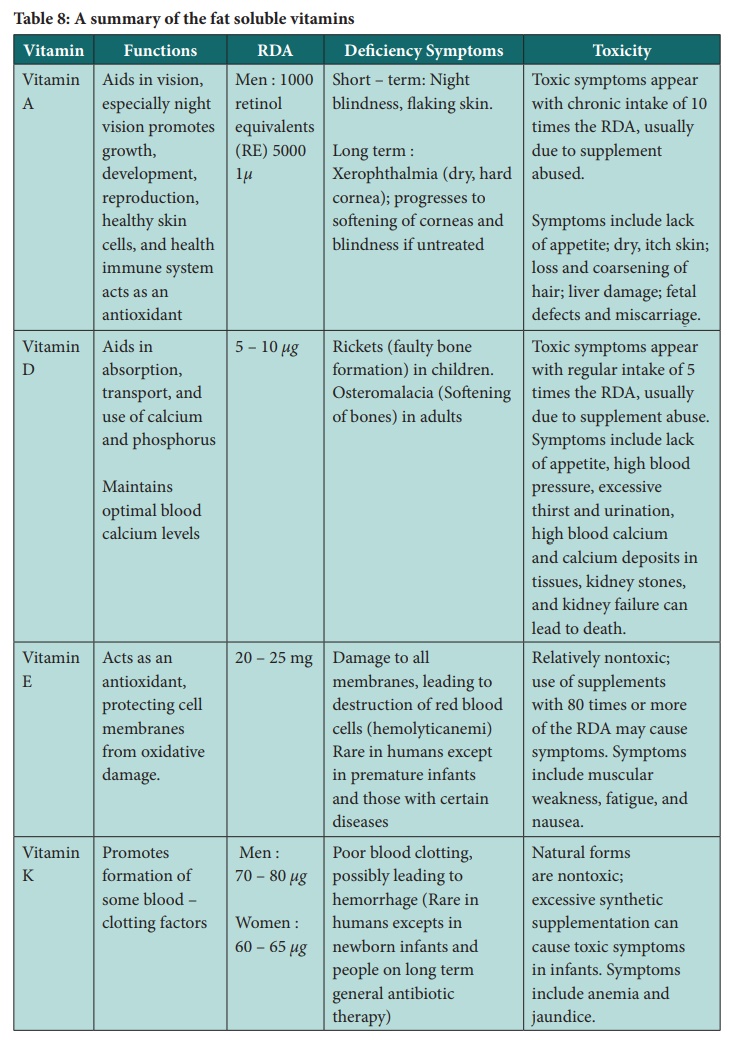
Vitamin A (retinol and beta – carotene)
Vitamin A and carotene can be obtained from either animal or
vegetable sources. The animal form is divided between retinol and
dehydroretinol whereas the vegetable carotene can be split into four very
potent groups– alpha– carotene, beta–carotene, gamma carotene and crypto–
carotene.
Function
Vitamin A has a variety of functions in the body. It is required
for the synthesis of rhodopsin and other light – receptor pigments in the eye
and thus is essential for vision. Vitamin A is needed for normal growth and
development to occur in the body, including the formation of bone and
cartilage.
Healthy epithelial or skin cells, which line surfaces inside and
outside the body, require vitamin A. Vitamin A plays a role in reproduction,
metabolism, and immune system function also.
Digestion and absorption
Retinol esters in food are hydrolyzed by pancreatic and intestinal
enzymes to form free retinol. After absorption, the retinol, is reesterified
and transported to blood.
Carotenes are split in the intestines to form retinaldehyde, which
is then reduced to
Table 8: A summary of the fat soluble vitamins
retinol. Some carotene may be absorbed intact and later converted
to vitamin ‘A’ in the liver or kidney. Bile is necessary for the absorption of
vitamin A and carotene. Vitamin E in the intestinal tract prevents oxidation of
the vitamin. Mineral oil hinders absorption since it dissolves the vitamin but
is not absorbed.
Food sources

Liver, milk, egg – yolk, carrots, dark green leafy vegetables and
yellow fruits are high in vitamin A or beta – carotene.
Deficiency
A diet deficient in vitamin A for several months may lead to night
blindness and flaking skin.
A long – term vitamin A deficiency leads Xerophthalmia, major symptom
of which is dry, hard cornea. If this condition is left untreated, damage to
the cornea progresses, leading to a softening of the cornea and eventually
total blindness.
Vitamin A deficiency also affects the skin, causing it to become
dry and rough.
If xerophthalmia and the underlying vitamin A deficiency are
treated at an early stage, blindness can be prevented.
Vitamin D (Calciferol)
The human body can produce vitamin D from cholesterol present in
the skin. This conversion depends on exposure of the skin to the ultraviolet
rays in sunlight and yields
inactive pro-vitamin D. Both inactive vitamin D formed in the skin
and vitamin D absorbed from dietary sources are transported through the
bloodstream to the liver, where they are stored.
Functions
·
Vitamin D helps with the
absorption, transport and use of calcium.
·
Vitamin D assists in
bone growth and the integrity of bone and promotes strong teeth.
·
It also helps to
regulate the amount of phosphorus in the body as well as assisting in a healthy
heart and nervous system.
Food sources

Vitamin D is present in fatty fish like kipper, sardines, salmon,
tuna and mackerel, liver, egg yolk and butter. Smaller amounts are also present
in dark leafy vegetables.
Absorption
Dietary vitamin D is absorbed along with dietary fats in the small
intestines and transported to the lymph system. Bile is essential for the
absorption of this vitamin Excess vitamin is stored in the body.
Deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency affects the mineralization of bones and
teeth.
-Rickets, osteomalacia
Vitamin E (Tocopherol)
Vitamin E is an essential, fat – soluble vitamin that includes
eight naturally occurring compounds in two classes designated as tocopherols
and tocotrienols.
Vitamin E is an effective chain – breaking, lipid – soluble
antioxidant in biological membranes, and aids in membrane stability.

Function
·
Vitamin E is a powerful
antioxidant.
·
Antioxidant capability
helps to prevent degenerative diseases.
·
Vitamin E is also useful
in preventing blood clots forming and promotes fertility.
·
An increase in stamina
and endurance is also attributed to vitamin E.
·
Vitamin E is also used
to great effect for skin treatments.
Deficiency of vitamin E
Deficiency of vitamin E is a not common, and the symptoms not very
clear cut, but may include fatigue, inflamed varicose veins, slow wound
healing, premature ageing and sub – fertility.
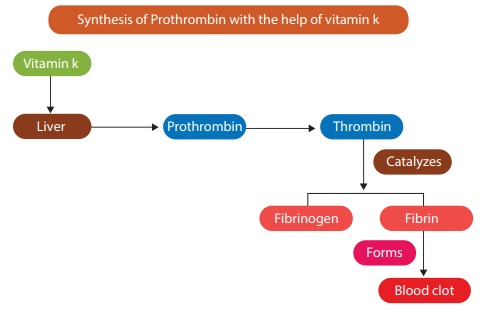
Vitamin K
Vitamin K can be produced in the intestines and this function is
improved with the presence of cultured milk, like yogurt, in the diet.
Functions
·
The major function of
vitamin K is to promote coagulation of blood after injury, thereby preventing
haemorrhage.
·
Vitamin K is necessary
for the synthesis of prothrombin, an inactive form of thrombin.
·
It is involved in the
formation of prothrombin.
It is also involved in bone formation and repair.
Food Source

The best dietary sources of this vitamin are green leafy
vegetables, cheese and liver.
Deficiency
Increased tendency to haemorrhage defective blood clotting
Table: 9 Water soluble vitamins
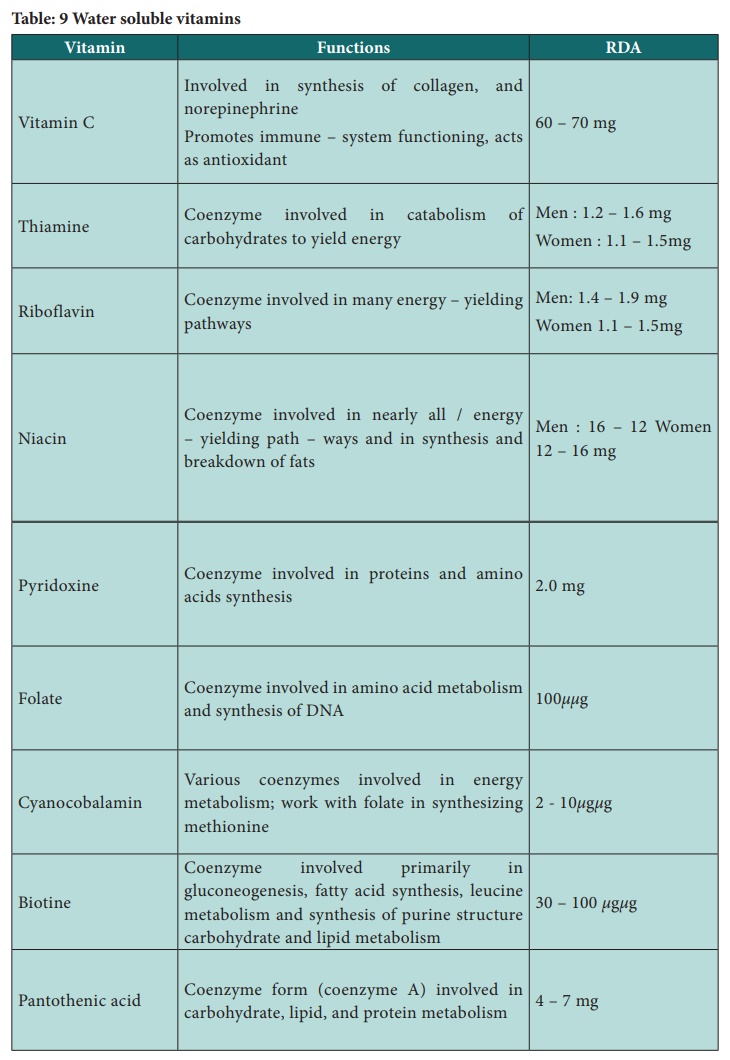
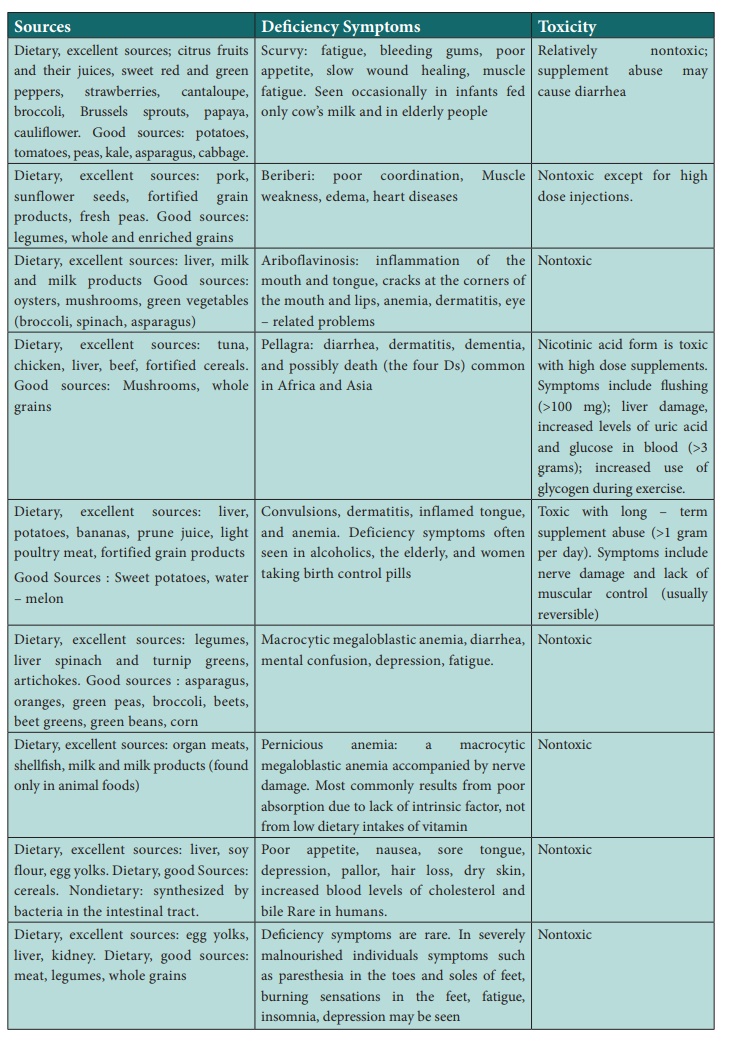
2. Water – soluble vitamins
Water – soluble vitamins are essential of health, and each one has
its own function in the body and due to its solubility in water. It is normally
easily lost in urine. The water soluble vitamins include vitamin C and 8 B
complex vitamins – thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, pyridoxine, folate,
cyanocobalamin, biotin and pantothenic acid. Most of these are unstable and
thus easily destroyed by exposure to water, heat, air or light.
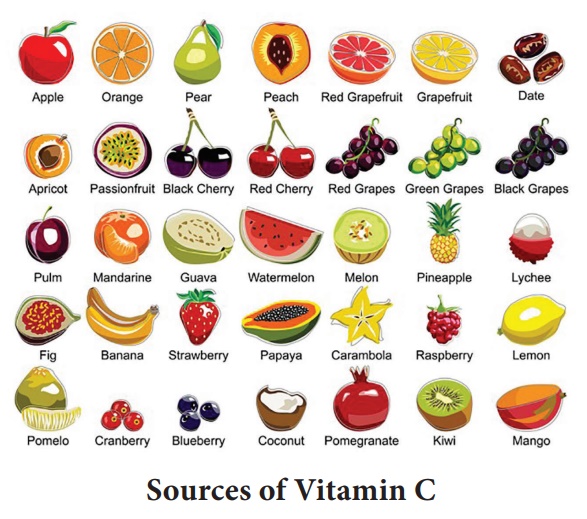
Vitamin C
Many fruits and vegetables are rich in vitamin C, also known as
ascorbic acid. To ensure optimal physiological functioning and to prevent
subclinical deficiencies, a person needs to consume a good source of vitamin C
every day because the body normally stores only small amounts of Vitamin C.
Functions
·
Vitamin C is required in
the synthesis of collagen in connective tissue, steroid hormones, carnitine,
etc.
·
Vitamin C is required
for the conversion of cholesterol to bile acids.
·
It enhances iron
bioavailability.
·
Ascorbic acid is a great
antioxidant and helps to protect the body against pollutants.
·
Ascorbic acid also
promotes healthy cell development.
·
Vitamin C is essential
for the formation and maintenance of intercellular cement substances such as
bone matrix, cartilage dentine, collagen, connective tissue, etc.
·
Vitamin C is needed for
healthy gums and to protect against infection.
Food sources
Good sources of vitamin C are green leafy vegetables, berries,
citrus fruits, guavas, tomatoes, melons, papayas, etc.
Deficiency
In infants and children, vitamin C deficiency results in defective
bone formation leading to retardation of growth.
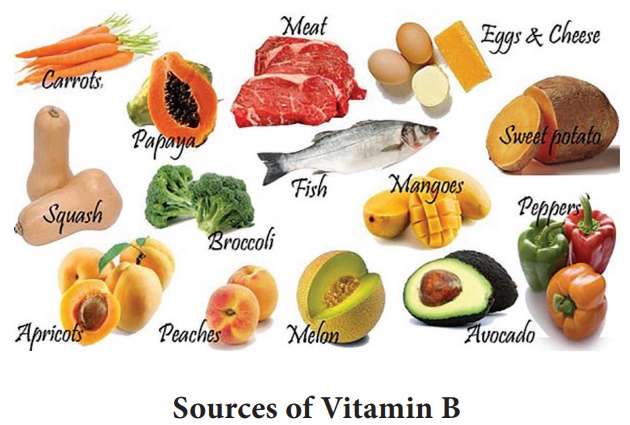
B – complex vitamins
The eight B – complex vitamins include thiamine (B1), riboflavin
(B2), niacin (B3), pyridoxine (B6), cyanocobalamin (B12), folic acid, biotin
(B7), and pantothenic acid. The B vitamins are easily lost in cooking water
because they are water soluble. With the exception of niacin, all other B
vitamins lose some activity when exposed to heat, oxygen, light, or alkaline conditions.
Thiamine (Vitamin B1)
Thiamine also called B1 is used in many different body functions
and deficiencies may have far reaching effects on the body, yet very little of
this vitamin is stored in the body and depletion of this vitamin can happen
within 14 days. Thiamine is integrally involved as a coenzyme in the catabolism
of carbohydrates to yield energy.
Functions
·
It is also required for
the health of the nervous system.
·
It is used in the
manufacture of hydrochloric acid, and therefore plays a part in digestion.
·
In children it is
required for good appetite and proper growth.
Food sources
Sunflower seeds, peanuts, wheat bran, beet liver, pork, seafood,
egg – yolk, beans whole grains and yeast contain good amounts of thiamine.
Deficiency
Beriberi occurs in two forms, wet beriberi and dry beriberi, whose
prominent symptoms differ.
Riboflavin – (Vitamin B2)
Riboflavin is another B – complex vitamin involved as a coenzyme
in the metabolism of carbohydrates, as well as of fats and proteins. The adult
RDA for riboflavin has been established at a minimum of 1.2 milligrams per day.
Functions
·
It is required by the
body to use oxygen and the metabolism of amino acids, fatty acids, and
carbohydrates.
·
It is a used for red
blood cell formation, antibody production, cell respiration, and growth.
·
It may be helpful in the
prevention and treatment of cataracts.
Food sources
Organ meats, nuts, cheese, eggs, milk and lean meat are best
sources of riboflavin. It is also available in good quantities in green leafy
vegetables, fish, legumes, whole grains, and yogurt.
Deficiency
A dietary deficiency of riboflavin leads to ariboflavinosis.
Niacin (B3)
Niacin also called nicotinic acid or niacin amide and can be
manufactured by body. Niacin is derived from two compounds – nicotinic acid and
niacin amide.
Functions
·
Niacin functions as a
coenzyme in nearly all the metabolic pathways yielding energy from
carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and alcohol.
·
Niacin also plays a role
in tissue respiration.
·
It is involved in the
synthesis and breakdown of fats, and helps to maintain healthy skin.
Food sources
Liver, lean meat, fish, nuts, cereals, legumes, asparagus, milk,
green leafy vegetables and fish. A cup of coffee also provides 3 milligrams of
niacin.
Deficiency
A deficiency of niacin is known as pellagra, which means rough
skin (from the Italian words pelle for skin and Agra for rough).
Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6)
Pyridoxine is part of the B group vitamins and is water – soluble
and is required for both mental and physical health.
Functions
Pyridoxine is required for the balancing of hormonal changes in
women.
·
It is essential for the
metabolism and proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
·
It assists in the
maintenance of serum level of sodium and potassium
·
It helps to promote red
blood cell production.
·
It is linked to cancer
immunity and fights the formation of the toxic chemical homocysteine.
Food sources
Good sources to obtain pyridoxine are brewer’s yeast, egg,
chicken, carrot, fish, liver, kidney, pea, wheat germ and walnuts. Roots and
tubers, cabbage, legumes, molasses, whole grains, etc., contain moderate amount
of this vitamin.
Deficiency
Irritability, nervousness, insomnia, anemia, general weakness,
skin changes such as dermatitis.
Folic acid (Vitamin B9) – folic acid, folacin, folate
Folic acid is also referred to as folacin or folate. Its chemical
name is pteroylglutamic acid. This vitamin can be produced by the body and be
stored in the liver.
Functions
·
Folic acid is required
for DNA synthesis and cell growth and is important for red blood cell
formation, energy production as well as the forming of amino acids.
·
Folic acid is essential
for synthesizing heme, the iron containing substance in hemoglobin, crucial for
oxygen transport.
·
Folic acid is very
important in the development of the nervous system of a developing fetus.
Food sources
Fresh green vegetable such as spinach and broccoli contains folic
acid. It is also found in fruit, starchy vegetables, beans, whole grains,
liver, kidney, egg, yeast etc.
Deficiency
A deficiency of folate can lead to macrocytic, megaloblastic
anemia, diarrhea, fatigue, depression, and mental confusion.
Cyanocobalamin (Vitamin B12)
Cyanocobalamin also known as cobalamin is referred to as the
energy vitamin. It is a very widely researched vitamin, and used in
supplementation to a very large degree.
Functions
·
Cobalamin is required in
the metabolism of fats, proteins and carbohydrates.
·
It is needed in the
manufacture of red blood cells and the maintenance of red blood cells.
·
It stimulates appetite
and Promotes growth.
Food sources
Liver, organ meat, muscle meat, shellfish, egg, cheese and fish
are rich sources of this vitamin. It can be manufactured in the body. Milk
contains vitamin B 12 however processing of milk may destroy the vitamin.
Deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency results in macrocytic, megaloblastic anemia
(pernicious anemia) similar to that occurring with folate deficiency.
Biotin (Vitamin B7)
Biotin is also referred to as anti – egg white injury factor.
Biotin present in foods in not affected by exposure to light.
Biotin is also produced by bacteria in the intestine.
Function
Biotin is involved in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
·
Biotin is also indicated
for healthy hair and skin, healthy sweat glands, nerve tissue, and bone marrow.
·
Biotin is also helps in
maintaining a steady blood sugar level.
Food sources
Biotin is widely distributed in both animal and plant foods.
Liver, kidney, egg, yolk, milk, tomatoes are rich sources.
Deficiency
Dietary deficiency of biotin is rare. Symptoms of biotin
deficiency include lack of appetite, nausea, an enlarged tongue, mental
depression, pallor, loss of hair.
Pantothenic acid (vitamin B6)
Pantothenic acid referred to as the “anti – stress vitamin” is
part of the B group vitamins. This vitamin can be produced in the body by the
intestinal flora.
Functions
·
Pantothenic acid plays
an important role in the secretion of hormones, such as cortisone because of
the role it plays in supporting the adrenal gland.
·
Pantothenic acid is also
used in the release of energy as well as the metabolism of fat, protein and
carbohydrates.
·
It is used in the
synthesis of lipids, neurotransmitters and haemoglobin.
Food sources
Beef, brewer’s yeast, egg, fresh vegetables, kidney, legumes,
liver, mushrooms, nuts, pork, royal jelly, saltwater fish, torula yeast, whole
rye flour, and whole wheat contain this vitamin.
Deficiency
Symptoms of a pantothenic acid deficiency though rare, may occur
in severely malnourished individuals and include fatigue, irritability, low
blood pressure upon standing, lack of appetite, constipation, and tingling and
numbness in both the feet and hands.
Related Topics