Dietary sources, Functions, Digestion, absorption and storage, metabolism of carbohydrates, Deficien - Carbohydrates | 12th Nursing : Chapter 5 : Applied Nutrition
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 5 : Applied Nutrition
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the main source of energy for daily activities.
Carbohydrates (primarily starches) are the least expensive, the most available,
easily obtainable and readily digestible form of nutrient.
Composition of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are organic compounds of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen with the latter elements in the ratio of 2: 1. The general formula is C6H12O6. Carbohydrates are widely distributed in plants. Foods which contain carbohydrates are called energy foods.
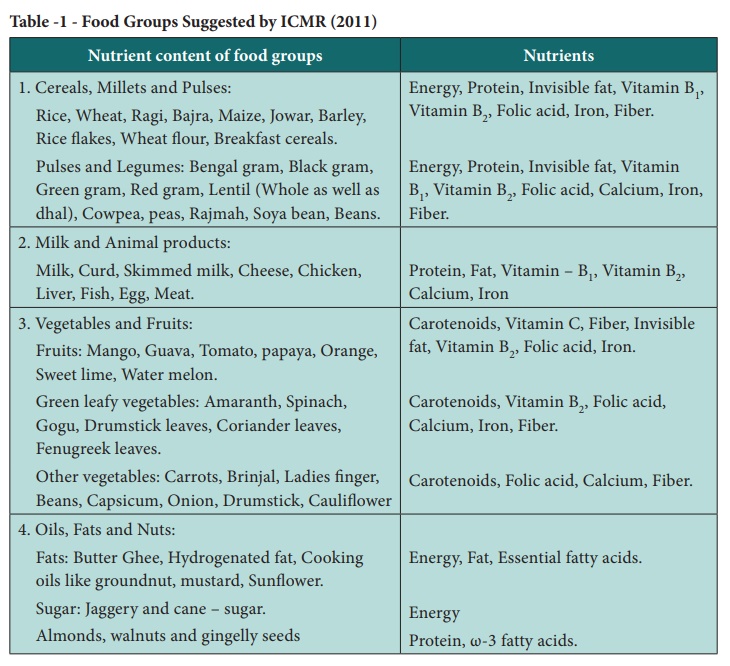
Classification of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are classified according to the number of saccharide (sugar) groups present. They are broadly classified as simple carbohydrates and complex carbohydrates. The simple carbohydrates include monosaccharides (Single sugar) and disaccharides (Double sugars). Complex carbohydrates include starch, glycogen and fibers. The classification of carbohydrates is schematically represented below:
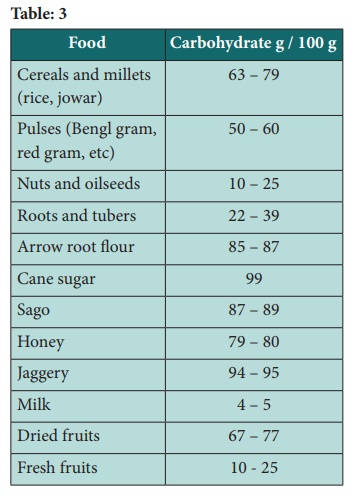
Recommended daily allowances
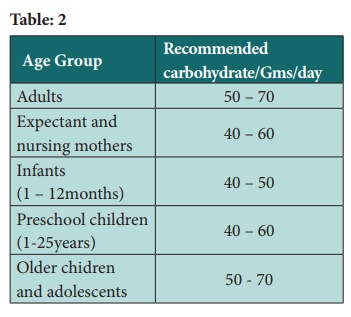
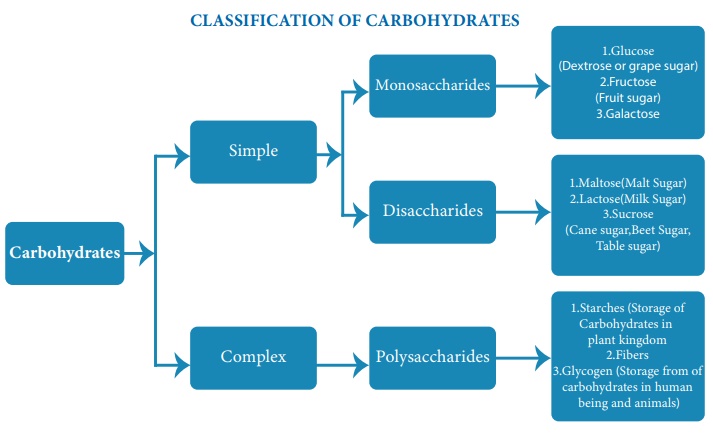
Dietary sources
The important sources of carbohydrates in the diets are cereals,
millets, roots, tubers pulses, sugar and jaggery.
Functions
·
Supply energy for body
functions and for doing work. Each gram of carbohydrate yield 4 kcal of energy.
·
Essential for the
oxidation of fats
·
Exert a sparing action
on proteins.
·
Provide carbon skeleton
for the synthesis of some non – essential amino acids.
·
Add flavor to the diet.
Digestion, absorption and storage, metabolism of carbohydrates
The first stage of digestion takes place in the mouth while the
food is chewed. In saliva the enzyme called alpha – amylase which is called as
ptyalin acts on starch. The enzyme acts on starch splitting it into dextrin and
maltose. As soon as the food reaches the stomach it mixes with acidic gastric
juices for digestion. The main digestion takes place in the intestines.
The final products of digestion of carbohydrates are glucose,
fructose and galactose, these products are absorbed in the intestines. The non
– digestible carbohydrates present in the food such as cellulose,
hemicelluloses, pentosans, galactans, fructosans etc add bulk to the contents
of large intestine and are excreted in the faeces.
Storage, metabolism of carbohydrates
Glucose, galactose and fructose absorbed in the intestines pass
through the portal circulation to the liver. In the liver a part of the glucose
and the entire galactose and fructose are converted into glycogen. A portion of
glucose enters into the general circulation and to the various tissues for
being oxidized and used as energy. A small portion of the glucose is stored in
liver and muscle as glycogen and some portion of the glucose is converted into
fat and stored in adipose tissue. The oxidation of glucose in the tissues
occurs in two stages as indicated below;
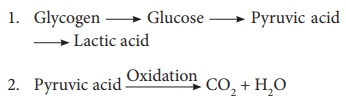
The first stage is called ‘glycolysis. The oxidation of pyruvic
acid takes place through a series of reactions known as tricarboxylic acid
cycle (Krebs’s cycle).
Deficiencies
A deficiency of carbohydrates makes the body to utilize fats for
energy, if it is not rectified it leads to ketone bodies formation which occurs
due to oxidation of fats.
Excessive carbohydrates
Excessive consumption of carbohydrates leads to heart disease,
diabetes, and obesity.
Related Topics