Functions, Classification, Digestion, absorption and storage metabolism - Fat | 12th Nursing : Chapter 5 : Applied Nutrition
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 5 : Applied Nutrition
Fat
Fat
The name fat may make it sound like something you shouldn't eat.
But fat is an important part of a healthy diet. Fat from your diet gives you
energy. As a bonus, fat in food helps you feel full, so you don't eat too much.
Some foods, including most fruits and vegetables, have almost no
fat. Other foods have plenty of fat. They include nuts, oils, butter, and meats
like beef.
The lipids are a heterogeneous group of substances found in plant
and animal tissues, which share the property of being relatively insoluble in
water, and soluble in organic solvents, such as ether, chloroform and benzene.
Fat contain 9 kcal per gram.
Functions of fats
·
They are the chief
energy stores of the body, which form an important source of energy during
starvation or other emergencies.
·
Fats play a role in the
absorption of fats soluble vitamins like vitamins A, D, E and K.
·
Fats are the
constituents of cell membrane structure and regulate the membrane permeability.
·
Subcutaneous fat acts as
an insulator and helps in retaining body heat.
·
Fats are important as
cellular metabolic regulators (Steroid hormones and prostaglandin).
Fat is the main energy store in the body and the most concentrated
source of energy in the diet – 1 g of fat provides 37kJ (9Kcal), more than
double that provided by either protein or carbohydrate (4Kcal).
Classification of lipids
Lipids are classified into 4 categories as follows:
I. On the basis of chemical composition
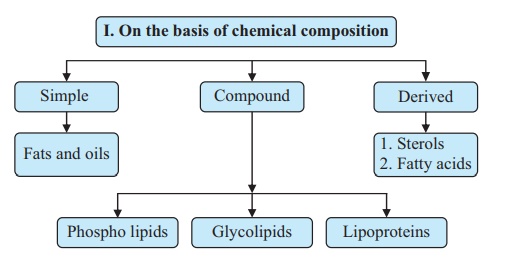
II. On the basis of sources
Fats are divided into 2 types based on their source, namely visible
and invisible fats.
III. On the basis of fatty acids
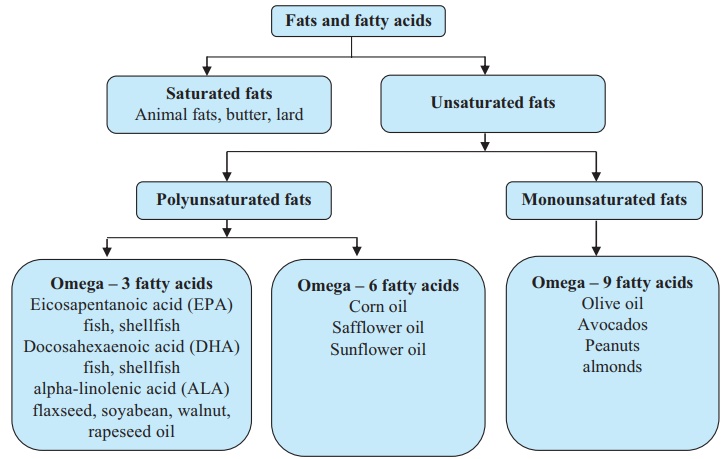
IV. On the basis of requirement
Fatty acids are of 2 types:
Essential fatty acids: Fatty acids which are essential to be taken
in our diet because they cannot be synthesized in our body are known as
essential fatty acids. (eg.) Linoleic, linolenic and arachidonic acids.
Non-essential fatty acids: Non-essential fatty acids are those
which can be systhesized by the body and which need not be supplied through the
diet. Palmitic acid, oleic acid and butyric acid are examples of non-essential fatty
acids.
Digestion, absorption and storage metabolism
Fats are not digested in the stomach. Fats delay emptying of the
stomach. Fats are hydrolyzed by the pancreatic and intestinal lipases in the
intestines into diglycerides, monoglycerides and fatty acids. Bile is essential
for the digestion and absorption of fats.

Storage of fats
Fat is stored in the adipose tissues. In normal human beings adipose tissue constitutes of
10 – 15% of the body weight.
Fat metabolism
Fatty acids are oxidized by certain enzymes in the tissues to carbon dioxide
and water. The oxidation takes place through the tricarboxylic acid cycle.
Deficiencies

Over consumption
·
Over weight
·
Obesity
·
Coronary heart disease
·
Cancer
·
High cholesterol
Related Topics