Chapter: Biochemistry: Protein Metabolism
Urea Cycle
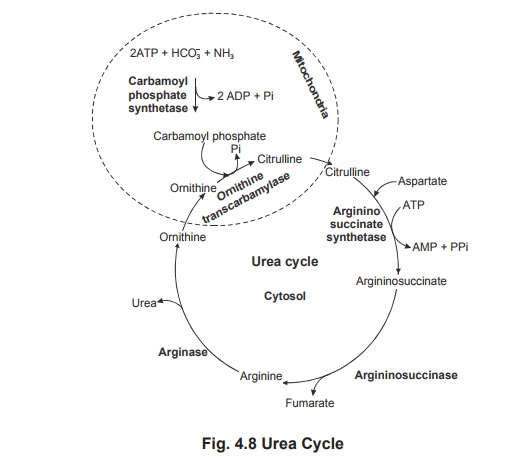
Urea Cycle
Living organisms excrete the excess nitrogen
resulting from the metabolic breakdown of amino acids in one of three ways.
Many aquatic animals simply excrete ammonia. Where water is less, plentiful
processes have evolved that convert ammonia to less toxic waste products which
require less water for excretion. One such product is urea, which is excreted
by most terrestrial vertebrates; another is uric acid, which is excreted by
birds and terrestrial reptiles.
Accordingly, living organisms are classified as
being either ammonotelic (ammonia excreting), urotelic (urea excreting) and
uricotelic (uric acid excreting). Some animals can shift from ammonotelism to
urotelism or uricotelism if their water supply becomes restricted.
Urea is synthesised in the liver by the enzymes
of the urea cycle. It is then secreted into the blood stream and sequestered by
the kidneys for excretion in the urine.The urea cycle reactions were elucidated
by Hans Krebs and Kurt Henseleit. This cycle starts with the amino acid
ornithine. The cycle is confined only to the mitochondria and cytoplasm of the
cells of liver and it is found that the enzyme, arginase which is required in
the final step of urea formation is present only in the liver and absent in all
the other tissues.
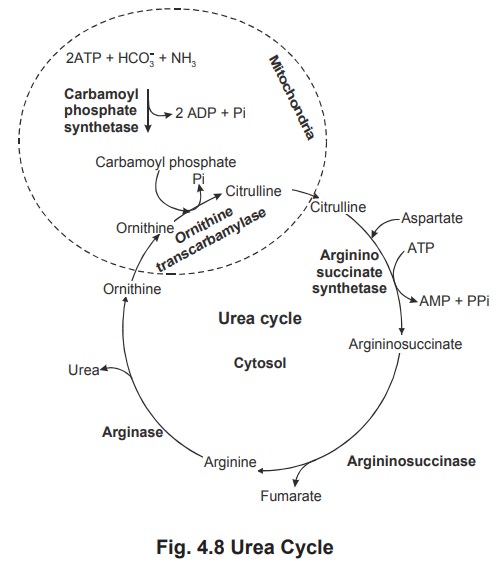
Urea cycle occurs partially in the mitochondria
and partially in the cytosol with ornithine and citrulline being transported
across the mitochondrial membrane by specific membrane systems. The following
are the various reactions in the process of urea formation.
1. Carbamoyl phosphate formation
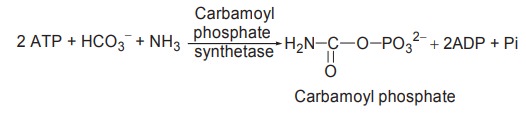
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase catalyses the
condensation and activation of NH4+ and HCO3- to form
carbamoyl phosphate.
2. Citrulline formation from ornithine
Ornithine transcarbamylase transfers the
carbamoyl group of carbamoyl phosphate to ornithine, yielding citrulline.
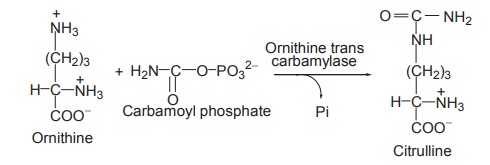
The reaction occurs in the mitochondria so that
ornithine, which is produced in the cytosol, must enter the mitochondria via a
specific transport system. Like wise, since the remaining urea cycle reactions
occur in the cytosol, citrulline must be transported from the mitochondria.
3. Argininosuccinate formation
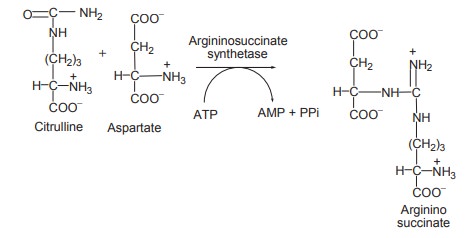
Citrulline undergoes condensation with amino
group of aspartate to form arigininosuccinate this reaction requires ATP, Mg2+
and the enzyme argininosuccinate synthetase.
4. Formation of arginine and fumarate
The enzyme argininosucccinase catalyses the
elimination of arginine from the aspartate carbon skeleton forming fumarate
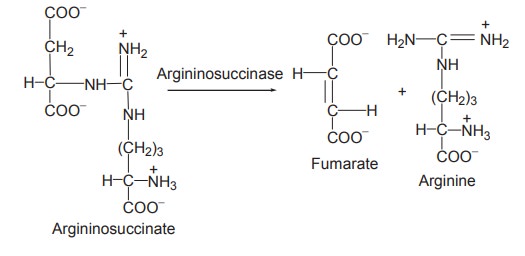
5. Formation of urea
The fifth and the final reaction in the urea
cycle is the hydrolysis of arginine by the enzyme arginase to yield urea and ornithine.
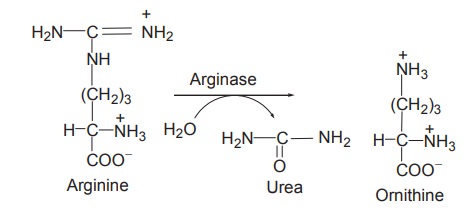
Ornithine is then returned to the mitochondria
for another round of the cycle.
Related Topics