Chapter: Biochemistry: Protein Metabolism
Protein biosynthesis
Protein biosynthesis
In a protein molecule amino acids are joined
together by peptide bonds. In the process of protein synthesis also known as
translation of mRNA, the amino acids are added sequentially in a specific
number. The protein synthesizing mechanism involves the following steps:
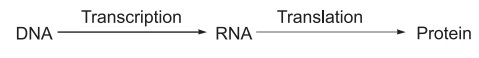
Transcription
The formation of RNA complementary to a DNA
strand is called transcription. In this process, the RNAs required for protein
synthesis are synthesized on DNA strands. This reaction is catalyzed by the
enzyme RNA polymerase.
The enzyme, RNA polymerase I, II, III are
involved in the synthesis of rRNA (ribosomal RNA) mRNA (messenger RNA) and tRNA
(transfer RNA) respectively in the eukaryotes. In prokaryotes only one type of
RNA polymerase is present to synthesize all the three classes of RNA.
In the DNA double helix, one of the strands
serves as a template to produce RNA. The RNA produced by transcription is
inactive and is called pre-RNA. They become active after further processing.
All these RNA are processed through chemical reactions and structural modifications.
Related Topics