Chapter: Biochemistry: Protein Metabolism
Formation of thyroid hormone
Formation of thyroid hormone
The thyroid gland is a bilobed organ in the anterior
portion of the neck. Thyroid gland in normal adult weighs 20-25 grams.
Thyroxine the hormone is secreted by this gland. Thyroxine is stored in the
colloid of the thyroid follicles, a form of glycoprotein called thyroglobulin.
Hydrolysis of thyoglobulin yields
monoiodotyrosine, diiodotyrosine, triiodotyrosine and thyroxine. Of these,
triiodothyroxine is considered to possess a biological potency greater than
thyroxine.
Thyroxine is synthesised in thyroid gland from
tyrosine. First inorganic iodide is oxidised to organic iodide (2I→I2).Tyrosine
is iodinated in the third position to form 3 - monoiodotyrosine. The next
iodination occurs in the fifth position to form 3,5-diiodotyrosine.
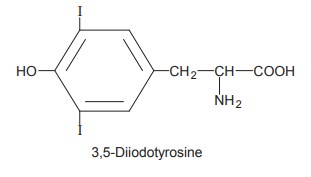
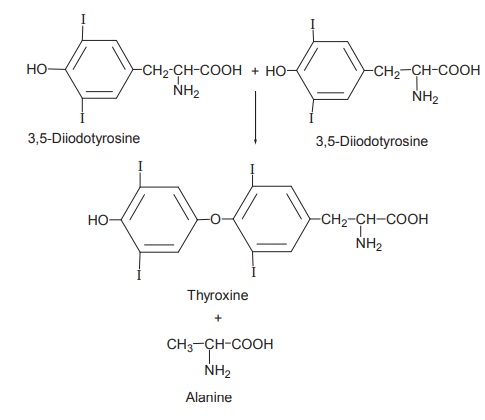
Two molecules of diiodotyrosine couple to form a
mole of tetraiodotyrosine which is thyroxine. Alanine is liberated.
Synthesis of thyroxine is accelerated by thyroid
stimulating hormone (TSH) and inhibited by antithyroid drugs like
thiocarbamides and aminobenzenes. Thyroid has the capacity of trapping
inorganic iodine from circulation and storing it for utilization in the
synthesis of thyroxine and its precursors. Depending upon the need for
thyroxine and its iodinated derivatives, a proteolytic enzyme hydrolyses
thyroglobulin, under the stimulating influence of TSH.
Related Topics