Chapter: Civil : Railway Airport Harbour Engineering : Railway Engineering : Locomotives and Other Rolling Stock
Types of Traction
The locomotive is a powerhouse
mounted on a frame that produces the motive power needed for traction on
railways. There are three distinct locomotives used on the railways, each
drawing its power from a different energy source. In a steam locomotive, the
motive power is the steam generated in a pressure vessel called the boiler.
Thus the thermal energy of fuel is converted into the mechanical energy of
motion. In a diesel locomotive, the motive power is an internal combustion
engine, which uses high-speed diesel oil as its source of energy. An electric
locomotive derives its power from an electric conductor running along the
track.
Types of Traction
There are three types of traction on Indian Railways.
(a) Steam
traction by steam locomotives
(b) Diesel
traction by diesel locomotives
(c) Electric
traction by electric locomotives
Diesel and electric locomotives
are comparatively more efficient than steam locomotives. They have greater
hauling capacity, permit better acceleration and deceleration, and are capable
of carrying heavy loads at higher speeds. In view of these factors, diesel and
electric locomotives are fast replacing steam locomotives, as can be seen from
Table 24.1.
Table 24.1 Different types of
locomotives on Indian Railways
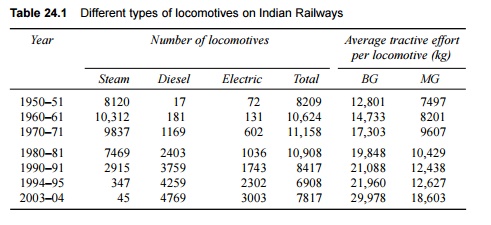
It may be noted here that though
the total holdings of locomotives on Indian Railways have been decreasing since
the last 25 years, the average tractive effort has increased progressively due
to the provision of more efficient diesel as well as electric traction in place
of steam traction.
Related Topics