Chapter: Civil : Railway Airport Harbour Engineering : Railway Engineering : Locomotives and Other Rolling Stock
Railway: Preventive Maintenance of Locomotives
Preventive Maintenance of Locomotives
The efficient operation of
railways depends on the reliability and availability of locomotives. The proper
and efficient maintenance of locomotive is the basis for economical train
operation. Maintenance practices have evolved on the basic principle that
necessary attention should be paid to all assets before deterioration through
wear and tear makes them prone to failure. This is known as preventive maintenance.
The preventive maintenance of locomotives can be broadly classified under
two heads, namely, periodical overhaul and schedule repairs.
1 Steam and Diesel Locomotives
The prescribed life of steam and
diesel locomotives is 40 and 36 years, respectively. In view of the long
lifespan, it is imperative that both these assets are properly and periodically
maintained to ensure that there is no deterioration in their condition. The
preventive maintenance of steam and diesel locomotives is done in the following
manner.
Periodical overhaul
Periodical overhaul (POH) of these locomotives is undertaken
in railway repair workshops. The frequency of the periodical overhauling of
steam and diesel locomotives is as follows:
Diesel locomotives 6
years (or 0.8 million km for BG and
0.6 million km for MG lines)
Steam locomotives
(a) Passenger 0.3-0.35 million km
(b) Goods 0.2-0.25 million km
(c) Inferior
services 5 years (or about 0.2 million
km)
During POH, the loco is
completely stripped and all its parts and components are repaired and/or
replaced, as their condition warrants. After POH, the locomotives are in an
'almost new' condition.
Schedule shed maintenance
Various examination schedules
have been drawn up as a part of preventive maintenance so that specific
components and parts of the locomotives may be given need-based attention at
intervals. The examination schedules list all the various aspects that should
be taken care of at the time of maintenance, which are dependent on the wear
and tear of the components. The total number of kilometres that should have
been covered before these examinations can be carried out have also been
specified:
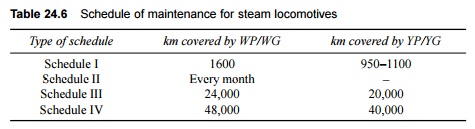
Steam locomotives Table
24.6 outlines the various types of schedules approved for the
maintenance of steam locomotives based on the total distance in kilometres
covered by the locomotives.
Table 24.6 Schedule of maintenance
for steam locomotives
Diesel locomotives A trip
(or weekly) schedule, a fortnightly schedule, a monthly schedule, a
three-month schedule, a six-month schedule, a yearly schedule, a three-year
schedule, and a six-year schedule (POH) have been drafted for diesel
locomotives.
These preventive maintenance
schedules have been worked out on the basis of experience and informed
investigations into the causes leading to the breakdown of locomotives.
Compared to a steam locomotive, the diesel traction unit is far more complex,
usually incorporating an indirect control system with much more elaborate
ancillary equipment. As a result of this greater complexity, it is more liable
to be rendered unserviceable by the failure of a particular component.
Therefore, in order to ensure a high standard of reliability, various schedules
have been instituted for its inspection and maintenance. The 'servicing' of
minor schedules, i.e., trip, fortnightly, monthly, etc., involving routine
inspections, minor attention, and the like, takes about 4 to 12 hours. The major
schedules take a longer time, lasting from 6 to 14 days, since they require
repair and replacement of major components.
2 Electric Locomotives
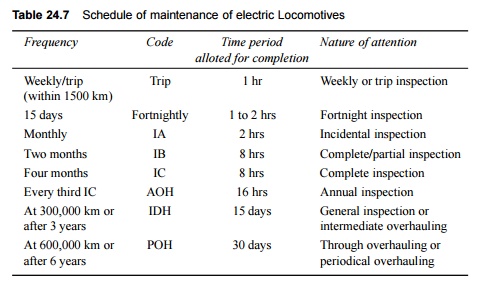
The schedules for inspection and
checks given in Table 24.7 are generally followed on Indian Railways to ensure
the proper maintenance of electric locomotives.
Table 24.7 Schedule of maintenance
of electric Locomotives
The frequency and duration of
various schedules have been defined after taking the several failures of
locomotives, the existence of indigenous components, and the atmospheric levels
of heat and dust in the country into consideration. Compared to steam and
diesel locomotives, electric locomotives include more contactors, relays, and
auxiliaries/equipment. Electrical quantities and changes in the condition of
the locomotive are not physically visible. Therefore, it is essential to check
the equipment, contactors, and relays periodically to ascertain the condition
of the various equipment without too much of dismantling. Most of the equipment
gets inspected during four monthly inspections and, therefore, these equipment
are excluded from the annual inspections. During such inspections, the
equipment are disconnected from mechanical fixtures, assemblies are stripped
and cleaned, and worn out or damaged parts are replaced and reconnected.
Trip or weekly and fortnightly
inspections are conducted at outstation running sheds, and all other schedule
inspections, except POH, are carried out at sheds. POH is, however, carried out
in the workshops.
Related Topics