Chapter: Civil : Railway Airport Harbour Engineering : Railway Engineering : Locomotives and Other Rolling Stock
Railway Rolling Stock
Rolling Stock
Rolling stock includes
locomotives, passenger coaches, goods wagons, and all other types of coaches
and wagons such as electric multiple units (EMUs), diesel rail cars, and
special wagons such as BOX wagons. This section gives some of the details of
passenger coaches and goods wagons.
1 Coaching Stock
The different types of passenger
coaches include the electric multiple units that are a part of suburban trains
and conventional coaches such as II class, I class, II sleeper, ac three tier,
ac two tier and ac I class coaches.
In 1994-95, Indian Railways had a
stock of about 3600 EMU coaches and 30,000 conventional coaches capable of
carrying a total of about 3.7 million passengers. These coaches have three
basic structural designs.
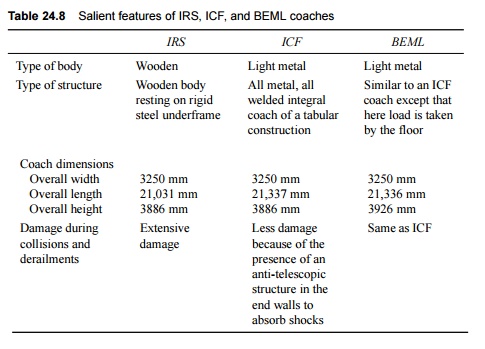
(a) Integral
coaches built by the Integral Coach Factory (ICF), Perambur, Chennai
(b) Integral
coaches built by Bharat Earth Movers Ltd (BEML), Bangalore
(c) Non-integral
wooden body coaches made in accordance with the Indian
Railways
standard design (IRS)
Some of the salient features of
these three types of coaches are given in Table 24.8.
Table 24.8 Salient features of IRS,
ICF, and BEML coaches
2 Goods Wagons
Goods wagons are primarily meant
for the carriage of goods traffic. Indian Railways presently has a stock of
about 0.29 million goods wagons with a haulage capacity of about 10 million t.
These goods wagons mostly consist of covered and open wagons as well as special
wagons such as BOX wagons for carrying coal and other bulk traffic.
Until the middle of the last
century, practically all the goods traffic was transported in general-purpose
wagons or in covered, open high-sided, and open low-sided wagons. The standard
wagon on the broad gauge was a four wheeler with a 22.19 t haulage capacity,
while the standard wagon on the metre gauge weighed 5.69 t and had the capacity
of carrying 18.69 t of goods. Recently, a number of new bogie wagons have been
designed and put into service, which lay emphasis on a higher payload and on
the provision of facilities for the loading and unloading of special type of
traffic. These include the BOX, BCX, BOBX, BOY, BOXN, CRT, wagons, etc. It has
been decided that only bogie wagons will be put into service on the Railways,
as the four wheeler wagon is a non-viable unit in the present context of the
bulk movement of commodities. In the above-mentioned classification of wagons,
B stands for bogie wagon, C for centre discharge, O for open wagon, X for
high-sided (also for both centre and side discharge), and Y for low-sided
walls. N is used for air braked, C for covered wagon, R for rail-carrying
wagon, and T for transition coupler. The B indication is sometimes omitted as
all new wagons are bogie stock.
Related Topics