Plant Physiology - Types of Respiration | 10th Science : Chapter 12 : Anatomy and Plant Physiology
Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 12 : Anatomy and Plant Physiology
Types of Respiration
TYPES OF RESPIRATION
Respiration involves
exchange of gases between the organism and the external environment. The plants
obtain oxygen from their environment and release carbon dioxide and water
vapour. This exchange of gases is known as external respiration . It is
a physical process. Biochemical process occurs within cells where the food is
oxidized to obtain energy, this is known as cellular respiration
1. Aerobic respiration
Aerobic respiration is
the type of celluar respiration in which organic food is completely oxidized
with the help of oxygen into carbon dioxide, water and energy. It occurs in
most plants and animals.
C6H12O6
+ 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
Stages
of Aerobic respiration
a. Glycolysis (Glucose splitting): It
is the breakdown of one molecule of glucose (6 carbon) into two
molecules of pyruvic acid (3 carbon) . Glycolysis takes place in cytoplasm of
the cell. It is the first step of both aerobic and anerobic respiration.
b. Krebs Cycle: This cycle occurs in mitochondria
matrix. At the end of glycolysis, 2 molecules of pyruvic acid enter into
mitochondria. The oxidation of pyruvic acid into CO2 and water takes
place through this cycle. It is also called Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle
(TCA).
c. Electron Transport
Chain: This
is accomplished through a system of electron carrier complex called electron
transport chain (ETC) located on the inner membrane of the
mitochondria. NADH2 and FADH2 molecules formed during
glycolysis and Krebs cycle are oxidised to NAD+ and FAD+ to release the energy
via electrons. The electrons, as they move through the system, release energy
which is trapped by ADP to synthesize ATP. This is called oxidative phosphorylation.
In this process, O2 the ultimate acceptor of electrons gets reduced
to water.
2. Anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic respiration
takes place without oxygen. Glucose is converted into ethanol (in plants) or
lactate (in some bacteria)
C6H12O6
→ 2CO2 + 2C2H5OH + Energy (ATP)
3. Respiratory quotient (R.Q)
Respiratory quotient is
the ratio of volume of carbon dioxide liberated and the volume of oxygen
consumed during respiration. It is expressed as
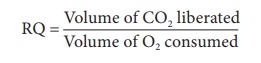
Related Topics