Functions, Structure - Mitochondria | 10th Science : Chapter 12 : Anatomy and Plant Physiology
Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 12 : Anatomy and Plant Physiology
Mitochondria
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are
filamentous or granular cytoplasmic organelles present in cells. The
mitochondria were first discovered by Kolliker in 1857 as granular structures
in striated muscles. Mitochondria (singular: mitochondrion) are organelles
within eukaryotic cells that produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) which form
the energy currency of the cell, for this reason, the mitochondria is referred
to as the “Power house of the cell”. Mitochondria vary in size
from 0.5 µm to 2.0 µm. Mitochondria contain 60-70% protein, 25-30% lipids,
5-7% RNA and small amount of DNA and minerals.
1. Structure of Mitochondria
Mitochondrial Membranes:
It consists two
membranes called inner and outer membrane. Each membrane is 60 -70 A˚ thick.
Outer mitochondrial membrane is smooth and freely permeable to most small
molecules. It contains enzymes, proteins and lipids. It has porin molecules
(proteins) which form channels for passage of molecules through it.
Inner mitochondrial membrane
is semi permeable membrane and regulates the passage of materials into and out
of the mitochondria. It is rich in enzymes and carrier proteins. It consists of
80% proteins and lipids.
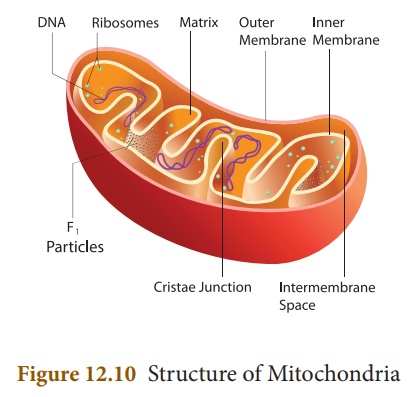
Cristae: The inner mitochondrial
membrane gives rise to finger like projections called cristae. These
cristae increase the inner surface area (fold in inner membrane) of the
mitochondria to hold variety of enzymes.
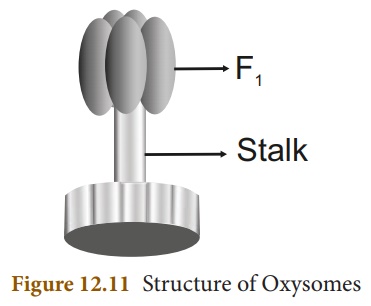
Oxysomes: The inner mitochondrial
membrane bear minute regularly spaced tennis racket shaped particles known
as oxysomes (F1 particle). They involve in ATP synthesis.
Mitochondrial matrix - It is a complex mixture
of proteins and lipids. Matrix contains enzymes for Krebs cycle, mitochondrial
ribosomes(70 S), tRNAs and mitochondrial DNA.
2. Functions of Mitochondria
·
Mitochondria is the main organelle of cell respiration. They
produce a large number of ATP molecules. So they are called as power houses
of the cell or ATP factory of the cell.
·
It helps the cells to maintain normal concentration of calcium
ions.
·
It regulates the metabolic activity of the cell.
Related Topics