Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 12 : Anatomy and Plant Physiology
Internal Structure of Dicot Root (Bean)
Internal Structure of Dicot Root (Bean)
A thin transverse section of dicot root shows the following structures.
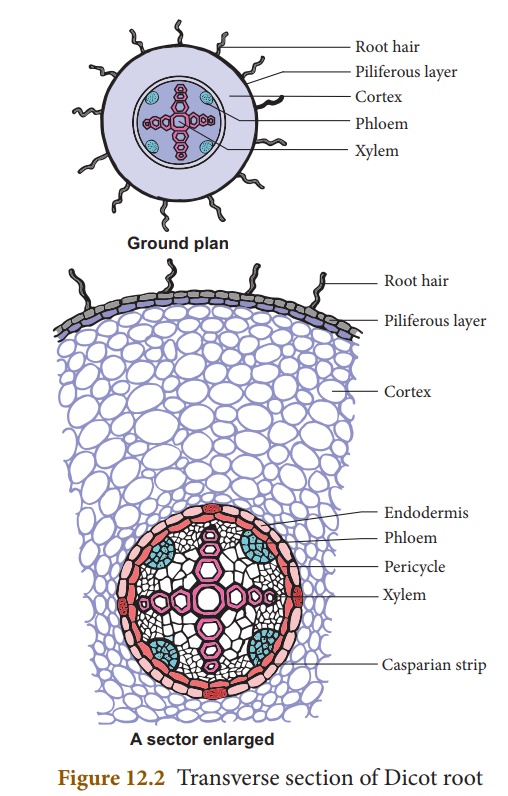
(i) Epiblema: It is the outermost layer. Cuticle and stomata are absent. Unicellular root hairs are present. It is also known as Rhizodermis orPiliferous layer.
(ii) Cortex: It is a multilayered large zone made of thin-walled parenchymatous cells with intercellular spaces. It stores food and water.
(iii) Endodermis: It is the innermost layer of cortex. The cells are barrel - shaped, closely packed, and show band like thickenings on their radial and inner tangential walls called casparian strips. It helps in the movement of water and dissolved salts from cortex into xylem.
(iv) Stele: All tissues inner to endodermis constitute stele. It includes pericycle and vascular bundle.
(a) Pericycle: Inner to endodermis lies a single layer of pericycle. It is the site of origin of lateral roots.
(b) Vascular bundle: It is radial. Xylem is exarch and tetrach. The tissue present between xylem and phloem is called conjunctive tissue. In dicot root, it is made up of parenchyma.
(c) Pith: Young root contains pith whereas in old root pith is absent.
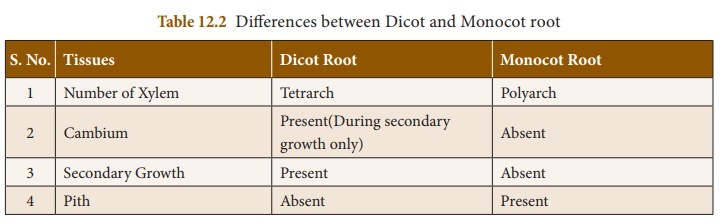
Differences between Dicot and Monocot root
Related Topics