Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 12 : Anatomy and Plant Physiology
Internal Structure of Dicot Stem (Sunflower)
Internal
Structure of Dicot Stem
(Sunflower)
The transverse section
of a dicot stem reveals the following structures.
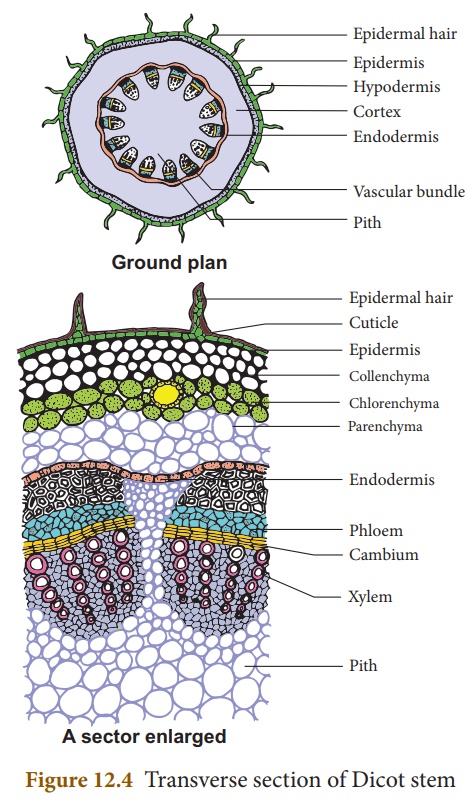
1. Epidermis: It is the outermost
layer. It is made up of single layer of parenchyma cells, its outer wall
is covered with cuticle. It is protective in function.
2. Cortex:- It is divided into
three regions:
(i) Hypodermis: It consists of 3 - 6 layers of collenchyma cells. It gives mechanical support.
(ii) Middle cortex: It is made up of few layers of chlorenchyma
cells. It is involed in photosynthesis due to the presence of chloroplast.
(iii) Inner cortex: It is made up of few layers of parenchyma
cells. It helps in gaseous exchange and stores food materials.
Endodermis is the inner most layer
of cortex it consists of a single layer of barrel shaped cells, these
cells contain starch grains. So it is also called starch sheath.
3.
Stele: The
central part of the stem inner to endodermis is known as stele. It
consists of pericycle, vascular bundle and pith.
(i) Pericycle: It occurs between vascular bundle and
endodermis. It is multilayered, parenchymatous with alternating patches of
sclerenchyma.
(ii) Vascular bundle: Vascular bundles are conjoint,
collateral, endarch and open. They are arranged in the form of a ring around
the pith.
(iii) Pith: The large central
parenchymatous zone with intercellular spaces is called pith. It helps
in the storage of food materials.
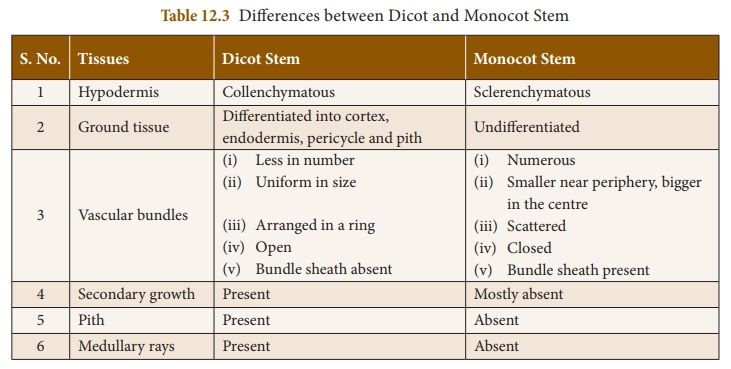
Differences between Dicot and Monocot Stem
Related Topics