Chapter: Business Science : Human Resource Management : Training and Executive Development
Types of Employee Training
Types of Employee Training
Some
commentator use a similar term for workplace learning to improve performance:
―training and development‖. One can generally categorize such training as
on-the-job or off-the-job:
On-the-job training takes place in a normal working
situation, using the actual tools, equipment, documents or materials that
trainees will use when fully trained. On-the-job training has a general
reputation as most effective for vocational work.
Off-the-job training takes place away from normal
work situations — implying that the employee does not count as a directly
productive worker while such training takes place. Off-the-job training has the
advantage that it allows people to get away from work and concentrate more
thoroughly on the training itself. This type of training has proven more
effective in inculcating concepts and ideas.
The most
frequently used method in smaller organizations that is on the job training.
This method of training uses more knowledgeable, experienced and skilled
employees, such as mangers, supervisors to give training to less knowledgeable,
skilled, and experienced employees. OJT can be delivered in classrooms as well.
This type of training often takes place at the work place in informal manner.
On the
Job Training is characterized by following points
It is
done on ad-hoc manner with no formal procedure, or content
At the
start of training, or during the training, no specific goals or objectives are
developed Trainers usually have no formal qualification or training experience
for training
Training
is not carefully planned or prepared
The
trainer are selected on the basis of technical expertise or area knowledge
Formal
OJT programs are quite different from informal OJT. These programs are carried
out by identifying the employees who are having superior technical knowledge
and can effectively use one-to-one interaction technique. The procedure of
formal on the job training program is:
1. The
participant observes a more experienced, knowledgeable, and skilled trainer
(employee)
2. The
method, process, and techniques are well discussed before, during and after
trainer has explained about performing the tasks
3. When the
trainee is prepared, the trainee starts performing on the work place
4. The
trainer provides continuing direction of work and feedback
5. The
trainee is given more and more work so that he accomplishes the job flawlessly
The four
techniques for on the job development are:
COACHING
MENTORING
JOB
ROTATION
JOB
INSTRUCTION TECHNIQUE (JIT)
1.) Coaching is one of
the training methods, which is considered as a corrective method for inadequate performance. According to a survey
conducted by International Coach Federation (ICF), more than 4,000 companies
are using coach for their executives. These coaches are experts most of the
time outside consultants.
A coach
is the best training plan for the CEO‘s because
It is one
to one interaction
It can be
done at the convenience of CEO
It can be
done on phone, meetings, through e-mails, chat
It
provides an opportunity to receive feedback from an expert
It helps
in identifying weaknesses and focus on the area that needs improvement
This
method best suits for the people at the top because if we see on emotional
front, when a person reaches the top, he gets lonely and it becomes difficult
to find someone to talk to. It helps in finding out the executive‘s specific
developmental needs. The needs can be identified through 60 degree performance
reviews.
Procedure of the Coaching
The
procedure of the coaching is mutually determined by the executive and coach.
The procedure is followed by successive counseling and meetings at the
executive‘s convenience by the coach.
1. Understand
the participant‘s job, the knowledge, skills, and attitudes, and resources
required to meet the desired expectation
2. Meet the
participant and mutually agree on the objective that has to be achieved
3. Mutually
arrive at a plan and schedule
4. At the
job, show the participant how to achieve the objectives, observe the
performance and then provide feedback
5. Repeat
step 4 until performance improves
For the
people at middle level management, coaching is more likely done by the
supervisor; however experts from outside the organization are at times used for
up and coming managers. Again, the personalized approach assists the manger
focus on definite needs and improvement.
2.) Mentoring is an
ongoing relationship that is developed between a senior and junior employee.
Mentoring provides guidance and
clear understanding of how the organization goes to achieve its vision and
mission to the junior employee.
The
meetings are not as structured and regular than in coaching. Executive
mentoring is generally done by someone inside the company. The executive can
learn a lot from mentoring. By dealing with diverse mentee‘s, the executive is
given the chance to grow professionally by developing management skills and
learning how to work with people with diverse background, culture, and language
and personality types.
Executives
also have mentors. In cases where the executive is new to the organization, a
senior executive could be assigned as a mentor to assist the new executive
settled into his role. Mentoring is one of the important methods for preparing
them to be future executives. This method allows the mentor to determine what
is required to improve mentee‘s performance. Once the mentor identifies the
problem, weakness, and the area that needs to be worked upon, the mentor can
advise relevant training. The mentor can also provide opportunities to work on
special processes and projects that require use of proficiency.
Some key
points on Mentoring
Mentoring
focus on attitude development
Conducted
for management-level employees
Mentoring is done by someone inside the company It
is one-to-one interaction
It helps
in identifying weaknesses and focus on the area that needs improvement
3.) For the
executive, job rotation takes on
different perspectives. The executive is usually not simply going to another department. In some vertically integrated
organizations, for example, where the supplier is actually part of same
organization or subsidiary, job rotation might be to the supplier to see how
the business operates from the supplier point of view.
Learning
how the organization is perceived from the outside broadens the executive‘s
outlook on the process of the organization. Or the rotation might be to a
foreign office to provide a global perspective. For managers being developed
for executive roles, rotation to different functions in the company is regular
carried out.
This
approach allows the manger to operate in diverse roles and understand the
different issues that crop up. If someone is to be a corporate leader, they
must have this type of training. A recent study indicated that the single most
significant factor that leads to leader‘s achievement was the variety of
experiences in different departments, business units, cities, and countries.
An
organized and helpful way to develop talent for the management or executive
level of the organization is job rotation. It is the process of preparing
employees at a lower level to replace someone at the next higher level. It is
generally done for the designations that are crucial for the effective and
efficient functioning of the organization.
Some of
the major benefits of job rotation are:
It provides the employees with opportunities to
broaden the horizon of knowledge, skills, and abilities by working in different
departments, business units, functions, and countries
Identification of Knowledge, skills, and attitudes
(KSAs) required It determines the areas where improvement is required
Assessment
of the employees who have the potential and caliber for filling the position
4.) Job Instruction Technique
(JIT) uses a strategy with focus on knowledge (factual and procedural), skills and attitudes development.
JIT Consists of Four Steps:
Plan – This step
includes a written breakdown of the work to be done because the trainer and the
trainee must understand that documentation is must and important for
the familiarity of work. A trainer who is aware of the work well is likely to
do many things and in the process might miss few things. Therefore, a
structured analysis and proper documentation ensures that all the points are
covered in the trainingprogram. The second step is to find out what the trainee
knows and what training should focus on. Then, the next step is to create a
comfortable atmosphere for the trainees‘ i.e. proper orientation program,
availing the resources, familiarizing trainee with the training program, etc.
Present – In this
step, trainer provides the synopsis of the job while presenting the
participants the different aspects of the work. When the trainer finished, the
trainee demonstrates how to do the job and why is that done in that specific
manner. Trainee actually demonstrates the procedure while emphasizing the key
points and safety instructions.
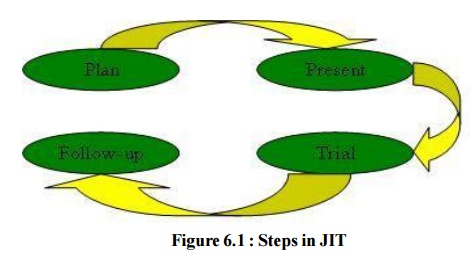
Figure 6.1 : Steps in JIT
Trial – This step
actually a kind of rehearsal step, in which trainee tries to perform the work
and the trainer is able to provide instant feedback. In this step, the
focus is on improving the method of instruction because a trainer considers
that any error if occurring may be a function of training not the trainee. This
step allows the trainee to see the after effects of using an incorrect method.
The trainer then helps the trainee by questioning and guiding to identify the
correct procedure.
Follow-up
– In this step, the trainer checks the trainee‘s job
frequently after the training program is over to prevent bad work
habits from developing. There are various methods of training, which can be
divided in to cognitive and behavioral methods. Trainers need to understand the
pros and cons of each method, also its impact on trainees keeping their
background and skills in mind before giving training.
OFF THE JOB TRAINING –
There are
many management development techniques that an employee can take in off the
job. The few popular methods are:
SENSITIVITY
TRAINING
TRANSACTIONAL
ANALYSIS
STRAIGHT
LECTURES/ LECTURES
SIMULATION
EXERCISES
1.) Sensitivity Training is about
making people understand about themselves and others reasonably, which is done by developing in them
social sensitivity and behavioral flexibility.
Social
sensitivity in one word is empathy. It is ability of an individual to sense
what others feeland think from their own point of view. Behavioral flexibility
is ability to behave suitably in light of understanding.
Sensitivity
Training Program requires three steps:
Unfreezing the Old Values –
It
requires that the trainees become aware of the inadequacy of the old values.
This can be done when the trainee faces dilemma in which his old values is not
able to provide proper guidance. The first stepconsists of a small procedure:
An
unstructured group of 10-15 people is formed.
Unstructured
group without any objective looks to the trainer for its guidance But the
trainer refuses to provide guidance and assume leadership
Soon, the
trainees are motivated to resolve the uncertainty
Then, they try to form some hierarchy. Some try
assume leadership role which may not be liked by other trainees
Then, they started realizing that what they desire
to do and realize the alternative ways of dealing with the situation
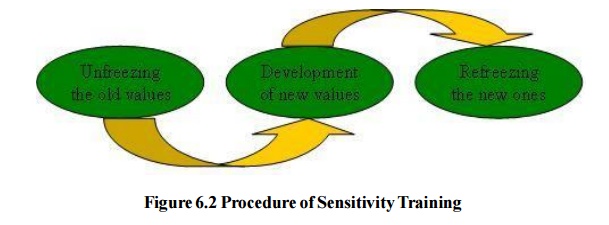
Figure 6.2 Procedure of
Sensitivity Training
Development of New Values – With the
trainer‘s support, trainees begin to examine their interpersonal behavior and giving each other
feedback. The reasoning of the feedbacks are discussed which motivates trainees
to experiment with range of new behaviors and values. This process constitutes
the second step in the change process of the development of these values.
Refreezing the new ones – This step
depends upon how much opportunity the trainees get to practice their new behaviors and values at
their work place.
2.) Transactional Analysis provides
trainees with a realistic and useful method for analyzing and understanding the behavior of others.
In every social interaction, there is a motivation provided by one person and a
reaction to that motivation given by another person. This motivation reaction
relationship between two persons is a transaction.
Transactional analysis can be
done by the ego states of an individual. An ego state is a system of feelings accompanied by a related set
of behaviors. There are basically three ego states:
Child: It is a
collection of recordings in the brain of an individual of behaviors, attitudes,
and impulses which come to her
naturally from her own understanding as a child. The characteristics of this
ego are to be spontaneous, intense, unconfident, reliant, probing, anxious,
etc. Verbal clues that a person is operating from its child state are the use
of words like ―I guess‖, ―I suppose‖, etc. and non verbal clues like, giggling,
coyness, silent, attention seeking etc.
Parent: It is a collection of recordings
in the brain of an individual of behaviors, attitudes, and impulses imposed on her in her childhood from
various sources such as, social, parents, friends, etc. The characteristics of
this ego are to be overprotective, isolated, rigid, bossy, etc. Verbal clues
that a person is operating from its parent states are the use of words like,
always, should, never, etc and non-verbal clues such as, raising eyebrows,
pointing an accusing finger at somebody, etc.
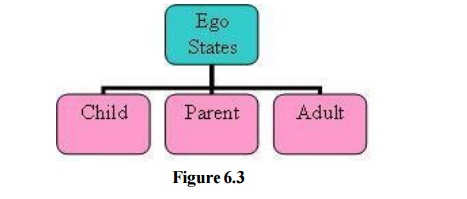
Adult: It is a
collection of reality testing, rational behavior, decision making, etc. A
person in this ego state verifies,
updates the data which she has received from the other two states. It is a
shift from the taught and felt concepts to tested concepts. All of us evoke
behavior from one ego state which is responded to by the other person from any
of these three states.
3.) Lecture is
telling someone about something. Lecture is given to enhance the knowledge of
listener or to give him the
theoretical aspect of a topic. Training is basically incomplete without
lecture. When the trainer begins the training session by telling the aim, goal,
agenda, processes, or methods that will be used in training that means the
trainer is using the lecture method. It is difficult to imagine trainingwithout
lecture format. There are some variations in Lecture method. The variation here
means that some forms of lectures are interactive while some are not.
Straight Lecture: Straight
lecture method consists of presenting information, which the trainee attempts to absorb. In this method, the trainer
speaks to a group about a topic. However, it does not involve any kind of
interaction between the trainer and the trainees. A lecture may also take the
form of printed text, such as books, notes, etc. The difference between the
straight lecture and the printed material is the trainer‘s intonation, control
of speed, body language, and visual image of the trainer. The trainer in case
of straight lecture can decide to vary from the training script, based on the
signals from the trainees, whereas same material in print is restricted to what
is printed. A good lecture consists of introduction of the topic, purpose of
the lecture, and priorities and preferences of the order in which the topic
will be covered. Some of the main features of lecture method are:
Inability to identify and correct misunderstandings
Less expensive
Can be
reached large number of people at once Knowledge building exercise
Less
effective because lectures require long periods of trainee inactivity
4.) Games and Simulations are
structured and sometimes unstructured, that are usually played for enjoyment sometimes are used for
training purposes as an educational tool. Training games and simulations are
different from work as they are designed to reproduce or simulate events,
circumstances, processes that take place in trainees‘ job.
A
Training Game is defined as spirited activity or exercise in which trainees
compete with each other according to the defined set of rules. Simulation is
creating computer versions of real-life games. Simulation is about imitating or
making judgment or opining how events might occur in a real situation. It can
entail intricate numerical modeling, role playing without the support of
technology, or combinations. Training games and simulations are now seen as an
effective tool for training because its key components are:
Challenge
Rules
Interactivity
These
three components are quite essential when it comes to learning. Some of the
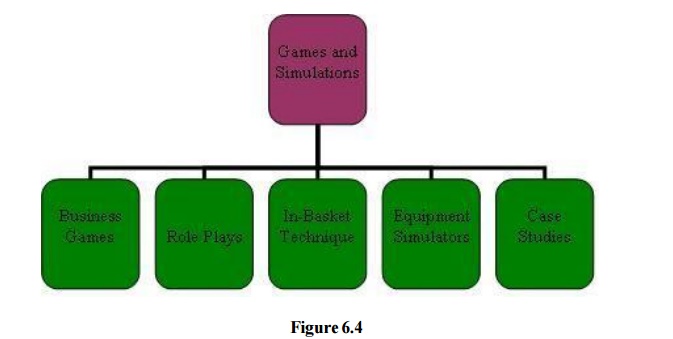
examples of this technique are:
Trainees
can therefore experience these events, processes, games in a controlled setting
where they can develop knowledge, skills, and attitudes or can find out
concepts that will improve their performance. The various methods that come
under Games and Simulations are:
BEHAVIOR-MODELLING
BUSINESS
GAMES
CASE
STUDIES
EQUIPMENT
STIMULATORS
IN-BASKET
TECHNIQUE
ROLE
PLAYS
Objectives and Process of Employee Training
The
training design process refers to a systematic approach for developing training
programs. It includes the seven steps in this process. Training is one of the
most profitable investments an organization can make. No matter what business
or industry you are in the steps for an effective training process are the same
and may be adapted anywhere. If you have ever thought about developing a
training program within your organization consider the following four basic
training steps. You will find that all four of these steps are mutually
necessary for any training program to be effective and efficient.
Step1 is to
conduct a needs assessment, which is necessary to identify whether training is
needed. This step identifies
activities to justify an investment for training. The techniques necessary for
the data collection are surveys, observations, interviews, and customer comment
cards. Several examples of an analysis outlining specific training needs are
customer dissatisfaction, low morale, low productivity, and high turnover.
The
objective in establishing a needs analysis is to find out the answers to the
following questions:
―Why‖ is
training needed?
―What‖
type of training is needed? ―When‖ is the training needed? ―Where‖ is the
training needed?
―Who‖
needs the training? and ―Who‖ will conduct the training? ―How‖ will the
training be performed?
By
determining training needs, an organization can decide what specific knowledge,
skills, and attitudes are needed to improve the employee‘s performance in
accordance with the company‘s standards.
The needs
analysis is the starting point for all training. The primary objective of all
training is to improve individual and organizational performance. Establishing
a needs analysis is, and should always be the first step of the training
process.
Step 2 is to
ensure that employees have the motivation and basic skills necessary to master
training content. This step
establishes the development of current job descriptions and standards and
procedures. Job descriptions should be clear and concise and may serve as a
major training tool for the identification of guidelines. Once the job
description is completed, a complete list of standards and procedures should be
established from each responsibility outlined in the job description. This will
standardize the necessary guidelines for any future training.
Step 3 is to
create a learning environment that has the features necessary for learning to
occur. This step is responsible for
the instruction and delivery of the training program. Once you have designated
your trainers, the training technique must be decided. One-on-one training,
on-the-job training, group training, seminars, and workshops are the most
popular methods.
Before
presenting a training session, make sure you have a thorough understanding of
the following characteristics of an effective trainer. The trainer should have:
- A desire
to teach the subject being taught.
- A working
knowledge of the subject being taught.
- An
ability to motivate participants to ―want‖ to learn.
- A good
sense of humour.
- A dynamic
appearance and good posture.
- A strong
passion for their topic.
- A strong
compassion towards their participants.
- Appropriate
audio/visual equipment to enhance the training session.
For a
training program to be successful, the trainer should be conscious of several
essential elements, including a controlled environment, good planning, the use
of various training methods, good communication skills and trainee participation.
Step 4 is to
ensure that trainees apply the training content to their jobs.
This step
will determine how effective and profitable your training program has been.
Methods for evaluation are pre-and post- surveys of customer comments cards,
the establishment of a cost/benefit analysis outlining your expenses and
returns, and an increase in customer satisfaction and profits. The reason for
an evaluation system is simple. The evaluations of training programs are
without a doubt the most important step in the training process. It is this
step that will indicate the effectiveness of both the training as well as the
trainer.
There are
several obvious benefits for evaluating a training program. First, evaluations
will provide feedback on the trainer‘s performance, allowing them to improve
themselves for future programs. Second, evaluations will indicate its
cost-effectiveness. Third, evaluations are an efficient way to determine the
overall effectiveness of the training program for the employees as well as the
organization.
The
importance of the evaluation process after the training is critical. Without
it, the trainer does not have a true indication of the effectiveness of the
training. Consider this information the next time you need to evaluate your training
program. You will be amazed with the results.
The need
for training your employees has never been greater. As business and industry
continues to grow, more jobs will become created and available. Customer
demands, employee morale, employee productivity, and employee turnover as well
as the current economic realities of a highly competitive workforce are just
some of the reasons for establishing and implementing training in an
organization. To be successful, all training must receive support from the top
management as well as from the middle and supervisory levels of management. It
is a team effort and must be implemented by all members of the organization to
be fully successful.
Advantages of On the Job Training Methods
On the
job training method has the following advantages that can be considered:
Generally
most cost-effective
Employees are actually productive Opportunity to
learn whilst doing Training alongside real colleagues.
Training
can be delivered on time and at the optimum time.
The trainee
will have the good opportunities to practice and implement. The trainee will
have feedbacks.
Trainee
builds confidence by working with own speed and productivity.
Related Topics