Chapter: Electrical Engineering and Instrumentation : Induction Machines and Synchronous Machines
Types, Construction and Working of 3 Phase Induction Motor
Types, Construction and Working of 3 Phase Induction Motor
Three phase induction motor has two types.
i. Squirrel cage induction motor
ii. Slip ring induction motor
The stator of both motors is same and the rotor is different.
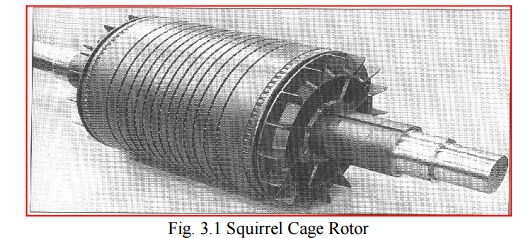
Squirrel cage rotor
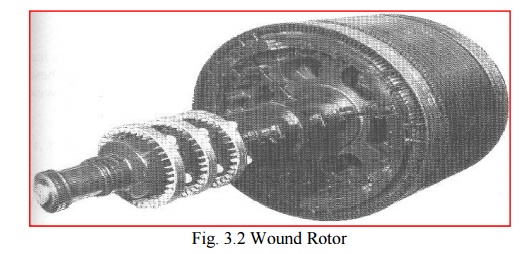
Wound rotor
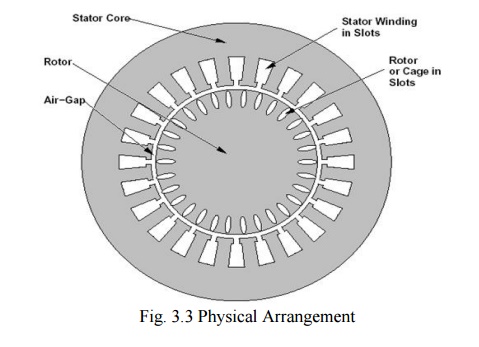
A stator consists of steel frame that supports a hollow cylindrical core of stacked laminations.
Slots on the internal circumference of stator house the stator winding.
A rotor also composed of punched laminations, with rotor slots for the rotor winding.
There are two types of rotor windings:
Squirrel cage windings, which produce squirrel cage induction motor.
Conventional three phase windings made up of insulated wire, which produce a wound rotor induction motor.
Squirrel cage rotor consists of copper bars slightly longer than rotor which is pushed in to the slots.
The ends are welded to copper end rings, so that all the bars are short circuited.
A wound rotor has three phase winding similar to the stator winding.
The rotor winding terminals are connected to three slip rings which turn with the rotor.
The slip rings/brushes allow external resistors to be connected in series with the winding.
The external resistors are mainly used during start up. Under normal running conditions the windings short circuited externally.
Working
Induction motor works on the principle of Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction.
When the three supply is given to the stator of an induction motor, rotating magnetic field is produced around the stator.
This field cuts the rotor conductors; an emf is produced as per Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction.
The induced voltage produces currents which circulate in a loop around the conductors.
Since the current carrying conductors lie in the magnetic field, they experience mechanical force (Torque).
The force is always acts in a direction to drag the conductor along with the magnetic field.
Related Topics