Chapter: Electrical Engineering and Instrumentation : Transformer
Important Short Questions and Answers: Electrical Engineering and Instrumentation - Transformer
TRANSFORMERS
1. Distinguish between core and shell type
transformer.
In core
type, the windings surround the core considerably and in shell type the core
surround the winding.
2.
What is
an ideal transformer and how does it differ from a practical transformer.
Ø An ideal
transformer is one which does not involve any power loss and does not have any
change in frequency. It decreases or increases the input voltage.
Ø Practical
transformer is one which involves power loss and does not have any change in
frequency. It decreases or increases the input voltage.
3. Define voltage regulation in a transformer.
When a
transformer is loaded with a constant primary voltage, the secondary voltage
decreases for lagging Power factor load, and increases for leading power factor
load because of its internal resistance and leakage reactance. The change in
secondary terminal voltage from no load to full load expressed as a percentage
of no loads or full load voltage is termed as regulation.
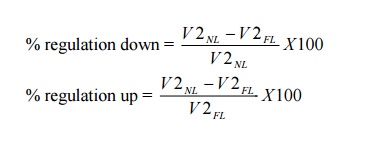
4. Write down the emf equation of a transformer.
Emf
induced in primary coil E1 = 4.44 fΦ mN1 volt Emf induced in secondary coil E2
= 4.44fΦ mN2 volt
Where f
is the frequency of AC input Φ m is the maximum value of flux in the core N1,
N2 are the number of primary and secon dary turns.
5. Define a transformer.
The
transformer is a static piece of apparatus by means of which electrical power
is transformed from one alternating current circuit to another with desired
change in voltage and current without any change in the frequency. It works on
the principle of mutual induction.
6. Why transformers are rated in kVA?
Copper
loss of a transformer depends on current and iron loss on voltage. Hence total
losses depend on Volt- Ampere and not on the power factor. That is why the
rating of transformers is in kVA and not in kW.
7. Why the core of a transformer is is laminated?
The
purpose of laminating the co re in a transformer is to reduce eddy current
loss.
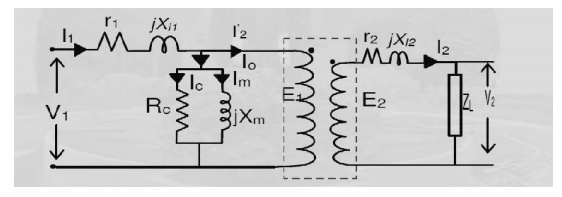
8. Draw the equivalent circuit of a transformer.
9. An 1100/400 V, 50 Hz single phase transformer
has 100 turns on the secondary winding. Calculate the number of turns on its
primary.
We know
V1 / V2 = k = N2 / N1
Substituting
400/1100 = 100/N1
N1 =
100/400 x 1100 = 275 turns.
10.
What are
the advantages of a transformer?
Ø Less I2R
loss in the transmission line
Ø Less
voltage drop in the line
Ø Efficiency
of the transmission line is increased
Ø Volume of
the conductor required is less.
11.
Define
voltage transformation ratio of transformer.
The ratio
of secondary induced emf to primary induced emf is called as voltage regulation
ratio devoted by K.
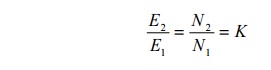
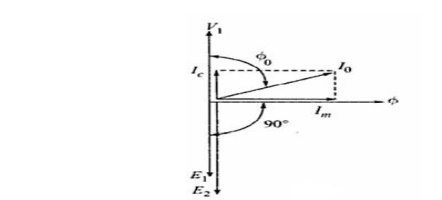
12. Draw the no load phasor diagram of a
transformer.
13. Define all day efficiency.
All day
efficiency is the ratio energy (in kwh) delivered in a 24 hours period to the
energy (in kwh) input for the same length of time.
All day
efficiency = Output in kwh/Input in kwh (for 24 hrs)
14.
Give the
factors that determine the thickness of the lamination or stampings.
i.
Iron loss
ii.
Frequency
15.
What are
the properties of ideal transformer?
It has no
loss
ii) Its
winding has zero resistance.
iii)
Leakage flux is zero i.e 100% flux produced by
primary links with the secondary
iv) Permeability
of core is so high that negligible current is required to establish the flues
is it.
16.
What are
the losses occurring in a transformer?
i) Core
losses
ii) Copper
losses
17.
What is
meant by core or iron losses?
Core or
iron losses are caused as the core gets subjected to an alternating flux.
18. What is meant by copper loss?
The
copper losses are due to the power wasted in the form of I2R due to the
resistances of the primary and secondary windings.
19. What is meant by eddy current loss?
The
induced emf in the core tries to set up eddy currents in the core and hence
responsible for the eddy current losses.
20. What is meant by hysteresis losses?
Due to
alternating flux set up in the magnetic core of the transformer, it undergoes a
cycle of magnetization and demagnetization.
Due to
hysteresis effect there is loss of energy in this process which is called
hysteresis loss.
21. What do you mean by step down transformer?
If the
secondary voltage is greater than primary value, the transformer is called step
down transformer.
22. What are the functions of no-load current in a
transformer?
No-load
current produces flux and supplies iron loss and copper loss on no-load.
23.
What are
the typical uses of auto transformer?
Ø To give
small boost to a distribution cable to correct for the voltage drop
Ø As
induction motor starters
Ø As
furnace transformers
Ø As
interconnecting transformers
Ø In
control equipment for single phase and 3 phase elective locomotives
Related Topics