Chapter: Mechanical Engineering : Internal Combustion Engines
Two Stroke Cycle Petrol Engines
PETROL ENGINES
Classification of Petrol Engines
•
Two Stroke cycle Petrol Engines
•
Four Stroke cycle petrol Engines
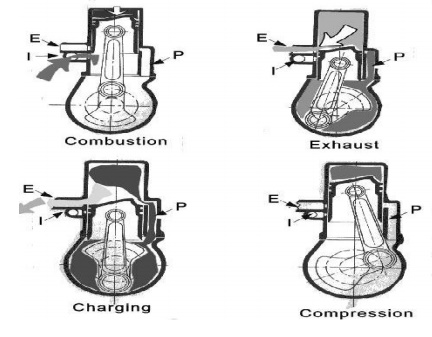
TWO STROKE CYCLE PETROL ENGINES:
Two Stroke Cycle Petrol Engine - Construction
Construction
:
•
A piston reciprocates inside the cylinder
•
It is connected to the crankshaft by means of
connecting rod and crank
•
There are no valves in two stroke engines, instead
of valves ports are cut on the cylinder walls.
•
There are three ports, namely inlet, exhaust and
transfer ports.
•
The closing and opening of the ports are obtained
by the movement of piston. The crown of piston is made in to a shape to perform
this.
•
A spark plug is also provided.
First Stroke : (Compression, ignition and
inductance) (Upward stroke of piston)
(a) compression:
•
The piston moves up from Bottom Dead Centre (BDC)
to Top Dead Centre (TDC)
•
Both transfer and exhaust ports are covered by the piston.
•
Air fuel mixture which is transferred already into
the engine cylinder is compressed by moving piston.
•
The pressure and temperature increases at the end
of compression.
First Stroke : (Compression, ignition and
inductance) (Upward stroke of piston)
(b) Ignition
and Inductance:
•
Piston almost reaches the top dead centre
•
The air fuel mixture inside the cylinder is
ignited by means of an electric spark
•
produced by a spark plug
•
At the same time, the inlet port is uncovered by
the plane.
•
Fresh air fuel mixture enters the crankcase
through the inlet port.
Second Stroke: (Downward Stroke
of the engine) : (c)Expansion and Crankcase compression
•
The burning gases expand in the cylinder
•
The burning gases force the piston to move down.
Thus useful work is obtained.
•
When the piston moves down, the air fuel mixture
in the crankcase is partially compressed. This compression is known as Crank
case compression.
Second Stroke: (Downward Stroke of the engine) :
(d) Exhaust
and transfer:
•
At the end of expansion, exhaust port is
uncovered.
•
Burnt gases escape to the atmosphere.
•
Transfer port is also opened. The partially
compressed air fuel mixture enters the cylinder through the transfer port.
•
The crown of the piston is made of a deflected
shape. So the fresh charge entering the cylinder is deflected upwards in the
cylinder.
•
Thus the escape of fresh charge along with the
exhaust gases is reduced.
Related Topics