Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio zoology Human Body higher secondary school
Two Kingdom System of Classification
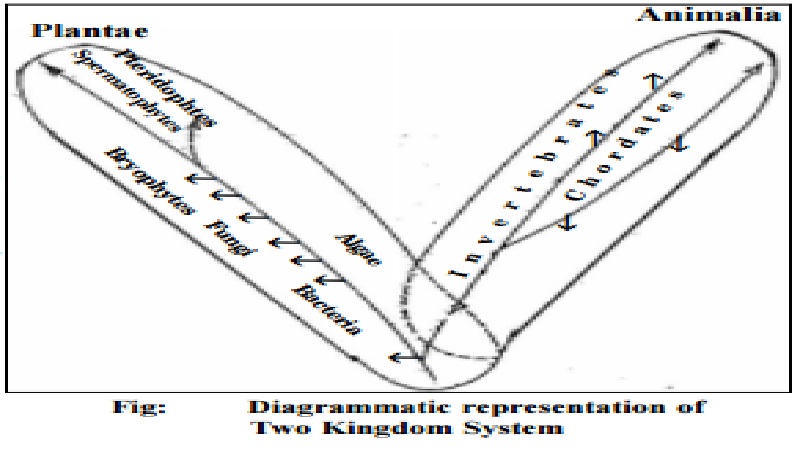
Two Kingdom System of Classification
Carolus Linnaeus(1758) divided all the living organisms into two kingdoms.
1. Kingdom Plantae
2. Kingdom Animalia
1. Kingdom Plantae:
This kingdom includes bacteria(Prokaryotes), photosynthetic plants and non - photosynthetic fungi. The characteristic features of this kingdom are:
Plants have branches, asymmetrical body with green leaves. Plants are non motile and fixed in a place.
During the day time plants more actively involve in photosynthesis than in respiration and hence take more of CO2 and liberate O2 during night O2 is taken in and CO2 is liberated.
They are autotrophic in their mode of nutrition since they synthesize their own food.
Plants have growing points which have unlimited growth.
Excretory system and nervous system are absent.
Reserve food material is starch.
Cells have a cell wall. Cells have a lager vacuole. Plant cells lack centrosome and they may have inorganic crystals.
Reproduction takes place with help of agents such as air, water and insects. Asexual and vegetative method of reproduction is also not uncommon.
2. Kingdom Animalia
This kingdom includes unicellular protozoans and multi-cellular animals or metazoans. They are characterized by
Definite shape of the body and absence of branches.
Ability to move from place to place.
During day and night take in O2 and release CO2 i.e only respiration takes place and there is no photosynthesis.
Holozoic mode of nutrition since no chlorophylls present and hence they are heterotrophs.
Growth is limited in animals. Growth stops after attaining a particular size and age.
Excretory system and nervous system are well developed.
Reserve food material is glycogen.
Lacks cell wall. They have small vacuoles. Centrosomes are present. Cells do not have inorganic crystals.
Animals do not depend on any external agents for sexual reproduction. Regeneration of body parts and asexual reproduction is found only in lower organisms.
Limitations of Two Kingdom System of Classification
The two kingdom system of Classification proposed by Linnaeus has been in use for a long time. But later it proved to be inadequate and unsatisfactory in view of new information and discoveries about the lower forms of organisms. The following are the shortcomings of the two kingdom system of classification.
1. Certain organisms share the characteristics j of both plants and animals. eg. Euglena and Sponges. In Euglena, some species have chlorophyll and are autotrophic like plants. However like animals they are dependent on an external supply of vitamins B, and B12 which they cannot synthesize themselves. A few species of Euglena lack chloroplasts and are therefore colourless and non-photosynthetic (heterotrophic). They have a saprotropic mode of nutrition, carrying out extra-cellular digestion.
Other colorless forms ingest small food particles and carryout intracellular digestion (holozoic nutrition). If green species of Euglena are kept in darkness they lose their chloroplasts and become colourless and survive saprotrophically. Chloroplasts return when the organisms are returned to light. Euglena is also characterized by the presence of an animal pigment astaxanthin in the eye spot.
Fungi are a group of organisms which have features of their own. They lack chlorophyll. They are heterotrophic like animals. They are placed along with green plants.
Many primitive organisms such as bacteria did not fit into either category and organisms like slime moulds are amoeboid but form fruiting bodies similar to fungi.
The status of virus whether they are living or non living is a point of debate even to -day.
For all these reasons the two hundred and fifty years old Linnaeus system of classifying organisms into two rigid groups animals and plants is considered highly arbitrary and artificial.
Related Topics