Chapter: Mechanical : Automobile Engineering : Engine Auxiliary Systems Ignition System
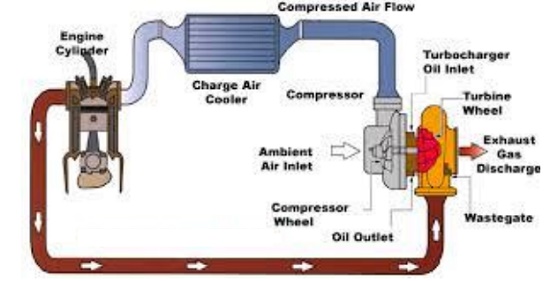
Turbocharger
Turbocharger
The turbo
charger utilizes the wasted heat energy in the exhaust system, to run a
compressor which compresses the intake air. Compressed intake air has more
density and hence more fuel can be injected increasing the power of the engine.
Turbo charging is an ideal way to increase the engine power without increasing
the engine size.
A
turbocharger, or turbo (colloquialism), from Greek
"τύρβη" ("wake"), (also from Latin
"turbo" ("spinning top"), is a turbine-driven forced
induction device that increases an engine's efficiency and power by forcing
extra air into the combustion chamber. This improvement over a naturally
aspirated engine's output results because the turbine can force more air, and
proportionately more fuel, into the combustion chamber than atmospheric
pressure alone.
Turbochargers
were originally known as turbosuperchargers when allforced induction devices
were classified as superchargers. Nowadays the term "supercharger" is
usually applied to only mechanically driven forced induction devices. The key
difference between a turbocharger and a conventional supercharger is that the
latter is mechanically driven by the engine, often through a belt connected to
the crankshaft, whereas a turbocharger is powered by a turbine driven by the
engine'sexhaust gas. Compared to a mechanically driven supercharger,
turbochargers tend to be more efficient, but less responsive. Twincharger
refers to an engine with both a supercharger and a turbocharger.
Turbochargers are commonly used on truck,
car, train, aircraft, and construction equipment engines. They are most often
used with Otto cycle and Diesel cycle internal combustion engines. They have
also been found useful in automotive fuel cells.
Related Topics