Chapter: Principles of Compiler Design : Syntax Analysis and Run-Time Environments
The Role of Parser
THE ROLE OF PARSER
The parser or syntactic
analyzer obtains a string of tokens from the lexical analyzer and verifies that
the string can be generated by the grammar for the source language. It reports
any syntax errors in the program. It also recovers from commonly occurring
errors so that it can continue processing its input.
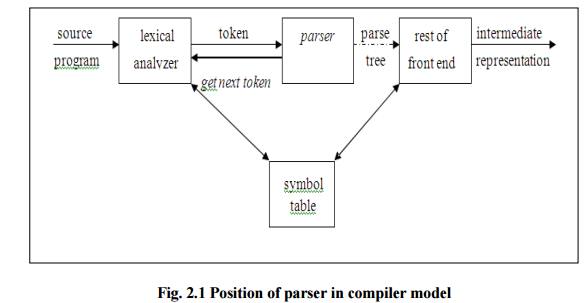
Fig. 2.1
Position of parser in comp Functions of the parser :
1. It
verifies the structure generated by the tokens based on the grammar.
2. It
constructs the parse tree.
3. It
reports the errors.
4. It
performs error recovery.
Issues :
Parser cannot detect errors such as:
1. Variable
re-declaration
2. Variable
initialization before use
3. Data type mismatch for an operation.
The above issues are handled by Semantic Analysis
phase.
Syntax error handling :
Programs can contain errors at many different
levels. For example :
1. Lexical,
such as misspelling an identifier, keyword or operator.
2. Syntactic,
such as an arithmetic expression with unbalanced parentheses.
3. Semantic,
such as an operator applied to an incompatible operand.
4. Logical,
such as an infinitely recursive call.
Functions of error handler :
1. It
should report the presence of errors clearly and accurately.
2. It
should recover from each error quickly enough to be able to detect subsequent
errors.
3. It
should not significantly slow down the processing of correct programs.
Error recovery strategies :
The different strategies that a parse uses to
recover from a syntactic error are:
1. Panic
mode
2. Phrase
level
3. Error
productions
4. Global
correction
Panic mode recovery:
On discovering an
error, the parser discards input symbols one at a time until a synchronizing
token is found. The synchronizing tokens are usually delimiters, such as
semicolon or end. It
has the advantage of simplicity and does not go into an infinite loop. When
multiple errors in the same statement are rare, this method is quite useful.
Phrase level recovery:
On discovering an
error, the parser performs local correction on the remaining input that allows
it to continue. Example: Insert a missing semicolon or delete an extraneous
semicolon etc.
Error productions:
The parser is
constructed using augmented grammar with error productions. If an error
production is used by the parser, appropriate error diagnostics can be
generated to indicate the erroneous constructs recognized by the input.
Global correction:
Given an incorrect
input string x and grammar G, certain algorithms can be used to find a parse
tree for a string y, such that the number of insertions, deletions and changes
of tokens is as small as possible. However, these methods are in general too
costly in terms of time and space.
Related Topics