Chapter: Principles of Compiler Design : Syntax Analysis and Run-Time Environments
Run-Time Environments - Source Language Issues
RUN-TIME ENVIRONMENTS -
SOURCE LANGUAGE ISSUES
Procedures:
A procedure definition
is a declaration that associates an identifier with a statement. The identifier
is the procedure name, and the statement is the procedure body. For example,
the following is the definition of procedure named readarray :
procedure readarray; var i : integer;
begin
for
i : = 1 to 9 do read(a[i])
end;
When a procedure name
appears within an executable statement, the procedure is said to be called at
that point.
Activation trees:
An activation tree is
used to depict the way control enters and leaves activations. In an activation
tree,
1.
Each node represents an activation of a
procedure.
2.
The root represents the activation of
the main program.
3.
The node for a is the parent of the node
for b if and only if control flows from activation a to b.
4. The
node for a is to the left of the node for b if and only if the lifetime of a
occurs before the lifetime of b.
Control stack:
A control stack is used
to keep track of live procedure activations. The idea is to push the node for
an activation onto the control stack as the activation begins and to pop the
node when the activation ends. The contents of the control stack are related to
paths to the root of the activation tree. When node n is at the top of control
stack, the stack contains the nodes along the path from n to the root.
The Scope of a Declaration:
A declaration is a
syntactic construct that associates information with a n Declarations may be
explicit, such as:
var
i : integer ;
or they may be
implicit. Example, any variable name starting with I is assumed to denote an integer.
The portion of the program to which a declaration applies is called the scope
of that declaration.
Binding of names:
Even if each name is
declared once in a program, the same name may denote different data objects at
run time. “Data object” corresponds to a storage location that holds values.
The term environment refers to a function that maps a name to a storage
location. The term state refers to a function that maps a storage location to
the value held there. When an environment associates storage location s with a
name x, we say that x is bound to s. This association is referred to as a
binding of x.
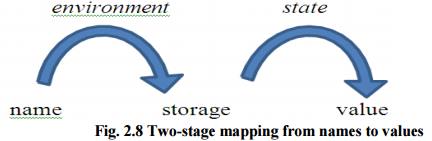
Fig. 2.8
Two-stage mapping from names to values
Related Topics