Chapter: Biochemistry: The Citric Acid Cycle
The Central Role of the Citric Acid Cycle in Metabolism
The Central Role of the Citric
Acid Cyclein Metabolism
The evolution of aerobic metabolism, by which nutrients are
oxidized to carbon dioxide and water, was an important step in the history of
life on the Earth. Organisms can obtain far more energy from nutrients by
aerobic oxidation than by anaerobic oxidation. (Even yeast—which is usually
thought of in terms of the anaerobic reactions of alcoholic fermentation and is
responsible for producing bread, beer, and wine—uses the citric acid cycle and
aerobically degrades glucose to carbon dioxide and water.) We saw that
glycolysis produces only two molecules of ATP for each molecule of glucose
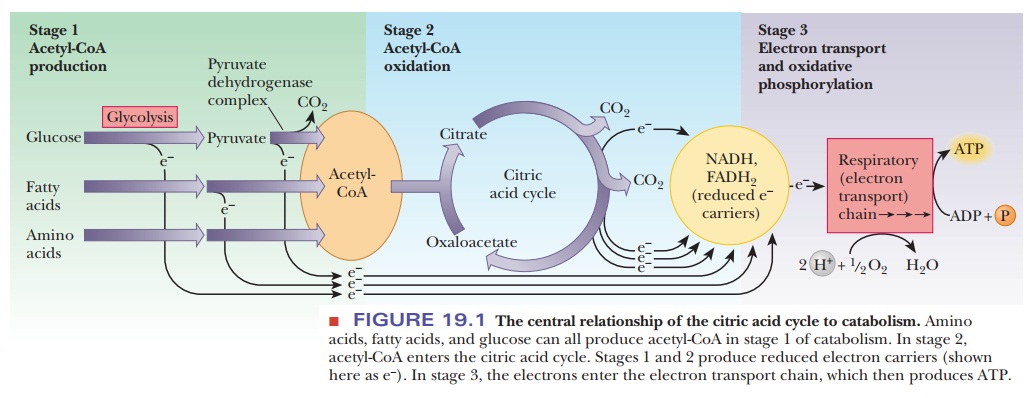
metabolized. In this Three processes play roles in aerobic metabolism: the citric acid cycle, which we discuss,
and electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation, both of which
we shall discuss (Figure19.1).
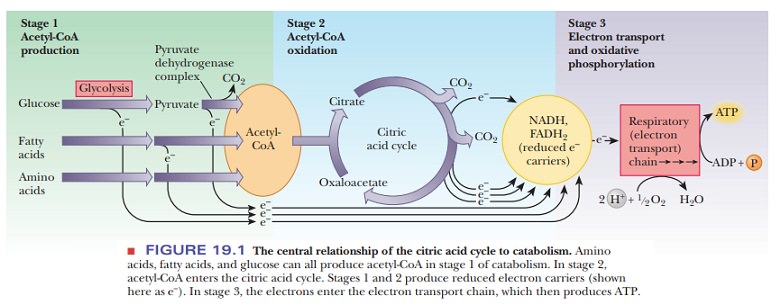
Metabolism consists of catabolism, which is the oxidative breakdown
of nutrients, and anabolism, which is reductive synthesis of biomolecules. The
citric acid cycle is amphibolic,
meaning that it plays a role in both catabolism and anabolism. Although the
citric acid cycle is a part of the pathway of aero-bic oxidation of nutrients,
some of the molecules that are included in this cycle are the starting points
of biosynthetic (anabolic) pathways. Metabolic pathways operate
simultane-ously, even though we talk about them separately. We should always
keep this point in mind.
The citric acid cycle has two other common names. One is the Krebs cycle, after Sir Hans Krebs, who
first investigated the pathway (work for which he received a Nobel Prize in
1953). The other name is the tricarboxylic
acid cycle(or TCA cycle), from the fact that some of the molecules involved
are acids withthree carboxyl groups. We shall start our discussion with a
general overview of the pathway and then go on to discuss specific reactions.
Summary
The citric acid cycle is amphibolic. It plays a role in both
catabolism and anabolism. It is the
central metabolic pathway.
Related Topics