Practical Experiment | Microbiology - Test for Catalase | 12th Microbiology : Practical Experiment Manual
Chapter: 12th Microbiology : Practical Experiment Manual
Test for Catalase
Test for Catalase
Aim
To test
whether the given culture is catalase positive by the catalase test
Theory and Principle
Catalase
test demonstrates the presence of catalase, an enzyme that catalyses the
release of oxygen from hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). It is
used to differentiate those bacteria that produces an enzyme catalase, such as staphylococci, from non-catalase
producing bacteria such as streptococci.
The
enzyme catalase mediates the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into oxygen and
water. The presence of the enzyme in a bacterial isolate is evident when a
small inoculum is introduced into hydrogen peroxide, and the rapid elaboration
of oxygen bubbles occurs. The lack of catalase is evident by a lack of or weak bubble
production. The culture should not be more than 24 hours old.
Requirements
• Slides
• Nichrome
loop or toothpick
• 24hour
old culture
• 3%hydrogen
peroxide
• Dropper
Procedure
Slide Method
1. Use a loop or sterile wooden stick to transfer a
small amount of colony growth in the surface of a clean, dry glass slide.
2. Place
a drop of 3% H2O2 in the glass slide.
3. Observe
for the evolution of oxygen bubbles.
Diagram
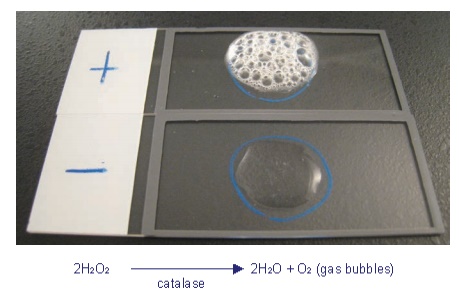
Observation (any one to be reported depending on the culture)
Positive: Copious bubbles produced, active bubbling
Examples: Staphylococci, E. coli, Enterobacter,
Klebsiella, Shigella, Yersinia, Pseudomonas.
Negative: No or very few bubbles produced.
Examples: Streptococcus and Enterococcus sps.
Result
The given
culture was found to be catalase positive as determined by the catalase slide
test.
Related Topics