Practical Experiment | Microbiology - Identification of the fungus (Aspergillus/Mucor/Rhizopus) by wet mount using LPCB | 12th Microbiology : Practical Experiment Manual
Chapter: 12th Microbiology : Practical Experiment Manual
Identification of the fungus (Aspergillus/Mucor/Rhizopus) by wet mount using LPCB
Identification of the fungus (Aspergillus/Mucor/Rhizopus) by wet
mount using LPCB
Aim:
To identify whether the given fungus is Aspergillus or Mucor or Rhizopus based on microscopic characteristics by wet
mount method using lactophenol cotton blue stain.
Theory and Principle :
Filamentous
fungi are reliably identified by their characteristics microscopic morphology
such as shape, size and arrangement of spores and hyphae. Fungi are eukaryotic
and range from unicellular yeast to multicellular molds. They reproduce by
producing spores.
Common
fungi are Aspergillus, Mucor and Rhizopus. They are filamentous and
collectively form mycelium. The morphology of the hyphae and spores can be
identified using a simple wet mount technique using lactophenol cotton blue
stain.
The
organism suspended in the stain are killed due to the presence of phenol.
Lactic acid preserves fungal structures and cotton blue stains the fungal cell
wall.
Requirements :
• Clean
grease free slide
• Coverslip
• Forcep
• Teasing needle
• Distilled water
• Lactophenol Cotton Blue
Procedure:
1. Take a clean slide.
2. Place a drop of water on the slide.
3. With the
help of forceps transfer the fungal mycelium.
4. Tease it with needle to separate the filaments
(hyphae).
5. Add a drop of lactophenolcotton blue.
6. Gently
place a coverslip avoiding air bubble formation.
7. Observe under low power and high power objective
lens.
8. Read the observations and interpret.
Diagram:
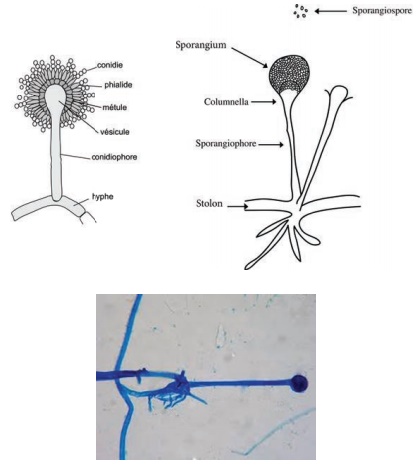
Observation;
Filamentous
hyphae bearing sporangia were observed.
Results:
Wet mount
using lactophenol cotton blue was carried to identify the fungus sample. Hyphae
with sporangium bearing sporangiospores were observed. It is likely to be of
mucor species.
Related Topics