Practical Experiment | Microbiology - Demonstration of rhizobium from root nodules and its isolation | 12th Microbiology : Practical Experiment Manual
Chapter: 12th Microbiology : Practical Experiment Manual
Demonstration of rhizobium from root nodules and its isolation
Demonstration of rhizobium from root nodules and its
isolation
Aim:
To demonstrate the presence of rhizobium in root
nodules by gram staining and isolate them on a nutrient medium.
Theory and Principle:
Leguminous
plants like cowpea, red gram , black gram contain root nodules formed by
rhizobium.Rhizobium in the soil enter into the roots of leguminous plant and
form nodules and establish symbiotic association. Bacteria derive nutrients
from the plants. The rhizobacteria fix nitrogen which is beneficial to the
plant. Rhizobium is a symbiotic N2 fixer found to occur as
bacteroids in the root nodules of leguminous plants. They can be easily
isolated and cultured in vitro.
Based on gram staining reaction bacteria can be
divided into two large groups called gram positive and gram negative. Gram
positive bacteria have thicker peptidoglycan compared to the gram negative
bacteria. The lipid content of the cell wall of gram negative bacteria is
higher than that of gram positive bacteria. Both gram positive and gram
negative bacteria take up the primary stain crystal violet and stain red. When
decolorized the porosity and permeability of the gram negative bacteria
increases due to which the crystal violet iodine complex is given out by the
gram negative bacteria. Further the gram negative bacteria takes up the
counterstain safranin and stains red. Hence when bacteria are observed under
microscope after gram staining the gram positive cells appear violet and gram
negative cells appear red. Rhizobia are
Gram- negative rods which are motile with
bi-polar, sub-polar and peritrichous flagella
Rhizobium grows well on Yeast Extract Mannitol Agar
(YEMA). Congo red added to the medium differentiates rhizobia that stand out as
white, translucent, glistening elevated, small colonies with entire margin, in
contrast to the red stained colonies of Agrobacterium and other bacteria.
Requirements:
1. Root
nodules (pink) of any leguminous plant
2. Congo red, Yeast Extract, Mannitol Agar (pH
6.8 – 7.0):
Mannitol
: 10.0 g
K2HPO4
: 0.5 g
MgSO4.7H2O
: 0..2 g
NaCl :
0.1 g
Yeast
extract : 1. G
CaCO3
: 3.0 g
Agar :
25.0 g
Congo red
(1% aqueous)
2.5 ml
(1.0 g in 100 ml)
Distilled
water 1000.0 ml
3. Inoculation
loop
4. Bunsen
burner/laminar clean air flow hood.
5. Slides
and glass rod.
6. Petri
plates with YEMACR medium.
7. Sterile
distilled water.
8. 95%
alcohol and 0.1% HgCl2.
Procedure:
1. Wash
the root system under a slow stream of running tap water, taking care to see
that the nodules are intact
2. Select
pink nodules and remove them
3. Wash
and keep the nodules in 95% ethanol for a minute, wash and transfer them to
0.1% HgCl2.
4. Remove
after five minutes and wash the nodules about four to five times with sterile
distilled water
5. Place
the nodule on a serile slide in a drop of sterile distied water and crush it
either with a sterile glass rod or a flat tipped forceps
6. Remove
a loopful of this cloudy suspension and streak inoculate on YEMACR plates and
label.
7. Incubate
in dark at 28°-30°C for 2-3 days and observe the colonies
.8. Make
a smear of the remaining crushed material and gram stain and observe the gram
negative bacilli. Even samples from the colonies can be gram stained.
Diagram:.
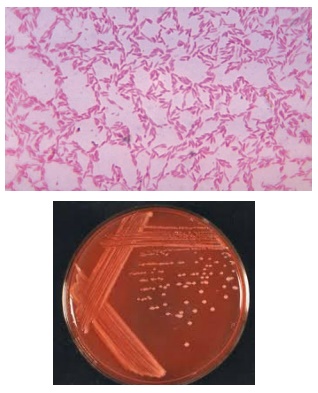
Observation
Gram’s stain
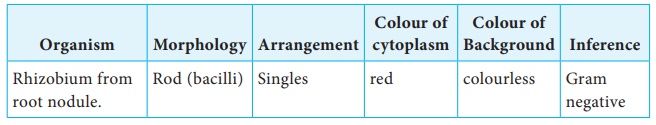
Colony characteristics of rhizobium on YEMA after incubation for 2-3 days at room temperature
Size –
2-4 mm
Shape-
circular
Colour –
White
Margin –
entire
Elevation
– convex, raised
Opacity –
semitranslucent
Texture –
creamy
Consistency
– mucilaginous
Gram
nature – gram negative
Motility
– actively motile
Results:
Gram staining of the root nodule exudate revealed the presence of
gram negative rods.
The
colony characteristics of rhizobia were studied after isolation on YEMA medium.
White,
creamy, mucoid colonies were obtained.
Related Topics